Growth arrest and DNA-damage-inducible protein GADD45 gamma is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GADD45G gene on chromosome 9. GADD45G is also known as CR6, DDIT2, GRP17, OIG37, and GADD45gamma.[5] GADD45G is involved in several different processes, including sexual development,[6] human-specific brain development,[7] tumor suppression,[8] and the cellular stress response.[9] GADD45G interacts with several other proteins that are involved in DNA repair, cell cycle control, apoptosis, and senescence.[6] Low expression of GADD45G has been associated with many types of cancer.[10]
| GADD45G | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | GADD45G, CR6, DDIT2, GADD45gamma, GRP17, growth arrest and DNA damage inducible gamma | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 604949; MGI: 1346325; HomoloGene: 21334; GeneCards: GADD45G; OMA:GADD45G - orthologs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
History
editGADD45G was originally cloned by Beadling under the name CR6 in 1993. In this experiment, several genes including GADD45G were noted for being induced by IL-2, and they were identified as immediate early response genes in T lymphocytes.[11] Its role as a tumor suppressor was discovered in 1999 by Zhang.[12] It received the name OIG37 from Nakayama due to its regulation by Oncostatin M, which was found to be able to inhibit growth.[13] Finally, it also became known as Gadd-related protein 17 during its isolation from a cDNA library by Suzuki due to its homology with Gadd45.[5]
Structure and function
editGADD45G is a member of a group of genes whose transcript levels are increased following stressful growth arrest conditions and treatment with DNA-damaging agents. The protein encoded by this gene responds to environmental stresses by mediating activation of the p38/JNK pathway via MTK1/MEKK4 kinase.[14] GADD45G is in turn regulated upstream by NF-κB.[8]
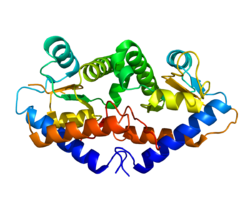
The crystal structure of GADD45G reveals a dimer made of four parallel helices. The central region contains a highly acidic patch where it allows for interaction with cdc2, PCNA, and p21. The parallel isoform of GADD45G is the active form.[15]
This gene plays a role in cell cycle regulation. GADD45G prevents the kinase ability of the cyclin b1/Cdk1 complex in a fashion that does not break apart the complex. It plays a role in the activation of the S and G2/M checkpoints.[16]
In the male sexual development pathway, GADD45G is essential for activating SRY, leading to proper formation of the gonads and sex-determination. This could occur through GADD45G interaction with the p38 MAPK signaling pathway.[6]
Deletion of an enhancer close to the GADD45G gene is correlated to increased proliferation of neuronal cells, which could account for part of the difference in neural development between humans and other species.[7] The deletion of the enhancer reduces the expression of the gene in the forebrain allowing for more brain growth in humans.[17]
GADD45G is involved with dental epithelial cell proliferation. GADD45G is expressed in enamel knots, where it regulates gene expression and cell growth. The gene modulates p21-mediated epithelial cell proliferation by activating the p38 MAPK pathway during the development of teeth.[18]
There is differential expression of the Xenopus homolog of GADD45G in embryonic development. It plays a large role in neural and brain development with GADD45A. GADD45G and GADD45A knockdowns are related to improper gastrulation, defective head growth, and shorter axes. GADD45G and GADD45A act redundantly to control cell growth, allow the cells to move from pluripotency helping cells differentiate.[19]
Memory
editDuring a learning experience, a set of genes is rapidly expressed in the brain. This induced gene expression is thought to be important for processing the information being learned. Such genes are known as immediate early genes. Within the prelimbic prefrontal cortex, the GADD45G gene is immediately expressed and is required for the consolidation of a type of learning in mice termed associative fear memory.[20] In general, gene expression often can be epigenetically induced by demethylation of 5-methylcytosine(s) in gene promoter regions. The GADD45G protein functions in repair of DNA damage. GADD45G may also be involved in recognition of 5-methylcytosine as an alteration in DNA that needs to be repaired to allow induction of learning-related genes. Thus GADD45G may guide the rapid demethylation of methylcytosine in the promoter regions of learning-related genes by a DNA repair process[20](see also Epigenetics in learning and memory).
