Harpalyce is a genus of flowering plants in the family Fabaceae. It belongs to the subfamily Faboideae. It includes 35 species of shrubs and small trees native to the tropical Americas. Their distribution is disjunct, ranging from Mexico to Nicaragua, Cuba, and northern to southeastern Brazil and Bolivia. Typical habitats include seasonally-dry tropical forest, warm-temperate humid forest, woodland, bushland and thicket, shrubland, and grassland. Most species are evergreen and flower during the dry season.[2]
| Harpalyce | |
|---|---|

| |
| Harpalyce brasiliana | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae |
| Subfamily: | Faboideae |
| Tribe: | Brongniartieae |
| Genus: | Harpalyce Moç. & Sessé ex DC. (1827) |
| Species | |
|
See text | |
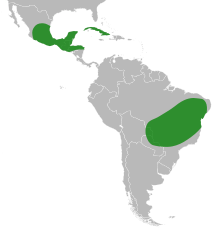
| |
| Range of Harpalyce[1] | |
Species
editHarpalyce comprises the following species:[2][3][4]
- Harpalyce acunae Borhidi & O.Muñiz
- Harpalyce alainii Leon
- Harpalyce arborescens A.Gray
- Harpalyce baracoensis Borhidi & O.Muñiz
- Harpalyce borhidii O.Muñiz
- Harpalyce brasiliana Benth.
- Harpalyce correntina São-Mateus, L.P.Queiroz & D.B.O.S.Cardoso
- Harpalyce cristalensis Borhidi & O.Muñiz
- Harpalyce cubensis Griseb.
- Harpalyce ekmanii Urb.
- Harpalyce flexuosa León & Alain ex Borhidi & O.Muñiz (unplaced)
- Harpalyce formosa DC.
- Harpalyce greuteri R.Rankin & P.A.González
- Harpalyce hilariana Benth.
- Harpalyce lanata L.P.Queiroz
- Harpalyce lepidota Taub.
- Harpalyce macedoi R.S.Cowan
- Harpalyce macrocarpa Britton & P.Wilson
- Harpalyce magnibracteata São-Mateus, D.B.O.S.Cardoso & L.P.Queiroz
- Harpalyce maisiana León & Alain
- Harpalyce mexicana Rose
- Harpalyce minor Benth.
- Harpalyce nipensis Urb.
- Harpalyce parvifolia H.S.Irwin & Arroyo
- Harpalyce pringlei Rose
- Harpalyce riparia São-Mateus, L.P.Queiroz & D.B.O.S.Cardoso[5]
- Harpalyce robusta H.S.Irwin & Arroyo
- Harpalyce rupicola Donn.Sm.
- Harpalyce sousae Arroyo
- Harpalyce speciosa Taub. ex Ule
- Harpalyce suberosa Urb.
- Harpalyce toaensis Borhidi & O.Muñiz
- Harpalyce tombadorensis São-Mateus, L.P.Queiroz & D.B.O.S.Cardoso
- Harpalyce torresii São-Mateus & M.Sousa
- Harpalyce villosa Britton & P.Wilson
- Harpalyce yucatanense Miranda ex São-Mateus & M.Sousa
References
edit- ^ Thompson IR, Ladiges PY, Ross JH (2001). "Phylogenetic studies of the tribe Brongniartieae (Fabaceae) using nuclear DNA (ITS-1) and morphological data". Syst Bot. 26 (3): 557–570. doi:10.1043/0363-6445-26.3.557 (inactive 1 November 2024). JSTOR 3093981.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of November 2024 (link) - ^ a b Harpalyce Moc. & Sessé ex DC. Plants of the World Online. Retrieved 1 September 2023.
- ^ "ILDIS LegumeWeb entry for Harpalyce". International Legume Database & Information Service. Cardiff School of Computer Science & Informatics. Retrieved 21 February 2014.
- ^ USDA; ARS; National Genetic Resources Program. "GRIN species records of Harpalyce". Germplasm Resources Information Network—(GRIN) [Online Database]. National Germplasm Resources Laboratory, Beltsville, Maryland. Retrieved 21 February 2014.
- ^ São-Mateus WM, de Queiroz LP, Gomes Jardim J, Cardoso DB (2018). "Harpalyce riparia (Leguminosae, Papilionoideae), a New Species from the Campos Rupestres of the Chapada Diamantina in Bahia, Brazil". Systematic Botany. 43 (1): 206–211. doi:10.1600/036364418X697102. S2CID 89752990.