The hypoglossal nerve, also known as the twelfth cranial nerve, cranial nerve XII, or simply CN XII, is a cranial nerve that innervates all the extrinsic and intrinsic muscles of the tongue except for the palatoglossus, which is innervated by the vagus nerve.[a]
| Hypoglossal nerve | |
|---|---|
 Hypoglossal nerve, cervical plexus, and their branches. | |
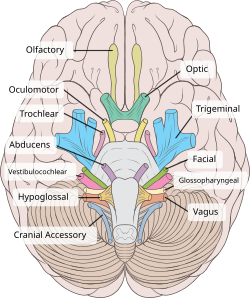 The hypoglossal nerve arises as a series of rootlets, from the caudal brain stem, here seen from below. | |
| Details | |
| To | Ansa cervicalis |
| Innervates | Genioglossus, hyoglossus, styloglossus, geniohyoid, thyrohyoid, intrinsic muscles of the tongue |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nervus hypoglossus |
| MeSH | D007002 |
| NeuroNames | 704 |
| TA98 | A14.2.01.191 |
| TA2 | 6357 |
| FMA | 50871 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
CN XII is a nerve with a sole motor function. The nerve arises from the hypoglossal nucleus in the medulla[1][2] as a number of small rootlets, pass through the hypoglossal canal and down through the neck, and eventually passes up again over the tongue muscles it supplies into the tongue.
The nerve is involved in controlling tongue movements required for speech and swallowing, including sticking out the tongue and moving it from side to side. Damage to the nerve or the neural pathways which control it can affect the ability of the tongue to move and its appearance, with the most common sources of damage being injury from trauma or surgery, and motor neuron disease. The first recorded description of the nerve was by Herophilos in the third century BC. The name hypoglossus springs from the fact that its passage is below the tongue, from hypo (Greek: "under") and glossa (Greek: "tongue").
Structure
editThe hypoglossal nerve arises as a number of small rootlets from the front of the medulla, the bottom part of the brainstem,[1][2] in the anterolateral sulcus which separates the olive and the pyramid.[3] The nerve passes through the subarachnoid space and pierces the dura mater near the hypoglossal canal, an opening in the occipital bone of the skull.[2][4]
After emerging from the hypoglossal canal, the hypoglossal nerve gives off a meningeal branch and picks up a branch from the anterior ramus of C1. It then travels close to the vagus nerve and spinal division of the accessory nerve,[2] spirals downwards behind the vagus nerve and passes between the internal carotid artery and internal jugular vein lying on the carotid sheath.[4]
At a point at the level of the angle of the mandible, the hypoglossal nerve emerges from behind the posterior belly of the digastric muscle.[4] It then loops around a branch of the occipital artery and travels forward into the region beneath the mandible.[4] The hypoglossal nerve moves forward lateral to the hyoglossus and medial to the stylohyoid muscles and lingual nerve.[5] It continues deep to the genioglossus muscle and continues forward to the tip of the tongue. It distributes branches to the intrinsic and extrinsic muscle of the tongue innervates as it passes in this direction, and supplies several muscles (hyoglossus, genioglossus and styloglossus) that it passes.[5]
The rootlets of the hypoglossal nerve arise from the hypoglossal nucleus near the bottom of the brain stem.[1] The hypoglossal nucleus receives input from both the motor cortices but the contralateral input is dominant; innervation of the tongue is essentially lateralized.[6] Signals from muscle spindles on the tongue travel through the hypoglossal nerve, moving onto the lingual nerve which synapses on the trigeminal mesencephalic nucleus.[2]
-
The hypoglossal nerve leaves the skull through the hypoglossal canal, which is situated near the large opening for the spinal cord, the foramen magnum.
-
After leaving the skull, the hypoglossal nerve spirals around the vagus nerve and then passes behind the deep belly of the digastric muscle.
-
The hypoglossal nerve then travels deep to the hyoglossus muscle, which it supplies. It then continues and supplies the genioglossus muscle, and towards the tip of the tongue, where it divides into branches supplying the tongue muscles.