Interactions
editGADD45G carries out its many previously stated functions with many different interactions. GADD45G was found to inhibit Cdk1 kinase activity, which would cause disruption of cell growth.[16] It also interacts with CRIF, which causes the inhibition of Cdc2-cyclin B1 and Cdk-cyclin E.[21] GADD45 also works with the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21, which can cause growth arrest as well.[22] GADD45G is found to be involved with the p38 MAPK pathway through interactions with MAP3K4, which can be important in sex-determination.[23] Additionally, GADD45G regulates DNA replication and repair through its interactions with PCNA.[13][22]
Tissue distribution
editIn humans, GADD45G is expressed most in the skeletal muscle, kidney and liver. This gene has a low expression in the heart, brain, spleen, lung and testis.[8] GADD45G is highly expressed in the placenta.[24]
In the embryonic mouse, Gadd45g is expressed in the neural tube, cranial and dorsal root ganglia and the dorsal midbrain.[25]
Mammalian renal inner medullary (IM) cells routinely face and resist hypertonic stress. Such stress causes DNA damage to which IM cells respond with cell cycle arrest. All three GADD45 isoforms GADD45A, GADD45B, and GADD45G are induced by acute hypertonicity in murine IM cells. Maximum induction occurs 16-18 h after the onset of hypertonicity. GADD45G is induced more strongly (7-fold) than GADD45B (3-fold) and GADD45A (2-fold). Hypertonicity of various forms (NaCl, KCl, sorbitol, or mannitol) always induces GADD45 transcripts, whereas non-hypertonic hyperosmolality (urea) has no effect. Actinomycin D does not prevent hypertonic GADD45 induction, indicating that mRNA stabilization is the mechanism that mediates this induction.[26]
Clinical significance
editIn numerous kinds of cancerous cells, GADD45G is down regulated.[10] There is a low expression due to methylation of the GADD45G promoter.[18] This low expression can also be explained by increased NF-κB activation.[27]
GADD45G methylation is seen in many cancers. In esophageal cancer the expression level and methylation status of the gene are involved in the prognosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Demethylation of the gene can have some beneficial effects.[18] Similar circumstances are seen in gastric cardio adenocarcinomas where GADD45G is silenced.[28] GADD45G methylation levels are also measured in the diagnosis of pancreatic and colorectal cancers.[29]
In the pituitary gland, GADD45G is a growth suppressor. There is a loss of expression of the gene in many pituitary cancerous masses.[30] The gene plays a role in prostate cancer as a tumor suppressor as well. In these cancerous cells, Vitamin D can induce the expression of GADD45G.[31] GADD45G could possibly be a target of therapeutic benefit for prostate cancer.[32]
In cancerous liver cells, GADD45G is down regulated. It participates in negatively regulating the JAK-STAT3 signaling pathway. It acts as a tumor suppressor in HCC cells by promoting cell death or growth arrest. When GADD45G expression is low, liver cells may be able to bypass the growth arrest stage, leading to cancerous cells.[10]
The presence of GADD45G in the urinary system is also related to renal disease. The renal cells expressing the gene were damaged.[33]
The upregulation of Gadd45g due to hormones may account for the changes in the mouse uterus.[34]
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000130222 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000021453 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ a b Suzuki M, Watanabe TK, Fujiwara T, Takahashi E, Tanigami A (Oct 1999). "Molecular cloning, expression, and mapping of a novel human cDNA, GRP17, highly homologous to human gadd45 and murine MyD118". J Hum Genet. 44 (5): 300–3. doi:10.1007/s100380050164. PMID 10496071.
- ^ a b c Johnen H, González-Silva L, Carramolino L, Flores JM, Torres M, Salvador JM (2013). "Gadd45g is essential for primary sex determination, male fertility and testis development". PLOS ONE. 8 (3): e58751. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...858751J. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0058751. PMC 3596291. PMID 23516551.
- ^ a b McLean CY, Reno PL, Pollen AA, Bassan AI, Capellini TD, Guenther C, Indjeian VB, Lim X, Menke DB, Schaar BT, Wenger AM, Bejerano G, Kingsley DM (March 2011). "Human-specific loss of regulatory DNA and the evolution of human-specific traits". Nature. 471 (7337): 216–9. Bibcode:2011Natur.471..216M. doi:10.1038/nature09774. PMC 3071156. PMID 21390129.
