Friction stir spot welding is a pressure welding process that operates below the melting point of the workpieces. It is a variant of friction stir welding.[1]
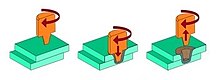
Process description
editIn friction stir spot welding, individual spot welds are created by pressing a rotating tool with high force onto the top surface of two sheets that overlap each other in the lap joint. The frictional heat and the high pressure plastify the workpiece material, so that the tip of the pin plunges into the joint area between the two sheets and stirs-up the oxides. The pin of the tool is plunged into the sheets until the shoulder is in contact with the surface of the top sheet. The shoulder applies a high forging pressure, which bonds the components metallurgically without melting. After a short dwell time, the tool is pulled out of the workpieces again so that a spot weld can be made about every 5 seconds.[2]
The tool consists of a rotating pin and a shoulder. The pin is the part of the tool that penetrates into the materials. Both the pin and the shoulder may be profiled to push the plasticized material in a particular direction and to efficiently break-up and disperse the oxide skins on the adjacent surfaces. After retracting the tool, a hole remains, when using one-piece tools, which have already proven themselves as very reliable in the automotive and the rail vehicle industry.[3] Often the rotating tool is surrounded by a non-rotating clamping ring with which the workpieces are pressed firmly against each other before and during welding by applying a clamping force. The clamping ring can also be used to reduce the pressing out of plasticized material to avoid the formation of burrs or beads to apply inert gas or to cool the tool via compressed air.[4]
The most important process parameters are the speed and contact pressure. This results in the plunge feed rate for a given workpiece material. Modern spot welding guns can be used either via position control or force control or via a product-specific programmed force-displacement control. Often, position control is used until a certain displacement is reached, and then the control system is switched to force control during the dwell time. Even during the force-controlled dwell time, certain position values can be specified, which should not be undermatched or exceeded.[2]
Spot welding guns
editFriction stir spot welding is performed with a spot welding gun, which is mounted on a console, flanged to an articulated robot or manually operated with a balancer to the component.[2]
Process advantages
editFriction spot welding is characterized by a number of process advantages. Any damage to the material caused by the extreme heat, such as that produced by laser or arc welding, will not occur. In particular, in the case of artificially aged aluminum alloys, the strength in the weld seam and the heat-affected zone is much higher than in conventional welding methods.[2]
Industrial use
editFriction stir spot welds have a high strength, so they are even suitable for parts that are exposed to particularly high loads. In addition to automotive and rail vehicle construction, the aerospace industry is developing the process e.g. for welding cockpit doors for helicopters.[3] In the electrical industry aluminum and copper can be friction stir spot welded. Other applications are in façade and furniture manufacture, where the low heat input, especially in anodized sheets, leads to excellent optical properties.[2]
References
edit- ^ AluStir: Friction Stir Spot Welding.
- ^ a b c d e Stephan Kallee und Ozan Caliskanoglu: Rührreibpunktschweißen im Fahrzeugbau: Neue Möglichkeiten. Der Praktiker, 11/2017, p. 548–551.
- ^ a b John Sprovieri: Friction stir spot welding. Assembly magazine, BNP Media, 7 April 2016.
- ^ ISO/FDIS 18785 (E): Friction stir spot welding — Aluminium — Parts 1–5, IIW Commission III, chaired by IIW.