Equine anatomy encompasses the gross and microscopic anatomy of horses, ponies and other equids, including donkeys, mules and zebras. While all anatomical features of equids are described in the same terms as for other animals by the International Committee on Veterinary Gross Anatomical Nomenclature in the book Nomina Anatomica Veterinaria, there are many horse-specific colloquial terms used by equestrians.
External anatomy
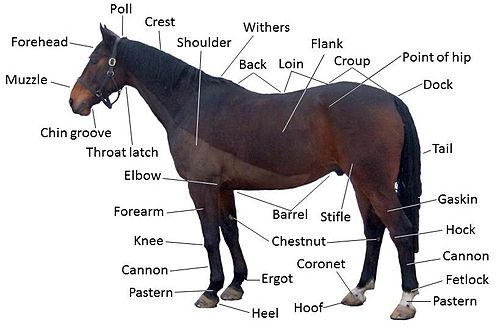
edit- Back: the area where the saddle sits, beginning at the end of the withers, extending to the last thoracic vertebrae (colloquially includes the loin or "coupling", though technically incorrect usage)
- Barrel: the body of the horse,[1][2] enclosing the rib cage and the major internal organs
- Buttock: the part of the hindquarters behind the thighs and below the root of the tail
- Cannon or cannon bone: the area between the knee or hock and the fetlock joint, sometimes called the "shin" of the horse, though technically it is the third metacarpal
- Chestnut: a callosity on the inside of each leg
- Chin groove: the part of the horse's head behind the lower lip and chin, the area that dips down slightly on the lower jaw; area where the curb chain of certain bits is fastened
- Coupling: see "Loin" below
- Coronet or coronary band: the ring of soft tissue just above the horny hoof that blends into the skin of the leg
- Crest: the upper portion of the neck where the mane grows
- Croup: the topline of the hindquarters, beginning at the hip, extending proximate to the sacral vertebrae and stopping at the dock of the tail (where the coccygeal vertebrae begin); sometimes called "rump"
- Dock: the living part of the tail,[3] consisting of the coccygeal vertebrae, muscles and ligaments. Sometimes used colloquially to refer to the root of the tail.
- Elbow: The joint of the front leg at the point where the belly of the horse meets the leg. Homologous to the elbow in humans
- Ergot: a callosity on the back of the fetlock
- Face: the area between the forehead and the tip of the upper lip
- Fetlock: sometimes called the "ankle" of the horse, though it is not the same skeletal structure as an ankle in humans; known to anatomists as the metacarpophalangeal (front) or metatarsophalangeal (hind) joint; homologous to the "ball" of the foot or the metacarpophalangeal joints of the fingers in humans
- Flank: where the hind legs and the barrel meet, specifically the area right behind the rib cage and in front of the stifle joint
- Forearm: the area of the front leg between the knee and elbow, consisting of the fused radius and ulna, and all the tissue around these bones; anatomically, the antebrachium.
- Forehead: the area between the poll, the eyes and the arch of the nose
- Forelock: the continuation of the mane, which hangs from between the ears down onto the forehead of the horse
- Frog: the highly elastic wedge-shaped mass on the underside of the hoof, which normally makes contact with the ground every stride, and supports both the locomotion and circulation of the horse
- Gaskin: the large muscle on the hind leg, just above the hock, below the stifle, homologous to the calf of a human
- Girth or heartgirth: the area right behind the elbow of the horse, where the girth of the saddle would go; this area should be where the barrel is at its greatest diameter in a properly-conditioned horse that is not pregnant or obese
- Hindquarters: the large, muscular area of the hind legs, above the stifle and behind the barrel. Can also be used to refer to the back end of a horse.