- ^ a b c Tamura RE, de Vasconcellos JF, Sarkar D, Libermann TA, Fisher PB, Zerbini LF (June 2012). "GADD45 proteins: central players in tumorigenesis". Curr. Mol. Med. 12 (5): 634–51. doi:10.2174/156652412800619978. PMC 3797964. PMID 22515981.
- ^ Liebermann DA, Hoffman B (2007). "Gadd45 in the response of hematopoietic cells to genotoxic stress". Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 39 (3): 329–35. doi:10.1016/j.bcmd.2007.06.006. PMC 3268059. PMID 17659913.
- ^ a b c Zhang L, Yang Z, Ma A, Qu Y, Xia S, Xu D, Ge C, Qiu B, Xia Q, Li J, Liu Y (January 2014). "Growth arrest and DNA damage 45G down-regulation contributes to Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 activation and cellular senescence evasion in hepatocellular carcinoma". Hepatology. 59 (1): 178–89. doi:10.1002/hep.26628. PMID 23897841. S2CID 39582166.
- ^ Beadling C, Johnson KW, Smith KA (April 1993). "Isolation of interleukin 2-induced immediate-early genes". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 90 (7): 2719–23. Bibcode:1993PNAS...90.2719B. doi:10.1073/pnas.90.7.2719. PMC 46167. PMID 7681987.
- ^ Zhang W, Bae I, Krishnaraju K, Azam N, Fan W, Smith K, Hoffman B, Liebermann DA (September 1999). "CR6: A third member in the MyD118 and Gadd45 gene family which functions in negative growth control". Oncogene. 18 (35): 4899–907. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1202885. PMID 10490824. S2CID 24659282.
- ^ a b Nakayama K, Hara T, Hibi M, Hirano T, Miyajima A (August 1999). "A novel oncostatin M-inducible gene OIG37 forms a gene family with MyD118 and GADD45 and negatively regulates cell growth". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (35): 24766–72. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.35.24766. PMID 10455148.
- ^ Takekawa M, Saito H (Dec 1998). "A family of stress-inducible GADD45-like proteins mediate activation of the stress-responsive MTK1/MEKK4 MAPKKK". Cell. 95 (4): 521–30. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81619-0. PMID 9827804. S2CID 18980341.
- ^ Zhang W, Fu S, Liu X, Zhao X, Zhang W, Peng W, Wu C, Li Y, Li X, Bartlam M, Zeng ZH, Zhan Q, Rao Z (2011). "Crystal structure of human Gadd45γ [corrected] reveals an active dimer". Protein Cell. 2 (10): 814–26. doi:10.1007/s13238-011-1090-6. PMC 4875293. PMID 22058036.
- ^ a b Vairapandi M, Balliet AG, Hoffman B, Liebermann DA (2002). "GADD45b and GADD45g are cdc2/cyclinB1 kinase inhibitors with a role in S and G2/M cell cycle checkpoints induced by genotoxic stress". J. Cell. Physiol. 192 (3): 327–38. doi:10.1002/jcp.10140. PMID 12124778. S2CID 19138273.
- ^ Iskow RC, Gokcumen O, Lee C (2012). "Exploring the role of copy number variants in human adaptation". Trends in Genetics. 28 (6): 245–257. doi:10.1016/j.tig.2012.03.002. ISSN 0168-9525. PMC 3533238. PMID 22483647.
- ^ a b c Ishida K, Yuge Y, Hanaoka M, Yasukawa M, Minami Y, Ogawa M, Masumoto KH, Shigeyoshi Y, Saito M, Tsuji T (August 2013). "Gadd45g regulates dental epithelial cell proliferation through p38 MAPK-mediated p21 expression". Genes Cells. 18 (8): 660–71. doi:10.1111/gtc.12067. PMID 23751077. S2CID 23664498.
- ^ Kaufmann LT, Niehrs C (2011). "Gadd45a and Gadd45g regulate neural development and exit from pluripotency in Xenopus". Mechanisms of Development. 128 (7–10): 401–411. doi:10.1016/j.mod.2011.08.002. ISSN 0925-4773. PMID 21854844.
