Hoffmannseggia is a genus of flowering plants in the pea family, Fabaceae, known generally as rushpeas. These are pod-bearing herbs and subshrubs native to the Americas. In North America they range from California and Nebraska to southern Mexico, and from Colombia, Ecuador, and Peru to southern Argentina and Chile in South America.[1] The generic name honors Johann Centurius, Count of Hoffmannsegg, a nineteenth-century German nobleman and botanist.[3][4]
| Hoffmannseggia | |
|---|---|
| |
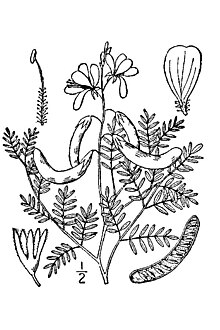
| Hoffmannseggia glauca | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae |
| Subfamily: | Caesalpinioideae |
| Tribe: | Caesalpinieae |
| Genus: | Hoffmannseggia Cav. (1798), nom. cons. |
| Type species | |
| Hoffmannseggia glauca (Ortega) Eifert.
| |
| Species[1] | |
|
See text | |
| Synonyms[1][2] | |
| |
Species
editHoffmannseggia comprises the following species:[4][5][6][1]
- Hoffmannseggia aphylla (Phil.) G.P.Lewis & Sotuyo
- Hoffmannseggia arequipensis Ulibarri
- Hoffmannseggia doelli Phil.
- subsp. argentina Ulibarri
- subsp. doellii Phil.
- Hoffmannseggia drepanocarpa A.Gray — sicklepod holdback
- Hoffmannseggia drummondii Torr. & A.Gray — dwarf nicker
- Hoffmannseggia erecta Phil.
- Hoffmannseggia eremophila (Phil.) Burkart ex Ulibarri
- Hoffmannseggia glauca (Ortega) Eifert—Indian rushpea, pig-nut, hog potato
- Hoffmannseggia humilis (M.Martens & Galeotti) Hemsl.
- Hoffmannseggia intricata Brandegee
- Hoffmannseggia microphylla Torr.—wand holdback
- Hoffmannseggia minor (Phil.) Ulibarri
- Hoffmannseggia miranda Sandwith
- Hoffmannseggia oxycarpa Benth.—sharppod rushpea
- subsp. arida (Rose) B. B. Simpson
- subsp. oxycarpa Benth.
- Hoffmannseggia peninsularis (Britton) Wiggins—Peninsular holdback
- Hoffmannseggia prostrata Lag. ex DC.
- Hoffmannseggia pumilio (Griseb.) B.B.Simpson
- Hoffmannseggia repens (Eastw.) Cockerell—creeping nicker
- Hoffmannseggia tenella Tharp & L.P.Williams—slender rushpea
- Hoffmannseggia trifoliata Cav.
- Hoffmannseggia viscosa (Ruiz & Pav.) Hook. & Arn.
- Hoffmannseggia watsonii (Fisher) Rose
- Hoffmannseggia yaviensis Ulibarri
References
editWikimedia Commons has media related to Hoffmannseggia.
- ^ a b c d Hoffmannseggia Cav. Plants of the World Online. Retrieved 1 September 2023.
- ^ "Hoffmannseggia Cav". Germplasm Resources Information Network. United States Department of Agriculture. 2007-10-05. Retrieved 2010-02-01.
- ^ The Legume Phylogeny Working Group (LPWG). (2017). "A new subfamily classification of the Leguminosae based on a taxonomically comprehensive phylogeny". Taxon. 66 (1): 44–77. doi:10.12705/661.3. hdl:10568/90658.
- ^ a b Gagnon E, Bruneau A, Hughes CE, de Queiroz LP, Lewis GP. (2016). "A new generic system for the pantropical Caesalpinia group (Leguminosae)". PhytoKeys (71): 1–160. doi:10.3897/phytokeys.71.9203. PMC 5558824. PMID 28814915.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Simpson BB, Ulibarri EA (2006). "A synopsis of the genus Hoffmannseggia (Leguminosae)" (PDF). Lundellia. 9: 7–33. doi:10.25224/1097-993X-9.1.7. S2CID 134611192.
- ^ Lewis GP, Solange Sotuyo J (2010). "Hoffmannseggia aphylla (Leguminosae: Caesalpinieae), a new name for a Chilean endemic". Kew Bull. 65 (2): 221–224. Bibcode:2010KewBu..65..221L. doi:10.1007/s12225-010-9201-8. S2CID 34248431.
External links
editWikispecies has information related to Hoffmannseggia.