Entomophaga is a genus of entomopathogenic fungi in the Entomophthoraceae family and also the order Entomophthorales.[2] This has been supported by molecular phylogenetic analysis (Gryganskyi et al. 2012).[3]
| Entomophaga | |
|---|---|
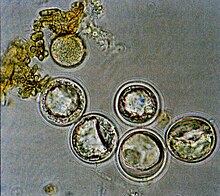
| |
| Entomophaga maimaiga azygospores | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Fungi |
| Division: | Entomophthoromycota |
| Class: | Entomophthoromycetes |
| Order: | Entomophthorales |
| Family: | Entomophthoraceae |
| Genus: | Entomophaga A. Batko, 1964 [1] |
Well-known species are Entomophaga grylli and Entomophaga maimaiga, which can infect grasshoppers and gypsy moths respectively.
The genus name of Entomophaga was derived from combining two words in the Greek, entomon means insect and phaga means to eat. The genus was created in 1964 by the Polish mycologist Andrzej Batko (1933 - 1997). He wrote “... to commemorate the international journal Entomophaga devoted to problems of biological control of insect pests.”[1] The journal later ceased publication in 1998 and was replaced by BioControl.
Species
editAs accepted by Species Fungorum;[4]
- Entomophaga antochae S. Keller, 2007
- Entomophaga apiculata (Thaxt.) S. Keller, 1991
- Entomophaga aulicae (E. Reichardt) Humber, 1984
- Entomophaga batkoi (Balazy) S. Keller, 1988
- Entomophaga bukidnonensis Villac. & Wilding, 1994
- Entomophaga calopteni (Bessey) Humber, 1989
- Entomophaga caroliniana (Thaxt.) Samson, H.C. Evans & Latgé, 1988
- Entomophaga conglomerata (Sorokin) S. Keller, 1988
- Entomophaga destruens (Weiser & A. Batko) A. Batko, 1964
- Entomophaga diprionis Balazy, 1993
- Entomophaga domestica S. Keller, 1988
- Entomophaga gigantea (S. Keller) S. Keller, 1988
- Entomophaga grylli (Fresen.) A. Batko, 1964
- Entomophaga kansana (J.A. Hutchison) A. Batko, 1964
- Entomophaga lagriae Balazy, 1993
- Entomophaga limoniae S. Keller, 1988
- Entomophaga maimaiga Humber, Shimazu & R.S. Soper, 1988
- Entomophaga major (Thaxt.) S. Keller, 1991
- Entomophaga obscura (I.M. Hall & P.H. Dunn) A. Batko, 1964
- Entomophaga papillata (Thaxt.) S. Keller, 1988
- Entomophaga ptychopterae (S. Keller & Eilenberg) A.E. Hajek & Eilenberg, 2003
- Entomophaga pyriformis Balazy, 1993
- Entomophaga saccharina (Giard) A. Batko, 1964
- Entomophaga tabanivora (J.F. Anderson & Magnar.) Humber, 1984
- Entomophaga tenthredinis (Fresen.]]) A. Batko, 1964
- Entomophaga thaxteriana A. Batko, 1964
- Entomophaga thuricensis S. Keller, 2007
- Entomophaga tipulae (Fresen.) Humber, 1989
- Entomophaga transitans (S. Keller) A.E. Hajek & Eilenberg, 2003
References
edit- ^ a b Batko, A. 1964. Bull. Acad. Pol. Sci., Série des sciences biologiques 12, 323-326
- ^ Elya, Carolyn; De Fine Licht, Henrik H. (12 November 2021). "The genus Entomophthora: bringing the insect destroyers into the twenty-first century &". IMA Fungus. 12 (34).
- ^ Gryganskyi AP, Humber RA, Smith ME et al (2012) Molecular phylogeny of the Entomophthoromycota. Mol Phylogenet Evol 65:682–694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2012.07.026
- ^ "Entomophaga - Search Page". www.speciesfungorum.org. Species Fungorum. Retrieved 31 December 2022.