- ^ a b Li X, Marshall PR, Leighton LJ, Zajaczkowski EL, Wang Z, Madugalle SU, et al. (February 2019). "The DNA Repair-Associated Protein Gadd45γ Regulates the Temporal Coding of Immediate Early Gene Expression within the Prelimbic Prefrontal Cortex and Is Required for the Consolidation of Associative Fear Memory". The Journal of Neuroscience. 39 (6): 970–983. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2024-18.2018. PMC 6363930. PMID 30545945.
- ^ Chung HK, Yi YW, Jung NC, Kim D, Suh JM, Kim H, Park KC, Song JH, Kim DW, Hwang ES, Yoon SH, Bae YS, Kim JM, Bae I, Shong M (July 2003). "CR6-interacting factor 1 interacts with Gadd45 family proteins and modulates the cell cycle". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (30): 28079–88. doi:10.1074/jbc.M212835200. PMID 12716909.
- ^ a b Azam N, Vairapandi M, Zhang W, Hoffman B, Liebermann DA (Jan 2001). "Interaction of CR6 (GADD45gamma ) with proliferating cell nuclear antigen impedes negative growth control". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (4): 2766–74. doi:10.1074/jbc.M005626200. PMID 11022036.
- ^ Warr N, Carre GA, Siggers P, Faleato JV, Brixey R, Pope M, Bogani D, Childers M, Wells S, Scudamore CL, Tedesco M, del Barco Barrantes I, Nebreda AR, Trainor PA, Greenfield A (November 2012). "Gadd45γ and Map3k4 interactions regulate mouse testis determination via p38 MAPK-mediated control of Sry expression". Dev. Cell. 23 (5): 1020–31. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2012.09.016. PMC 3526779. PMID 23102580.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: GADD45G growth arrest and DNA-damage-inducible, gamma".
- ^ Kaufmann LT, Gierl MS, Niehrs C (2011). "Gadd45a, Gadd45b and Gadd45g expression during mouse embryonic development". Gene Expression Patterns. 11 (8): 465–470. doi:10.1016/j.gep.2011.07.005. ISSN 1567-133X. PMID 21843656.
- ^ Chakravarty D, Cai Q, Ferraris JD, Michea L, Burg MB, Kültz D (November 2002). "Three GADD45 isoforms contribute to hypertonic stress phenotype of murine renal inner medullary cells". American Journal of Physiology. Renal Physiology. 283 (5): F1020–9. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00118.2002. PMID 12372778.
- ^ Liebermann DA, Tront JS, Sha X, Mukherjee K, Mohamed-Hadley A, Hoffman B (2011). "Gadd45 stress sensors in malignancy and leukemia". Crit Rev Oncog. 16 (1–2): 129–40. doi:10.1615/critrevoncog.v16.i1-2.120. PMC 3268054. PMID 22150313.
- ^ Guo W, Dong Z, Guo Y, Chen Z, Kuang G, Yang Z (2013). "Methylation-mediated repression of GADD45A and GADD45G expression in gastric cardia adenocarcinoma". International Journal of Cancer. 133 (9): 2043–2053. doi:10.1002/ijc.28223. ISSN 0020-7136. PMID 23616123. S2CID 36324243.
- ^ Zhang W, Li T, Shao Y, Zhang C, Wu Q, Yang H, Zhang J, Guan M, Yu B, Wan J (August 2010). "Semi-quantitative detection of GADD45-gamma methylation levels in gastric, colorectal and pancreatic cancers using methylation-sensitive high-resolution melting analysis". J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 136 (8): 1267–73. doi:10.1007/s00432-010-0777-z. PMID 20111973. S2CID 37780631.
- ^ Zhang X, Sun H, Danila DC, Johnson SR, Zhou Y, Swearingen B, Klibanski A (2002). "Loss of expression of GADD45 gamma, a growth inhibitory gene, in human pituitary adenomas: implications for tumorigenesis". J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 87 (3): 1262–7. doi:10.1210/jcem.87.3.8315. PMID 11889197.
- ^ Flores O, Burnstein KL (2010). "GADD45gamma: a new vitamin D-regulated gene that is antiproliferative in prostate cancer cells". Endocrinology. 151 (10): 4654–64. doi:10.1210/en.2010-0434. PMC 2946153. PMID 20739400.
- ^ Liebermann DA, Hoffman B (October 2011). "Prostate cancer: JunD, Gadd45a and Gadd45g as therapeutic targets". Cell Cycle. 10 (20): 3428. doi:10.4161/cc.10.20.17528. PMID 22030693.