- Hock: the tarsus of the horse (hindlimb equivalent to the human ankle and heel), the large joint on the hind leg
- Hoof: the foot of the horse; the hoof wall is the tough outside covering of the hoof that comes into contact with the ground and is, in many respects, a much larger and stronger version of the human fingernail
- Jugular groove: the line of indentation on the lower portion of the neck, can be seen from either side, just above the windpipe; beneath this area run the jugular vein, the carotid artery and part of the sympathetic trunk
- Knee: the carpus of the horse (equivalent to the human wrist), the large joint in the front legs, above the cannon bone
- Loin: the area right behind the saddle, going from the last rib to the croup, anatomically approximate to the lumbar spine
- Mane: long and relatively coarse hair growing from the dorsal ridge of the neck
- Muzzle: the chin, mouth, and nostrils of the face
- Pastern: the connection between the coronet and the fetlock, made up of the middle and proximal phalanx
- Poll: commonly refers to the poll joint at the beginning of the neck, immediately behind the ears, a slight depression at the joint where the atlas (C1) meets the occipital crest; anatomically, the occipital crest itself is the "poll"
- Root of the tail or root of the dock: the point where the tail is "set on" (attached) to the rump;[3] Sometimes also called the "dock"
- Shoulder: made up of the scapula and associated muscles, runs from the withers to the point of shoulder (the joint at the front of the chest, i.e. the glenoid); the angle of the shoulder has a great effect on the horse's movement and jumping ability, and is an important aspect of equine conformation
- Splints: bones found on each of the legs, on either side of the cannon bone (8 total); partially vestigial, these bones support the corresponding carpal bones in the forelimb, and the corresponding tarsal bones in the hindlimb;[4] anatomically referred to as metacarpal/metatarsal II (on the medial aspect (inside)) and IV (on the lateral aspect (outside))
- Stifle joint: corresponds to the knee of a human, consists of the articulation between femur and tibia, as well as the articulation between patella and femur
- Tail: the long hairs which grow from the dock; may also include the dock[3] The long hairs alone are sometimes called the skirt.
- Throatlatch[5][6][7][8][9][10] (also, throttle, throatlash[citation needed], throat[11]): the point at which the windpipe meets the head at the underside of the jaw,[3] corresponding to where the eponymous part of a bridle goes.[12]
- Withers: the highest point of the thoracic vertebrae, the point just above the tops of the shoulder blades, seen best with horse standing square and head slightly lowered; the height of the horse is measured at the withers.
Digestive system
editHorses and other equids evolved as grazing animals, adapted to eating small amounts of the same kind of food all day long. In the wild, the horse adapted to eating prairie grasses in semi-arid regions and traveling significant distances each day in order to obtain adequate nutrition.[13] Therefore, the digestive system of a horse is about 30 m (100 ft) long, and most of this is intestines.
Mouth
editDigestion begins in the mouth, which is also called the "oral cavity." It is made up of the teeth, the hard palate, the soft palate, the tongue and related muscles, the cheeks and the lips. Horses also have three pairs of salivary glands, the parotoid (largest salivary gland and located near the poll), mandibular (located in the jaw), and sublingual (located under the tongue). Horses select pieces of forage and pick up finer foods, such as grain, with their sensitive, prehensile lips. The front teeth of the horse, called incisors, clip forage, and food is then pushed back in the mouth by the tongue, and ground up for swallowing by the premolars and molars.[14]
Esophagus
editThe esophagus is about 1.2 to 1.5 m (4 to 5 ft) in length, and carries food to the stomach. A muscular ring, called the cardiac sphincter, connects the stomach to the esophagus. This sphincter is very well developed in horses. This and the oblique angle at which the esophagus connects to the stomach explains why horses cannot vomit.[14] The esophagus is also the area of the digestive tract where horses may suffer from choke.
Stomach
editHorses have a relatively small stomach for their size, and this limits the amount of feed a horse can take in at one time. The average sized horse (360 to 540 kg [800 to 1,200 lb]) has a stomach with a capacity of around 19 L (5 US gal), and works best when it contains about 7.6 L (2 US gal). Because the stomach empties when 2⁄3 full, whether stomach enzymes have completed their processing of the food or not, and doing so prevents full digestion and proper utilization of feed, continuous foraging or several small feedings per day are preferable to one or two large ones.[14] The horse stomach consists of a non-glandular proximal region (saccus cecus), divided by a distinct border, the margo plicatus, from the glandular distal stomach.[15]
In the stomach, assorted acids and the enzyme pepsin break down food. Pepsin allows for the further breakdown of proteins into amino acid chains.[14] Other enzymes include resin and lipase. Additionally, the stomach absorbs some water, as well as ions and lipid-soluble compounds.
