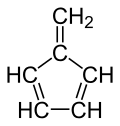
Fulvene (pentafulvene) is a hydrocarbon with the formula (CH=CH)2C=CH2. It is a prototype of a cross-conjugated hydrocarbon.[2] Fulvene is rarely encountered,[3] but substituted derivatives (fulvenes) are numerous. They are mainly of interest as ligands and precursors to ligands in organometallic chemistry.
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
5-Methylidenecyclopenta-1,3-diene[1] | |||
| Other names
Fulvene[1]
5-Methylene-1,3-cyclopentadiene | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C6H6 | |||
| Molar mass | 78.114 g·mol−1 | ||
| -42.9·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Fulvene is an isomer of benzene, which when irradiated at 237 to 254 nm forms small amounts of fulvene along with benzvalene.[4]
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ a b Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. p. 379. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^ Preethanuj Preethalayam; Syam krishnan, K.; Sreeja Thulasi; Sarath Chand, S.; Jomy Joseph; Vijay Nair; Florian Jaroschik; K.V.Radhakrishnan (2017). "Recent Advances in the Chemistry of Pentafulvenes". Chemical Reviews. 117 (5): 3930–3989. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00210. PMID 28151643.
- ^ Bergmann, E. D. (1968). "Fulvenes and Substituted Fulvenes". Chemical Reviews. 68: 41–84. doi:10.1021/cr60251a002.
- ^ Kaplan, Louis; Wilzbach, K. E. (1968). "Photolysis of benzene vapor. Benzvalene formation at wavelengths 2537-2370 A". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 90 (12): 3291–3292. doi:10.1021/ja01014a086. ISSN 0002-7863.