Cytisine, also known as baptitoxine, cytisinicline, or sophorine, is an alkaloid that occurs naturally in several plant genera, such as Laburnum and Cytisus of the family Fabaceae. It has been used medically to help with smoking cessation.[1] It has been found effective in several randomized clinical trials, including in the United States and New Zealand,[1] and is being investigated in additional trials in the United States and a non-inferiority trial in Australia in which it is being compared head-to-head with the smoking cessation aid varenicline (sold in the United States as Chantix).[2] It has also been used entheogenically via mescalbeans by some Native American groups, historically in the Rio Grande Valley predating even peyote.[3]
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Cytisine; Baptitoxine; Sophorine |
| License data | |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.924 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
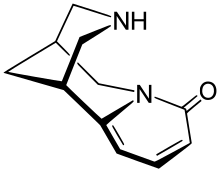
| Formula | C11H14N2O |
| Molar mass | 190.246 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 152 °C (306 °F) |
| Boiling point | 218 °C (424 °F) |
| |
| |
Sources
editCytisine is extracted from the seeds of Cytisus laburnum L. (Golden Rain acacia), and is found in several genera of the subfamily Faboideae of the family Fabaceae, including Laburnum, Anagyris, Thermopsis, Cytisus, Genista, Retama and Sophora. Cytisine is also present in Gymnocladus of the subfamily Caesalpinioideae.[citation needed]
Uses
editSmoking cessation
editCytisine has been available in post-Soviet states for more than 40 years as an aid to smoking cessation under the brand name Tabex from the Bulgarian pharmaceutical company Sopharma AD.[4] In 1961, Bulgarian pharmacist Strashimir Ingilizov synthesized Tabex using the alkaloid Cytisine which was derived from the seeds of the yellow acacia (Cytisus laburnum), a European decorative shrub prevalent in Bulgaria and commonly referred to as “golden rain”.[5] It was first marketed in Bulgaria in 1964 and then became widely available in the Soviet Union.[6] In Poland, it is sold under the brand name Desmoxan, and it is also available in Canada under the brand name Cravv.[7][8]
Its molecular structure has some similarity to that of nicotine, and it has similar pharmacological effects. Like the smoking cessation aid varenicline, cytisine is a partial agonist of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs).[9] Cytisine has a short half-life of 4.8 hours.[10] As a result, the extract provides smokers with satisfaction similar to smoking a cigarette, alleviating the urge to smoke and reducing the severity of nicotine withdrawal symptoms, while also reducing the reward experience of any cigarettes smoked.[11]
In 2011, a randomized controlled trial with 740 patients found cytisine improved 12-month abstinence from nicotine from 2.4% with placebo to 8.4% with cytisine.[12] A 2013 meta-analysis of eight studies demonstrated that cytisine has similar effectiveness to varenicline but with substantially lower side effects.[13] A 2014 systematic review and economic evaluation concluded that cytisine was more likely to be cost-effective for smoking cessation than varenicline.[14]
Recreational
editPlants containing cytisine, including the scotch broom and mescalbean, have also been used recreationally. Positive effects are reported to include a nicotine-like intoxication.[12]
Reagent for organic chemistry
edit(−)-Cytisine extracted from Laburnum anagyroides seeds was used as a starting material for the preparation of "(+)-sparteine surrogate", for the preparation of enantiomerically enriched lithium anions of opposite stereochemistry to those anions obtained from sparteine.[15]
Toxicity
editCytisine has been found to interfere with breathing and cause death in test mice; LD50 i.v. in mice is about 2 mg/kg.[16] Cytisine is also teratogenic.[17]
Māmane (Sophora chrysophylla) can contain amounts of cytisine that are lethal to most animals. The palila (Loxioides bailleui, a bird), Uresiphita polygonalis virescens and Cydia species (moths), and possibly sheep and goats are not affected by the toxin for various reasons, and consume māmane, or parts of it, as food. U. p. virescens caterpillars are possibly able to sequester the cytisine to give themselves protection from predation; they have aposematic coloration which would warn off potential predators.[18]
References
edit- ^ a b Walker N, Howe C, Glover M, McRobbie H, Barnes J, Nosa V, et al. (December 2014). "Cytisine versus nicotine for smoking cessation". The New England Journal of Medicine. 371 (25): 2353–2362. doi:10.1056/nejmoa1407764. PMID 25517706. S2CID 13759117.
- ^ Thomas D, Farrell M, McRobbie H, Tutka P, Petrie D, West R, et al. (May 2019). "The effectiveness, safety and cost-effectiveness of cytisine versus varenicline for smoking cessation in an Australian population: a study protocol for a randomized controlled non-inferiority trial" (PDF). Addiction. 114 (5): 923–933. doi:10.1111/add.14541. PMID 30589984. S2CID 58621453.