Small intestine
editThe horse's small intestine is 15 to 21 m (50 to 70 ft) long and holds 38 to 45 L (10 to 12 US gal). This is the major digestive organ, and where most nutrients are absorbed.[16] It has three parts, the duodenum, jejunum and ileum. The majority of digestion occurs in the duodenum while the majority of absorption occurs in the jejunum. Bile from the liver aids in digesting fats in the duodenum combined with enzymes from the pancreas and small intestine. Horses, in common with mammals such as camels, do not have a gall bladder, meaning bile flows constantly.[14] Most food is digested and absorbed into the bloodstream from the small intestine, including proteins, simple carbohydrate, fats, and vitamins A, D, and E. Any remaining liquids and roughage move into the large intestine.
Large intestine
editThe large intestine, also known as the hindgut consists of the cecum, large colon, small colon and rectum, terminating in the anus.
Cecum
editThe cecum (called the "water gut" in old textbooks) is the first section of the large intestine, analogous to the appendix in humans. It is a cul-de-sac pouch,[16] about 1.2 m (4 ft) long that holds 26 to 30 L (7 to 8 US gal). It contains bacteria and other microbes that break down cellulose and other indigestible plant fiber through fermentation into volatile fatty acids.[17] These microbes feed upon the portion of chyme not absorbed by the small intestine, and produce vitamin K and B complex vitamins.[17]
Large colon
editThe large colon is 3.0 to 3.7 m (10 to 12 ft) long and holds up to 76 L (20 US gal) of semi-liquid matter. It is made up of the right ventral (lower) colon, the left ventral colon, the left dorsal (upper) colon, the right dorsal colon, and the transverse colon, in that order.[14] Three flexures are also named: the sternal flexure, between right and left ventral colon; the pelvic flexure, between left ventral and left dorsal colon; the diaphragmatic flexure, between left dorsal and right dorsal colon. Besides the transverse colon, these sections are all analogous to the ascending colon in humans. The large colon continues the fermentation process, and absorbs volatile fatty acids as an energy source. Due to its many twists and turns, the large colon is a common place for certain forms of colic including impaction, displacement and volvulus.[16][17]
Small colon
editThe small colon is 3.0 to 3.7 m (10 to 12 ft) in length and holds only 19 L (5 US gal) of material. It is the area where the majority of water in the horse's diet is absorbed, and is the place where fecal balls are formed.[14] This section is analogous to the descending colon in humans.
Rectum and anus
editThe rectum is about 30 cm (1 ft) long, and acts as a holding chamber for waste matter, which is then expelled from the body via the anus.[14]
Reproductive system
editMare
editThe mare's reproductive system is responsible for controlling gestation, birth, and lactation, as well as her estrous cycle and mating behavior. It lies ventral to the 4th or 5th lumbar vertebrae, although its position within the mare can vary depending on the movement of the intestines and distention of the bladder.
The mare has two ovaries, usually 7 to 8 cm (2.8 to 3.1 in) in length and 3 to 4 cm (1.2 to 1.6 in) thick, that generally tend to decrease in size as the mare ages. In equine ovaries, unlike in humans, the vascular tissue is cortical to follicular tissue, so ovulation can only occur at an ovulation fossa near the infundibulum. The ovaries connect to the fallopian tubes (oviducts), which serve to move the ovum from the ovary to the uterus. To do so, the oviducts are lined with a layer of cilia, which produce a current that flows toward the uterus. Each oviduct attaches to one of the two horns of the uterus, which are approximately 20 to 25 cm (7.9 to 9.8 in) in length. These horns attach to the body of the uterus (18 to 20 cm [7.1 to 7.9 in] long). The equine uterus is bipartite, meaning the two uterine horns fuse into a relatively large uterine body (resembling a shortened bicornuate uterus or a stretched simplex uterus). Caudal to the uterus is the cervix, about 5 to 7 cm (2.0 to 2.8 in) long, which separates the uterus from the vagina. Usually 3.5 to 4 cm (1.4 to 1.6 in) in diameter with longitudinal folds on the interior surface, it can expand to allow the passage of the foal. The vagina of the mare is 15 to 20 cm (5.9 to 7.9 in) long, and is quite elastic, allowing it to expand.[citation needed] The vulva is the external opening of the vagina, and consists of the clitoris and two labia.[18] It lies ventral to the rectum.[19][20] The mare has two mammary glands, which are smaller in maiden mares. They have two ducts each, which open externally.[citation needed]
