The hypogastric nerves (one on each side) are the continuation of the superior hypogastric plexus that descend into the pelvis anterior the sacrum and become the inferior hypogastric plexuses on either side of pelvic organs. The hypogastric nerves serve as a pathway for autonomic fibers to communicate between the lower abdomen and pelvis.
| Hypogastric nerve | |
|---|---|
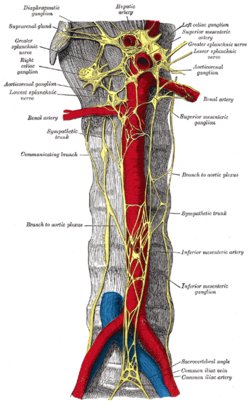 Autonomic plexuses and ganglia on the abdominal aorta. (Hypogastric nerves visible at the bottom of the image but not labeled.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nervus hypogastricus |
| TA98 | A14.3.03.047 |
| TA2 | 6714 |
| FMA | 77596 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
Structure
editThe hypogastric nerves begin where the superior hypogastric plexus splits into a right and left hypogastric nerves. The hypogastric nerves continue inferiorly on their corresponding side of the body, where they descends into the pelvis to form the inferior hypogastric plexuses.[1]
The hypogastric nerves likely contain three nerve fibers types:[2]
- Preganglionic and postganglionic sympathetic fibers descend from the superior hypogastric plexus from lumbar splanchnic nerves (from the sympathetic trunk at levels L1-L2). Sympathetic fibers are the most numerous fibers in the hypogastric nerves.[2]
- Preganglionic parasympathetic fibers that originate from pelvic splanchnic nerves (sacral spinal nerves, S2-S4) ascend from the inferior hypogastric plexuses into hypogastric nerves.[2][3]
- Visceral sensory fibers that project to the lumbar spinal cord.[2]
Clinical significance
editThe hypogastric nerve may be blocked for a local anaesthetic.[4] This endangers the nearby common iliac artery and common iliac vein.[4]
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ Aurore, Valerie; Röthlisberger, Raphael; Boemke, Nane; Hlushchuk, Ruslan; Bangerter, Hannes; Bergmann, Mathias; Imboden, Sara; Mueller, Michael D.; Eppler, Elisabeth; Djonov, Valentin (2020-05-19). "Anatomy of the female pelvic nerves: a macroscopic study of the hypogastric plexus and their relations and variations". Journal of Anatomy. 237 (3): 487–494. doi:10.1111/joa.13206. ISSN 0021-8782. PMC 7476201. PMID 32427364.
- ^ a b c d Kraima, Anne C.; van Schaik, Jan; Susan, Serhat; van de Velde, Cornelius J.H.; Hamming, Jaap F.; Lakke, Egbert A.J.F.; DeRuiter, Marcus C. (2015-02-13). "New insights in the neuroanatomy of the human adult superior hypogastric plexus and hypogastric nerves". Autonomic Neuroscience. 189: 60–67. doi:10.1016/j.autneu.2015.02.001. PMID 25704391. S2CID 23908051.
- ^ Standring, Susan (21 October 2020). Gray's anatomy: the anatomical basis of clinical practice (41 ed.). p. 1038. ISBN 978-0-7020-7705-0. OCLC 1202943188.
- ^ a b Waldman, Steven D. (2007-01-01), Waldman, Steven D.; Bloch, Joseph I. (eds.), "chapter 161 - Hypogastric Plexus Block and Impar Ganglion Block", Pain Management, Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders, pp. 1350–1357, ISBN 978-0-7216-0334-6, retrieved 2021-02-06
External links
edit- Anatomy photo:40:09-0203 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Posterior Abdominal Wall: The Abdominal Aorta and Paraaortic Nerve Plexus"
- Autonomics of the Pelvis - Page 5 of 12 anatomy module at med.umich.edu
- https://web.archive.org/web/20060709234151/http://www.downstate.edu/ginzler-painmanagement/ginzler-painmanagement.htm