This article contains too many pictures for its overall length. (November 2024) |
The Iapygia quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Iapygia quadrangle is also referred to as MC-21 (Mars Chart-21).[1] It was named after the heel of the boot of Italy. That name was given by the Greeks[2] It is part of a region of Italy named Apulia.[3][circular reference] The name Iapygia was approved in 1958.[4]
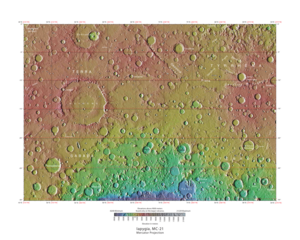 Map of Iapygia quadrangle from Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter (MOLA) data. The highest elevations are red and the lowest are blue. Terby (crater) contains many rock layers. | |
| Coordinates | 15°00′S 292°30′W / 15°S 292.5°W |
|---|---|

The Iapygia quadrangle covers the area from 270° to 315° west longitude and from 0° to 30° south latitude on Mars. Parts of the regions Tyrrhena Terra and Terra Sabaea are found in this quadrangle. The largest crater in this quadrangle is Huygens. Some interesting features in this quadrangle are dikes.[5] the many layers found in Terby crater, and the presence of carbonates on the rim of Huygens crater.[6]
Dikes
editNear Huygens, especially just to the east of it, are a number of narrow ridges which appear to be the remnants of dikes, like the ones around Shiprock, New Mexico. The dikes were once under the surface, but have now been eroded. Dikes are magma-filled cracks that often carry lava to the surface. Dikes by definition cut across rock layers. Some dikes on earth are associated with mineral deposits.[5] Discovering dikes on Mars means that perhaps future colonists will be able to mine needed minerals on Mars, instead of transporting them all the way from the Earth.
Some features look like dikes, but may be what has been called linear ridge networks.[7] Ridges often appear as mostly straight segments that intersect in a lattice-like manner. They are hundreds of meters long, tens of meters high, and several meters wide. It is thought that impacts created fractures in the surface; these fractures later acted as channels for fluids. Fluids cemented the structures. With the passage of time, surrounding material was eroded away, thereby leaving hard ridges behind. Since the ridges occur in locations with clay, these formations could serve as a marker for clay which requires water for its formation. Water here could have supported life.[8][9][10]
-
Wide view of dike near the crater Huygens, as seen by HiRISE
-
Close view of dike near the crater Huygens, as seen by HiRISE
-
Possible dikes, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. Arrows point to possible dikes, which appear as relatively straight, narrow ridges.
-
Possible dike, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
-
Ridges, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. These may be dikes formed as a result of impact.
-
Close up of ridges, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. Note: this is an enlargement of the previous image.
Layers
editMany places on Mars show rocks arranged in layers. Rock can form layers in a variety of ways. Volcanoes, wind, or water can produce layers.[11] A detailed discussion of layering with many Martian examples can be found in Sedimentary Geology of Mars.[12] Layers can be hardened by the action of groundwater. Martian ground water probably moved hundreds of kilometers, and in the process it dissolved many minerals from the rock it passed through. When ground water surfaces in low areas containing sediments, water evaporates in the thin atmosphere and leaves behind minerals as deposits and/or cementing agents. Consequently, layers of dust could not later easily erode away since they were cemented together.
-
Layers in a valley East of Terby Crater, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
-
Layers in Terby crater, as seen by HiRISE. Layers may have formed when the Hellas basin was filled with water.
-
Terby Crater layers as seen by HiRISE
-
Mounds in craters like Henry are formed by the erosion of layers that were deposited after the impact.
-
Layers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
-
Layers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
-
Wide view of layered features, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
-
Close view of layers with rocks breaking up into cubes, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
-
Close view of layers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
-
Close view of layers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
-
Wide view of layers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
-
Close view of layers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
-
Close view of layers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. Rectangle shows the size of a football field for scale.
-
Close view of layers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
-
Layers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
-
Wide view of layers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
-
Close view of layers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
-
Close, color view of layers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
-
Close, color view of layers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
-
Layers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. Light toned layers may contain minerals rich in water.
-
Close, color view of layers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
Craters
editImpact craters generally have a rim with ejecta around them, in contrast volcanic craters usually do not have a rim or ejecta deposits.[13] Sometimes craters will display layers. Since the collision that produces a crater is like a powerful explosion, rocks from deep underground are tossed unto the surface. Hence, craters can show us what lies deep under the surface.
-
Small crater in Schaeberle Crater, as seen by HiRISE. Image on right is an enlargement of the other image. Scale bar is 500 meters long.