Stallion
editThe stallion's reproductive system is responsible for his sexual behavior and secondary sex characteristics (such as a large crest). The external genitalia include the urethra; the testes, which average 8 to 12 cm (3.1 to 4.7 in) long; the penis, which, when housed within the prepuce, is 50 cm (20 in) long and 2.5 to 6 cm (0.98 to 2.36 in) in diameter with the distal end 15 to 20 cm (5.9 to 7.9 in) and when erect, increases by 3 to 4 times. The internal genitalia accessory sex glands are the vesicular glands, prostate gland, and bulbourethral glands, which contribute fluid to the semen at ejaculation, but are not strictly necessary for fertility.[21]
Teeth
editA horse's teeth include incisors, premolars, molars, and sometimes canine teeth. A horse's incisors, premolars, and molars, once fully developed, continue to erupt throughout its lifetime as the grinding surface is worn down through chewing. Because of this pattern of wear, a rough estimate of a horse's age can be made from an examination of the teeth. Abnormal wear of the teeth, caused by conformational defects, abnormal behaviors, or improper diets, can cause serious health issues and can even result in the death of the horse.
Feet/hooves
editThe hoof of the horse encases part of the second and all of the third phalanx of the lower limbs, analogous to the fingertip or toe tip of a human. In essence, a horse travels on its "tiptoes". The hoof wall is a much larger, thicker and stronger version of the human fingernail or toenail, made up of similar materials, primarily keratin, a very strong protein molecule. The horse's hoof contains a high proportion of sulfur-containing amino acids which contribute to its resilience and toughness. Vascular fold-like structures called laminae suspend the distal phalanx from the hoof wall.
Skeletal system
editThe skeleton of the horse has three major functions in the body. It protects vital organs, provides framework, and supports soft parts of the body. Horses have 205 bones, which are divided into the appendicular skeleton (the legs) and the axial skeleton (the skull, vertebral column, sternum, and ribs). Both pelvic and thoracic limbs contain the same number of bones, 20 bones per limb. Bones are connected to muscles via tendons and other bones via ligaments. Bones are also used to store minerals, and are the site of red blood cell formation.
- The Appendicular system includes the limbs of the horse;
- The Axial system is composed of the spine, ribs and skull;
The bones of the horse are the same as those of other domestic species, but the third metacarpal and metatarsal are much more developed and the second and fourth are undeveloped, having the first and fifth metacarpal and metatarsal.[22]
| Spine | 54 |
| Ribs | 36 |
| Sternum | 01 |
| Head (including ear ) | 34 |
| Thoracic region | 40 |
| Pelvic region | 40 |
Ligaments and tendons
editLigaments
editLigaments attach bone to bone or bone to tendon, and are vital in stabilizing joints as well as supporting structures. They are made up of fibrous material that is generally quite strong. Due to their relatively poor blood supply, ligament injuries generally take a long time to heal.
Tendons
editTendons are cords of connective tissue attaching muscle to bone, cartilage or other tendons. They are a major contributor to shock absorption, are necessary for support of the horse's body, and translate the force generated by muscles into movement. Tendons are classified as flexors (flex a joint) or extensors (extend a joint). However, some tendons will flex multiple joints while extending another (the flexor tendons of the hind limb, for example, will flex the fetlock, pastern, and coffin joint, but extend the hock joint). In this case, the tendons (and associated muscles) are named for their most distal action (digital flexion).
Tendons form in the embryo from fibroblasts which become more tightly packed as the tendon grows. As tendons develop they lay down collagen, which is the main structural protein of connective tissue. As tendons pass near bony prominences, they are protected by a fluid filled synovial structure, either a tendon sheath or a sac called a bursa.