Development
editNeurons of the hypoglossal nucleus are derived from the basal plate of the embryonic medulla oblongata.[7][8] The musculature they supply develops as the hypoglossal cord from the myotomes of the first four pairs of occipital somites.[9][10] The nerve is first visible as a series of roots in the fourth week of development, which have formed a single nerve and link to the tongue by the fifth week.[11][12]
Function
editThe hypoglossal nerve provides motor control of the extrinsic muscles of the tongue: genioglossus, hyoglossus, styloglossus, and the intrinsic muscles of the tongue.[2] These represent all muscles of the tongue except the palatoglossus muscle, which is innervated by the vagus nerve.[2] The hypoglossal nerve is of a general somatic efferent (GSE) type.[2]
These muscles are involved in moving and manipulating the tongue.[2] The left and right genioglossus muscles in particular are responsible for protruding the tongue. The muscles, attached to the underside of the top and back parts of the tongue, cause the tongue to protrude and deviate towards the opposite side.[13] The hypoglossal nerve also supplies movements including clearing the mouth of saliva and other involuntary activities. The hypoglossal nucleus interacts with the reticular formation, involved in the control of several reflexive or automatic motions, and several corticonuclear originating fibers supply innervation aiding in unconscious movements relating to speech and articulation.[2]
Clinical significance
editDamage
editReports of damage to the hypoglossal nerve are rare.[14] The most common causes of injury in one case series were compression by tumours and gunshot wounds.[15] A wide variety of other causes can lead to damage of the nerve. These include surgical damage, medullary stroke, multiple sclerosis, Guillain-Barre syndrome, infection, sarcoidosis, and presence of an ectatic vessel in the hypoglossal canal.[15][16] Damage can be on one or both sides, which will affect symptoms that the damage causes.[2] Because of the close proximity of the nerve to other structures including nerves, arteries, and veins, it is rare for the nerve to be damaged in isolation.[16] For example, damage to the left and right hypoglossal nerves may occur with damage to the facial and trigeminal nerves as a result of damage from a clot following arteriosclerosis of the vertebrobasilar artery. Such a stroke may result in tight oral musculature, and difficulty speaking, eating and chewing.[2]
Progressive bulbar palsy, a form of motor neuron disease, is associated with combined lesions of the hypoglossal nucleus and nucleus ambiguus with wasting (atrophy) of the motor nerves of the pons and medulla. This may cause difficulty with tongue movements, speech, chewing and swallowing caused by dysfunction of several cranial nerve nuclei.[2] Motor neuron disease is the most common disease affecting the hypoglossal nerve.[17]
Examination
editThe hypoglossal nerve is tested by examining the tongue and its movements. At rest, if the nerve is injured a tongue may appear to have the appearance of a "bag of worms" (fasciculations) or wasting (atrophy). The nerve is then tested by sticking the tongue out. If there is damage to the nerve or its pathways, the tongue will usually but not always deviate to one side, due to the genioglossus muscle receiving nerve signals on one side but not the other.[6][19] When the nerve is damaged, the tongue may feel "thick," "heavy," or "clumsy." Weakness of tongue muscles can result in slurred speech, affecting sounds particularly dependent on the tongue for generation (i.e., lateral approximants, dental stops, alveolar stops, velar nasals, rhotic consonants etc.).[17] Tongue strength may be tested by poking the tongue against the inside of their cheek, while an examiner feels or presses from the cheek.[6]
The hypoglossal nerve carries lower motor neurons that synapse with upper motor neurons at the hypoglossal nucleus. Symptoms related to damage will depend on the position of damage in this pathway. If the damage is to the nerve itself (a lower motor neuron lesion), the tongue will curve toward the damaged side, owing to weakness of the genioglossus muscle of affected side which action is to deviate the tongue in the contralateral side .[19][20] If the damage is to the nerve pathway (an upper motor neuron lesion) the tongue will curve away from the side of damage, due to action of the affected genioglossus muscle, and will occur without fasciculations or wasting,[19] with speech difficulties more evident.[6] Damage to the hypoglossal nucleus will lead to wasting of muscles of the tongue and deviation towards the affected side when it is stuck out. This is because of the weaker genioglossal muscle.[2]
Use in nerve repair
editThe hypoglossal nerve may be connected (anastomosed) to the facial nerve to attempt to restore function when the facial nerve is damaged. Attempts at repair by either wholly or partially connecting nerve fibres from the hypoglossal nerve to the facial nerve may be used when there is focal facial nerve damage (for example, from trauma or cancer).[21][22]
Hypoglossal nerve stimulator implant
editThe hypoglossal nerve has also been clinically implicated in the treatment of obstructive sleep apnea.[23][24] Certain patients with obstructive sleep apnea who are deemed eligible candidates (e.g., failed continuous positive airway pressure therapy, underwent appropriate testing with drug induced sleep endoscopy, and meet other criteria as outlined by the FDA)[25] may be offered the hypoglossal nerve stimulator as an alternative. The purpose of the hypoglossal nerve stimulator is to relieve tongue base obstruction during sleep by stimulating the tongue to protrude during inspiration (i.e., inhale).