- ^ Yu S, Cho J, Park I, Kim SJ, Kim H, Shin GT (2009). "Urinary GADD45gamma expression is associated with progression of lgA nephropathy". Am J Nephrol. 30 (2): 135–9. doi:10.1159/000209317. PMID 19293565. S2CID 46326535.
- ^ Ivanga M, Labrie Y, Calvo E, Belleau P, Martel C, Pelletier G, Morissette J, Labrie F, Durocher F (2009). "Fine temporal analysis of DHT transcriptional modulation of the ATM/Gadd45g signaling pathways in the mouse uterus". Molecular Reproduction and Development. 76 (3): 278–288. doi:10.1002/mrd.20949. ISSN 1040-452X. PMID 18671277. S2CID 9149501.
Further reading
edit- Fan W, Richter G, Cereseto A, Beadling C, Smith KA (2000). "Cytokine response gene 6 induces p21 and regulates both cell growth and arrest". Oncogene. 18 (47): 6573–82. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1203054. PMID 10597261.
- Gong R, Yu L, Zhang H, Tu Q, Zhao Y, Yang J, Xu Y, Zhao S (2000). "Assignment of human GADD45G to chromosome 9q22.1→q22.3 by radiation hybrid mapping". Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 88 (1–2): 95–6. doi:10.1159/000015496. PMID 10773677. S2CID 45495955.
- Yi YW, Kim D, Jung N, Hong SS, Lee HS, Bae I (2000). "Gadd45 family proteins are coactivators of nuclear hormone receptors". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 272 (1): 193–8. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2000.2760. PMID 10872826.
- Yang Q, Manicone A, Coursen JD, Linke SP, Nagashima M, Forgues M, Wang XW (2001). "Identification of a functional domain in a GADD45-mediated G2/M checkpoint". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (47): 36892–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.M005319200. PMID 10973963.
- Wan Y, Wang Z, Shao Y, Xu Y, Voorhees J, Fisher G (2001). "UV-induced expression of GADD45 is mediated by an oxidant sensitive pathway in cultured human keratinocytes and in human skin in vivo". Int. J. Mol. Med. 6 (6): 683–8. doi:10.3892/ijmm.6.6.683. PMID 11078829.
- Kovalsky O, Lung FD, Roller PP, Fornace AJ (2001). "Oligomerization of human Gadd45a protein". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (42): 39330–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M105115200. PMID 11498536.
- Sun L, Gong R, Wan B, Huang X, Wu C, Zhang X, Zhao S, Yu L (2004). "GADD45gamma, down-regulated in 65% hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) from 23 Chinese patients, inhibits cell growth and induces cell cycle G2/M arrest for hepatoma Hep-G2 cell lines". Mol. Biol. Rep. 30 (4): 249–53. doi:10.1023/A:1026370726763. PMID 14672412. S2CID 33065335.
- Jiang F, Wang Z (2004). "Gadd45gamma is androgen-responsive and growth-inhibitory in prostate cancer cells". Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 213 (2): 121–9. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2003.10.050. PMID 15062559. S2CID 54408868.
- Zerbini LF, Wang Y, Czibere A, Correa RG, Cho JY, Ijiri K, Wei W, Joseph M, Gu X, Grall F, Goldring MB, Zhou JR, Libermann TA, Zhou JR (2004). "NF-kappa B-mediated repression of growth arrest- and DNA-damage-inducible proteins 45alpha and gamma is essential for cancer cell survival". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101 (37): 13618–23. Bibcode:2004PNAS..10113618Z. doi:10.1073/pnas.0402069101. PMC 518803. PMID 15353598.
- Goehler H, Lalowski M, Stelzl U, Waelter S, Stroedicke M, Worm U, Droege A, Lindenberg KS, Knoblich M, Haenig C, Herbst M, Suopanki J, Scherzinger E, Abraham C, Bauer B, Hasenbank R, Fritzsche A, Ludewig AH, Büssow K, Buessow K, Coleman SH, Gutekunst CA, Landwehrmeyer BG, Lehrach H, Wanker EE (2004). "A protein interaction network links GIT1, an enhancer of huntingtin aggregation, to Huntington's disease". Mol. Cell. 15 (6): 853–65. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2004.09.016. PMID 15383276.