Tendons are easily damaged if placed under too much strain, which can result in a painful, and possibly career-ending, injury. Tendinitis is most commonly seen in high performance horses that gallop or jump. When a tendon is damaged the healing process is slow because tendons have a poor blood supply, reducing the availability of nutrients and oxygen to the tendon. Once a tendon is damaged the tendon will always be weaker, because the collagen fibres tend to line up in random arrangements instead of the stronger linear pattern. Scar tissue within the tendon decreases the overall elasticity in the damaged section of the tendon as well, causing an increase in strain on adjacent uninjured tissue.
Muscular system
editWhen a muscle contracts, it pulls a tendon, which acts on the horse's bones to move them. Muscles are commonly arranged in pairs so that they oppose each other (they are "antagonists"), with one flexing the joint (a flexor muscle) and the other extending it (extensor muscle). Therefore, one muscle of the pair must be relaxed in order for the other muscle in the pair to contract and bend the joint properly. A muscle is made up of several muscle bundles, which in turn are made up of muscle fibers. Muscle fibers have myofibrils, which are able to contract due to actin and myosin. A muscle together with its tendon and bony attachments form an extensor or flexor unit.
Respiratory system and smell
editThe horse's respiratory system consists of the nostrils, pharynx, larynx, trachea, diaphragm, and lungs. Additionally, the nasolacrimal duct and sinuses are connected to the nasal passage. The horse's respiratory system not only allows the animal to breathe, but also is important in the horse's sense of smell (olfactory ability) as well as in communicating. The soft palate blocks off the pharynx from the mouth (oral cavity) of the horse, except when swallowing. This helps prevent the horse from inhaling food, but also means that a horse cannot use its mouth to breathe when in respiratory distress—a horse can only breathe through its nostrils, also called obligate nasal breathing.[23] For this same reason, horses also cannot pant as a method of thermoregulation. The genus Equus also has a unique part of the respiratory system called the guttural pouch, which is thought to equalize air pressure on the tympanic membrane. Located between the mandibles but below the occiput, it fills with air when the horse swallows or exhales.
Circulatory system
editThe horse's circulatory system includes the four-chambered heart, averaging 3.9 kg (8.5 lb) in weight, as well as the blood and blood vessels. Its main purpose is to circulate blood throughout the body to deliver oxygen and nutrients to tissues, and to remove waste from these tissues. The hoof (including the frog - the V-shaped part on the bottom of the horses hoof) is a very important part of the circulatory system. As the horse puts weight onto the hoof, the hoof wall is pushed outwards and the frog compressed, driving blood out of the frog, the digital pad, and the laminae of the hoof. When weight is removed from the hoof, the release of pressure pulls blood back down into the foot again. This effectively creates an auxiliary blood-pumping system at the end of each leg. Some of this effect may be lost when a horse is shod (eliminating the expansion and contraction of the hoof wall and raising the frog higher from the ground).[24]
The eye
editThe horse has one of the largest eyes of all land mammals.[25] Eye size in mammals is significantly correlated to maximum running speed as well as to body size, in accordance with Leuckart's law; animals capable of fast locomotion require large eyes.[26] The eye of the horse is set to the side of its skull, consistent with that of a prey animal.[25] The horse has a wide field of monocular vision, as well as good visual acuity. Horses have two-color, or dichromatic vision, which is somewhat like red-green color blindness in humans.[27] Because the horse's vision is closely tied to behavior, the horse's visual abilities are often taken into account when handling and training the animal.
Hearing
editThe hearing of horses is good,[28] superior to that of humans, and the pinna of each ear can rotate up to 180°, giving the potential for 360° hearing without having to move the head.[29] Often, the eye of the horse is looking in the same direction as the ear is directed.
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ Goody, John (2000). Horse Anatomy (2nd ed.). J A Allen. ISBN 0851317693.
- ^ Pavord, Tony; Pavord, Marcy (2007). Complete Equine Veterinary Manual. David & Charles. ISBN 978-0715318836.
- ^ a b c d Brander, Michael (1971). The Complete Guide to Horsemanship. London: A & C Black. p. 444. ISBN 0-7136-1701-2. p.38
- ^ Getty, R (1975). "Equine Osteology". Sisson and Grossman's The Anatomy of the Domestic Animals Vol 1 (5th ed.). Saunders. pp. 290, 317. ISBN 0-7216-4102-4.