- ^ Howard JH (1957). "The Mescal Bean Cult of the Central and Southern Plains: An Ancestor of the Peyote Cult". American Anthropologist. 59 (1): 75–87. doi:10.1525/aa.1957.59.1.02a00070. JSTOR 666531.
- ^ Zatonski W, Cedzynska M, Tutka P, West R (December 2006). "An uncontrolled trial of cytisine (Tabex) for smoking cessation". Tobacco Control. 15 (6): 481–484. doi:10.1136/tc.2006.016097. PMC 2563682. PMID 17130378.
- ^ Gatsov, Nikolai (October 1964). "Ein Mittel Gegen Rauchen". Bulgarien. 1: 39.
- ^ "Old anti-smoking drug passes new test". Reuters. 28 September 2011. Retrieved 11 March 2022.
- ^ Prochaska JJ, Das S, Benowitz NL (August 2013). "Cytisine, the world's oldest smoking cessation aid". BMJ. 347 (aug23 1): f5198. doi:10.1136/bmj.f5198. PMID 23974638. S2CID 31845933.
- ^ Zatoński W, Janik-Koncewicz K, Stępnicka Z, Zatońska K, Połtyn-Zaradna K, Herbeć A (2020). "History of smoking cessation treatment in Poland – the strengthening role of cytisine as the most effective and safe pharmacotherapy". Journal of Health Inequalities. 6 (2): 116–123. doi:10.5114/jhi.2020.102969. ISSN 2450-5927. S2CID 234956118.
- ^ Dallanoce C, Frigerio F, Martelli G, Grazioso G, Matera C, Pomè DY, et al. (June 2010). "Novel tricyclic Delta(2)-isoxazoline and 3-oxo-2-methyl-isoxazolidine derivatives: synthesis and binding affinity at neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry. 18 (12): 4498–4508. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2010.04.065. PMID 20478710.
- ^ Jeong SH, Newcombe D, Sheridan J, Tingle M (June 2015). "Pharmacokinetics of cytisine, an α4 β2 nicotinic receptor partial agonist, in healthy smokers following a single dose". Drug Testing and Analysis. 7 (6): 475–482. doi:10.1002/dta.1707. PMID 25231024. S2CID 45441989.
- ^ Reinberg S (17 December 2014). "Cheap Natural Compound May Help Smokers Quit. But cytisinicline isn't widely available, study authors note". WebMD. Retrieved 4 June 2021.
- ^ a b West R, Zatonski W, Cedzynska M, Lewandowska D, Pazik J, Aveyard P, Stapleton J (September 2011). "Placebo-controlled trial of cytisine for smoking cessation". The New England Journal of Medicine. 365 (13): 1193–1200. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1102035. PMID 21991893.
- ^ Hajek P, McRobbie H, Myers K (November 2013). "Efficacy of cytisine in helping smokers quit: systematic review and meta-analysis". Thorax. 68 (11): 1037–1042. doi:10.1136/thoraxjnl-2012-203035. PMID 23404838.
- ^ Leaviss J, Sullivan W, Ren S, Everson-Hock E, Stevenson M, Stevens JW, et al. (May 2014). "What is the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of cytisine compared with varenicline for smoking cessation? A systematic review and economic evaluation". Health Technology Assessment. 18 (33): 1–120. doi:10.3310/hta18330. PMC 4780997. PMID 24831822.
- ^ "Synthesis of (+)-(1R,@S,9S)-11-Methyl-7,11-Diazatricyclo[7.3.1.02.7]tridecane, a (+)sparteine surrogate". Organic Syntheses. 83: 141. 2006. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.083.0141.
- ^ The Merck Index, 10th Ed. (1983) p.402, Rahway: Merck & Co.
- ^ Keeler RF. Handbook of Natural Toxins: Toxicology of Plant and Fungal Compounds. CRC Press. p. 43.
- ^ Banko PC, Cipollini ML, Breton GW, Paulk E, Wink M, Izhaki I (July 2002). "Seed chemistry of Sophora chrysophylla (mamane) in relation to diet of specialist avian seed predator Loxioides bailleui (palila) in Hawaii" (PDF). Journal of Chemical Ecology. 28 (7): 1393–1410. Bibcode:2002JCEco..28.1393B. doi:10.1023/A:1016248502927. PMID 12199503. S2CID 7064787. Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 December 2012. Retrieved 4 May 2007.
External links
edit- "Cytisinicline". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.