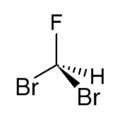
Dibromofluoromethane is a mixed halomethane.[1] It is soluble in alcohol, acetone, benzene and chloroform. It is prepared from dibromomethane and antimony(III) fluoride.[2]
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Dibromo(fluoro)methane | |
| Other names
Dibromofluoromethane
Fluorodibromomethane R-12B2 | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.148.872 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| CHBr2F | |
| Molar mass | 191.83 g/mol |
| Appearance | Liquid |
| Density | 2.421 g/cm3 at 20 °C |
| Melting point | −78 °C (−108 °F; 195 K) |
| Boiling point | 64.9 °C (148.8 °F; 338.0 K) |
| Insoluble | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  
| |
| Supplementary data page | |
| Dibromofluoromethane (data page) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Applications
editIt can be used to prepare bromofluoromethane by reductive debromination with organotin hydride as tributyltin hydride.[3]
Regulations
editIts ozone depletion potential (ODP) is 1.0 and it is included in list of Class I Ozone-Depleting Substances.
References
edit- ^ "Dibromofluoromethane solution". Sigma Aldrich. sigmaaldrich.com. Retrieved 7 June 2017.
- ^ Bernd Baasner (2014), Houben-Weyl Methods of Organic Chemistry Vol. E 10a, 4th Edition Supplement Organo-Fluorine Compounds - Fluorinating Agents and Their Application in Organic Synthesis, Georg Thieme Verlag, p. 517, ISBN 978-3-13-181544-6
- ^ US patent 5189229A, Robinson, John M., "Debrominating dibromofluoromethane with tributyltin hydride", published 28 February 1989, issued 23 February 1993, assigned to Glaxo Group