- ^ Interactive points of the horse chart Archived 29 February 2012 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "OSU Extension Catalog - Oregon State University" (PDF). extension.oregonstate.edu. Archived (PDF) from the original on 11 April 2013. Retrieved 1 May 2018.
- ^ Whittington, Beverly. "Body Parts of the Horse". Gaited Horses. Archived from the original on 30 March 2018. Retrieved 1 May 2018.
- ^ "Skeleton of the horse" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 29 September 2011. Retrieved 25 August 2011.
- ^ "Parts of the Horse" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 August 2011. Retrieved 25 August 2011.
- ^ "American Quarter Horse". Archived from the original on 29 August 2011. Retrieved 25 August 2011.
- ^ "Points - the Horse". HorseData.co.uk. Archived from the original on 26 September 2011.
- ^ "Definition of THROATLATCH". www.merriam-webster.com. Retrieved 1 May 2018.
- ^ Budiansky, Stephen. The Nature of Horses. Free Press, 1997. ISBN 0-684-82768-9
- ^ a b c d e f g h Giffen, James M.; Gore, Tom (1998) [1989]. Horse Owner's Veterinary Handbook (2nd ed.). New York: Howell Book House. ISBN 0-87605-606-0.
- ^ Andrews, F. M.; Buchanan, B. R.; Elliot, S. B.; Clariday, N. A.; Edwards, L. H. (2005). "Gastric ulcers in horses". J. Anim. Sci. 83 (13): E18–E21. doi:10.2527/2005.8313_supplE18x. Archived from the original on 23 February 2013.
- ^ a b c "Horse Nutrition - The Horse's Digestive System." Bulletin 762-00, Ohio State University. Web site accessed 9 February 2007.
- ^ a b c Williams, Carey A. (April 2004). "The Basics of Equine Nutrition". Equine Science Center. Rutgers University. FS #038.
- ^ Budras, Klaus-Dieter; Sack, W. O.; Rock, Sabine (2003). Anatomy of the Horse: An Illustrated Text. Schlütersche. ISBN 978-3-89993-003-0.
- ^ Mina C G Davies Morel (5 June 2015). Equine Reproductive Physiology, Breeding and Stud Management, 4th Edition. CABI. ISBN 978-1-78064-442-4.
- ^ Juan C. Samper (1 January 2009). Equine Breeding Management and Artificial Insemination. Elsevier Health Sciences. ISBN 978-1-4160-5234-0.
- ^ "The Stallion: Breeding Soundness Examination & Reproductive Anatomy". University of Wisconsin-Madison. Archived from the original on 16 July 2007. Retrieved 7 July 2007.
- ^ Riegal, Ronald J. DVM, and Susan E. Hakola RN. Illustrated Atlas of Clinical Equine Anatomy and Common Disorders of the Horse Vol. II. Equistar Publication, Limited. Marysville, OH. Copyright 2000.
- ^ Susan J. Holcombe (1998). "Neuromuscular Regulation of the Larynx and Nasopharynx in the Horse" (PDF). Proceedings of the Annual Convention of the AAEP. 44: 26.
- ^ Cook FRCVS PhD, Robert (2008), Shoeing your horse is like foot binding your daughter, Veterinary Times, p. 8, archived from the original (PDF) on 13 August 2017, retrieved 23 August 2011
- ^ a b Hartley, C; Grundon, RA (2016). "Chapter 5: Diseases and surgery of the globe and orbit". In Gilger, BC (ed.). Equine Ophthalmology (3rd ed.). John Wiley & Sons. p. 151. ISBN 9781119047742.
- ^ Heard-Booth, A. N.; Kirk, E. C. (2012). "The Influence of Maximum Running Speed on Eye Size: A Test of Leuckart's Law in Mammals". The Anatomical Record. 295 (6): 1053–62. doi:10.1002/ar.22480. PMID 22539450. S2CID 26726269.
- ^ McDonnell, Sue. "In Living Color." The Horse, Online edition, 1 June 2007. Web site accessed 27 July 2007 at "The Horse – Your Guide to Equine Health Care". Archived from the original on 27 September 2007. Retrieved 27 July 2007.
- ^ Ensminger, M.E. Horses and Horsemanship, p. 309
- ^ Myers Horse Safe p.7