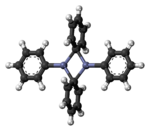
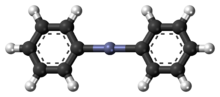
Diphenylzinc is an organozinc compound. It is commonly used as the synthetic equivalent of a Ph− synthon. Solvent-free diphenylzinc exists as dimeric PhZn(μ-Ph)2ZnPh molecules in the solid state.[1]
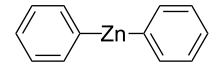
| |
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 3603125 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.012.803 |
| EC Number |
|
| 28161 | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H10Zn | |
| Molar mass | 219.59 g·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Danger | |
| H228, H250 | |
| P210, P222, P240, P241, P280, P302+P334, P370+P378, P422 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Diphenylzinc is commercially available. It may be prepared by reaction of phenyllithium with zinc bromide:[2]
- 2 PhLi + ZnBr2 → Ph2Zn + 2 LiBr
It may also be prepared by the reaction of phenylmagnesium bromide with zinc chloride or diphenylmercury with zinc metal.[3][4]
References
edit- ^ Markies, Peter R.; Schat, Gerrit; Akkerman, Otto S.; Bickelhaupt, Friedrich; Smeets, Wilberth J. J.; Spek, Anthony L. (1990). "Coordinational behavior of solvent-free diorganylzinc compounds: the remarkable x-ray structure of dimeric diphenylzinc". Organometallics. 9 (8): 2243. doi:10.1021/om00158a022.
- ^ Curtin, David Y.; Tveten, John L. (1961). "Reaction of Diarylzinc Reagents with Aryldiazonium Salts. Direct Formation of cis-Azo Compounds". J. Org. Chem. 26 (6): 1764. doi:10.1021/jo01065a017.
- ^ Markies, P; Schat, Gerrit; Akkerman, Otto S.; Bickelhaupt, F.; Spek, Anthony L. (1992). "Complexation of diphenylzinc with simple ethers. Crystal structures of the complexes Ph2Zn·glyme and Ph2Zn·diglyme". J. Organomet. Chem. 430: 1–13. doi:10.1016/0022-328X(92)80090-K.
- ^ Pelletier, Guillaume (2013), "Diphenylzinc", Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis, Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, doi:10.1002/047084289x.rn01548, ISBN 978-0-471-93623-7