-
Winslow Crater, as seen by HiRISE. Scale bar is 1000 meters long. Crater is named after the town of Winslow, Arizona, just east of Meteor Crater because of its similar size and infrared characteristics.
-
Saheki Crater Alluvial Fan, as seen by HiRISE
-
Saheki Crater, as seen by HiRISE
-
Close-up of Saheki Crater layers, as seen by HiRISE
-
Suzhi Crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter). Light-toned layer is visible on the floor.
-
Enlargement of light-toned layer on floor of Suzhi Crater, as seen by HiRISE, under HiWish program. Arrow points to a small crater that contains the light-toned material.
-
Jarry-Desloges Crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter)
-
Dunes on floor of Jarry-Desloges Crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter). Note: this is an enlargement of the previous image of Jarry-Desloges Crater.
-
Fournier Crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter). The central mound is visible in the middle.
-
Niesten Crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter) and MOLA. MOLA colors show elevations. The CTX image came from the rectangle shown in the MOLA image.
-
Millochau Crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter)
-
Layers on an unnamed crater wall, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
Carbonates
editCarbonates (calcium or iron carbonates) were discovered in a crater on the rim of Huygens Crater.[14][15] The impact on the rim exposed material that had been dug up from the impact that created Huygens. These minerals represent evidence that Mars once had a thicker carbon dioxide atmosphere with abundant moisture. These kinds of carbonates only form when there is a lot of water. They were found with the Compact Reconnaissance Imaging Spectrometer for Mars (CRISM) instrument on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. Earlier, the instrument had detected clay minerals. The carbonates were found near the clay minerals. Both of these minerals form in wet environments. It is supposed that billions of years age Mars was much warmer and wetter. At that time, carbonates would have formed from water and the carbon dioxide-rich atmosphere. Later the deposits of carbonate would have been buried. The double impact has now exposed the minerals. Earth has vast carbonate deposits in the form of limestone.[6]
-
Huygens Crater with circle showing place where carbonate was discovered. This deposit may represent a time when Mars had abundant liquid water on its surface. Scale bar is 259 km long.
Evidence of rivers
editThere is enormous evidence that water once flowed in river valleys on Mars. Images of curved channels have been seen in images from Mars spacecraft dating back to the early 1970s with the Mariner 9 orbiter.[16][17][18][19] Vallis (plural valles) is the Latin word for valley. It is used in planetary geology for the naming of landform features on other planets, including what could be old river valleys that were discovered on Mars, when probes were first sent to Mars. The Viking Orbiters caused a revolution in our ideas about water on Mars; huge river valleys were found in many areas. Space craft cameras showed that floods of water broke through dams, carved deep valleys, eroded grooves into bedrock, and traveled thousands of kilometers.[13][20][21] Some valles on Mars (Mangala Vallis, Athabasca Vallis, Granicus Vallis, and Tinjar Valles) clearly begin at graben. On the other hand, some of the large outflow channels begin in rubble-filled low areas called chaos or chaotic terrain. It has been suggested that massive amounts of water were trapped under pressure beneath a thick cryosphere (layer of frozen ground), then the water was suddenly released, perhaps when the cryosphere was broken by a fault.[22][23]
-
Channels, as seen by HiRISE
-
Channel within a larger channel, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
-
Libya Montes with valley networks (THEMIS)
-
Channel near Huygens crater - HiRISE under HiWish program
-
Channel - HiRISE under HiWish program
-
Channel, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
-
Channel, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
-
Channels, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
-
Channels, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
-
Channels, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
-
Wide view of layers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
-
Close view of layers from previous image, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
-
Channel, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
-
Channel, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
-
Channels, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
Dunes
editThe Iapygia quadrangle contains some dunes. Some of them are barchans. Pictures below show sand dunes in this quadrangle. When there are perfect conditions for producing sand dunes, steady wind in one direction and just enough sand, a barchan sand dune forms. Barchans have a gentle slope on the wind side and a much steeper slope on the lee side where horns or a notch often forms.[24] The whole dune may appear to move with the wind. Observing dunes on Mars can tell us how strong the winds are, as well as their direction. If pictures are taken at regular intervals, one may see changes in the dunes or possibly in ripples on the dune's surface. On Mars dunes are often dark in color because they were formed from the common, volcanic rock basalt. In the dry environment, dark minerals in basalt, like olivine and pyroxene, do not break down as they do on Earth. Although rare, some dark sand is found on Hawaii which also has many volcanoes discharging basalt. Barchan is a Russian term because this type of dune was first seen in the desert regions of Turkistan.[25] Some of the wind on Mars is created when the dry ice at the poles is heated in the spring. At that time, the solid carbon dioxide (dry ice) sublimates or changes directly to a gas and rushes away at high speeds. Each Martian year 30% of the carbon dioxide in the atmosphere freezes out and covers the pole that is experiencing winter, so there is a great potential for strong winds.[26]
-
Sand dunes often form in low areas (Mars Global Surveyor)
-
Dunes in Schaeberle (Martian crater), as seen by HiRISE under the HiWish program
-
Dunes and craters, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
Landslides
edit-
Landslide in a crater, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
Other features
edit-
Close view of transverse aeolian ridges (TAR's), as seen by HiRISE
-
Boulder rolled down crater wall and left a track
-
Surface breaking up into cube-shaped blocks, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
-
Gullies in crater, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
-
Rock breaking up into cubes, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
-
Contact showing light and dark-toned materials, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. Light-toned materials typically contain water in minerals.