In this procedure, an electrical stimulator lead is placed around branches of the hypoglossal nerve that control tongue protrusion (e.g., genioglossus) via an incision in the neck.[26] A sensor lead is then placed in the chest between the ribs in the layer between the internal intercostal muscles and external intercostal muscles. The stimulator and sensory lead are then connected via a tunneled wire to an implantable pulse generator. When turned on during sleep, the sensory lead in the chest detects the respiratory cycle. During inspiration (i.e., inhale), an electrical signal is fired via the stimulator lead in the neck, stimulating the hypoglossal nerve, and causing the tongue to protrude, thereby alleviating obstruction.
History
editThe first recorded description of the hypoglossal nerve was by Herophilos (335–280 BC), although it was not named at the time. The first use of the name hypoglossal in Latin as nervi hypoglossi externa was used by Winslow in 1733. This was followed though by several different namings including nervi indeterminati, par lingual, par gustatorium, great sub-lingual by different authors, and gustatory nerve and lingual nerve (by Winslow). It was listed in 1778 as nerve hypoglossum magnum by Soemmering. It was then named as the great hypoglossal nerve by Cuvier in 1800 as a translation of Winslow and finally named in English by Knox in 1832.[27]
Other animals
editThe hypoglossal nerve is one of twelve cranial nerves found in amniotes including reptiles, mammals and birds.[28] As with humans, damage to the nerve or nerve pathway will result in difficulties moving the tongue or lapping water, decreased tongue strength, and generally cause deviation away from the affected side initially, and then to the affected side as contractures develop.[29] The evolutionary origins of the nerve have been explored through studies of the nerve in rodents and reptiles.[30] The nerve is regarded as arising evolutionarily from nerves of the cervical spine,[2] which has been incorporated into a separate nerve over the course of evolution.[30]
The size of the hypoglossal nerve, as measured by the size of the hypoglossal canal, has been hypothesised to be associated with the progress of evolution of primates, with reasoning that larger nerves would be associated with improvements in speech associated with evolutionary changes. This hypothesis has been refuted.[31]
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ a b c Dale Purves (2012). Neuroscience. Sinauer Associates. p. 726. ISBN 978-0-87893-695-3.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o M. J. T. Fitzgerald; Gregory Gruener; Estomih Mtui (2012). Clinical Neuroanatomy and Neuroscience. Saunders/Elsevier. p. 216. ISBN 978-0-7020-4042-9.
- ^ Anthony H. Barnett (2006). Diabetes: Best Practice & Research Compendium. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 30. ISBN 978-0-323-04401-1.
- ^ a b c d Gray's Anatomy 2008, p. 460.
- ^ a b Gray's Anatomy 2008, p. 506-7.
- ^ a b c d Kandel, Eric R. (2013). Principles of neural science (5. ed.). Appleton and Lange: McGraw Hill. pp. 1541–1542. ISBN 978-0-07-139011-8.
- ^ "Neural - Cranial Nerve Development". embryology.med.unsw.edu.au. Retrieved 17 June 2016.
- ^ Pansky, Ben. "Chapter 147. The Brainstem: Myelencephalon (fifth Vesicle) – Basal Motor Plate – Review of Medical Embryology Book – LifeMap Discovery". discovery.lifemapsc.com. Archived from the original on 13 March 2017. Retrieved 12 March 2017.
- ^ Coley, Brian D.; Sperling, Vera (21 May 2013). Caffey's Pediatric Diagnostic Imaging. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 115. ISBN 978-1455753604. Retrieved 12 March 2017.
- ^ Sperber, Geoffrey H.; Sperber, Steven M.; Guttmann, Geoffrey D. (2010). Craniofacial Embryogenetics and Development. PMPH-USA. p. 193. ISBN 9781607950325.
- ^ Hill, Mark. "Carnegie stage 12 – Embryology". embryology.med.unsw.edu.au. Retrieved 12 March 2017.
- ^ O'Rahilly, Ronan; Müller, Fabiola (March 1984). "The early development of the hypoglossal nerve and occipital somites in staged human embryos". American Journal of Anatomy. 169 (3): 237–257. doi:10.1002/aja.1001690302. PMID 6720613.
- ^ Gray's Anatomy 2008, p. 953.
- ^ Hui, Andrew C. F.; Tsui, Ivan W. C.; Chan, David P. N. (2009-06-01). "Hypoglossal nerve palsy". Hong Kong Medical Journal = Xianggang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 15 (3): 234. ISSN 1024-2708. PMID 19494384.
- ^ a b Keane, James R. (1996-06-01). "Twelfth-Nerve Palsy: Analysis of 100 Cases". Archives of Neurology. 53 (6): 561–566. doi:10.1001/archneur.1996.00550060105023. ISSN 0003-9942. PMID 8660159.
- ^ a b Boban, Marina; Brinar, Vesna V.; Habek, Mario; Radoš, Marko (2007). "Isolated Hypoglossal Nerve Palsy: A Diagnostic Challenge". European Neurology. 58 (3): 177–181. doi:10.1159/000104720. PMID 17622725.
- ^ a b "Chapter 7: Lower cranial nerves". www.dartmouth.edu. Archived from the original on 2007-10-18. Retrieved 2016-05-12.
- ^ Mukherjee, Sudipta; Gowshami, Chandra; Salam, Abdus; Kuddus, Ruhul; Farazi, Mohshin; Baksh, Jahid (2014-01-01). "A case with unilateral hypoglossal nerve injury in branchial cyst surgery". Journal of Brachial Plexus and Peripheral Nerve Injury. 7 (1): 2. doi:10.1186/1749-7221-7-2. PMC 3395866. PMID 22296879.
- ^ a b c "Medical Neurosciences". Archived from the original on 2011-09-27. Retrieved 2011-12-04.
- ^ Brazis (2007). Localization in Clinical Neurology. p. 342.
- ^ Yetiser, Sertac; Karapinar, Ugur (2007-07-01). "Hypoglossal-Facial Nerve Anastomosis: A Meta-Analytic Study". Annals of Otology, Rhinology, and Laryngology. 116 (7): 542–549. doi:10.1177/000348940711600710. ISSN 0003-4894. PMID 17727086. S2CID 36311886.
- ^ Ho, Tang. "Facial Nerve Repair Treatment". WebMDLLC. Retrieved 9 December 2011.
- ^ Mashaqi, Saif; Patel, Salma Imran; Combs, Daniel; Estep, Lauren; Helmick, Sonia; Machamer, Joan; Parthasarathy, Sairam (2021-02-09). "The Hypoglossal Nerve Stimulation as a Novel Therapy for Treating Obstructive Sleep Apnea-A Literature Review". International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 18 (4): 1642. doi:10.3390/ijerph18041642. ISSN 1660-4601. PMC 7914469. PMID 33572156.
- ^ Yu, Jason L.; Thaler, Erica R. (February 2020). "Hypoglossal Nerve (Cranial Nerve XII) Stimulation". Otolaryngologic Clinics of North America. 53 (1): 157–169. doi:10.1016/j.otc.2019.09.010. ISSN 1557-8259. PMID 31699408. S2CID 207937455.
- ^ "LCD - Hypoglossal Nerve Stimulation for the Treatment of Obstructive Sleep Apnea (L38307)". www.cms.gov. Retrieved 2024-01-01.
- ^ "Hypoglossal Nerve Stimulator Implantation (Selective Upper Airway Stimulation) | Iowa Head and Neck Protocols". medicine.uiowa.edu. Retrieved 2024-01-01.
- ^ Swanson, Larry W. (2014-08-12). Neuroanatomical Terminology: A Lexicon of Classical Origins and Historical Foundations. Oxford University Press. p. 300. ISBN 978-0-19-534062-4.
- ^ Sharma, SK (2014). Objective Zoology. Krishna Prakashan Media. p. 3.84.
- ^ "Physical and Neurologic Examinations – Nervous System – Veterinary Manual". Veterinary Manual. Retrieved 2017-03-19.
- ^ a b Tada, Motoki N.; Kuratani, Shigeru (2015-01-01). "Evolutionary and developmental understanding of the spinal accessory nerve". Zoological Letters. 1: 4. doi:10.1186/s40851-014-0006-8. ISSN 2056-306X. PMC 4604108. PMID 26605049.
- ^ Hurford, James R. (2014-03-06). Origins of Language: A Slim Guide. OUP Oxford. pp. Chapter "we began to speak and hear differently". ISBN 9780191009662.
- Sources
- Susan Standring; Neil R. Borley; et al., eds. (2008). Gray's anatomy : the anatomical basis of clinical practice (40th ed.). London: Churchill Livingstone. ISBN 978-0-8089-2371-8.
Notes
edit- ^ These are the genioglossus, hyoglossus, styloglossus, and intrinsic muscles of the tongue.