Other Mars quadrangles
editInteractive Mars map
edit
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ Davies, M.E.; Batson, R.M.; Wu, S.S.C. “Geodesy and Cartography” in Kieffer, H.H.; Jakosky, B.M.; Snyder, C.W.; Matthews, M.S., Eds. Mars. University of Arizona Press: Tucson, 1992.
- ^ "Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography (1854), IABA´DIUS, IABA´DIUS, IAPY´GIA".
- ^ Apulia
- ^ "Planetary Names". planetarynames.wr.usgs.gov.
- ^ a b Head, J. et al. 2006. The Huygens-Hellas giant dike system on Mars: Implications for Late Noachian-Early Hesperian volcanic resurfacing and climatic evolution. Geology. 34:4: 285-288.
- ^ a b "Some of Mars' Missing Carbon Dioxide May be Buried". Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Archived from the original on 2011-06-29. Retrieved 2011-03-10.
- ^ Head, J., J. Mustard. 2006. Breccia dikes and crater-related faults in impact craters on Mars: Erosion and exposure on the floor of a crater 75 km in diameter at the dichotomy boundary, Meteorit. Planet Science: 41, 1675-1690.
- ^ Mangold et al. 2007. Mineralogy of the Nili Fossae region with OMEGA/Mars Express data: 2. Aqueous alteration of the crust. J. Geophys. Res., 112, doi:10.1029/2006JE002835.
- ^ Mustard et al., 2007. Mineralogy of the Nili Fossae region with OMEGA/Mars Express data: 1. Ancient impact melt in the Isidis Basin and implications for the transition from the Noachian to Hesperian, J. Geophys. Res., 112.
- ^ Mustard et al., 2009. Composition, Morphology, and Stratigraphy of Noachian Crust around the Isidis Basin, J. Geophys. Res., 114, doi:10.1029/2009JE003349.
- ^ "HiRISE | High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment". Hirise.lpl.arizona.edu?psp_008437_1750. Retrieved 2012-08-04.
- ^ Grotzinger, J. and R. Milliken (eds.). 2012. Sedimentary Geology of Mars. SEPM.
- ^ a b Hugh H. Kieffer (1992). Mars. University of Arizona Press. ISBN 978-0-8165-1257-7. Retrieved 7 March 2011.
- ^ Wray, J., et al. 2016. Orbital evidence for more widespread carbonate‐bearing rocks on Mars. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets: 121, Issue 4
- ^ Wray, James J.; Murchie, Scott L.; Bishop, Janice L.; Ehlmann, Bethany L.; Milliken, Ralph E.; Wilhelm, Mary Beth; Seelos, Kimberly D.; Chojnacki, Matthew (2016). "Orbital evidence for more widespread carbonate-bearing rocks on Mars". Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets. 121 (4): 652–677. Bibcode:2016JGRE..121..652W. doi:10.1002/2015JE004972.
- ^ Baker, V. 1982. The Channels of Mars. Univ. of Tex. Press, Austin, TX
- ^ Baker, V., R. Strom, R., V. Gulick, J. Kargel, G. Komatsu, V. Kale. 1991. Ancient oceans, ice sheets and the hydrological cycle on Mars. Nature 352, 589–594.
- ^ Carr, M. 1979. Formation of Martian flood features by release of water from confined aquifers. J. Geophys. Res. 84, 2995–300.
- ^ Komar, P. 1979. Comparisons of the hydraulics of water flows in Martian outflow channels with flows of similar scale on Earth. Icarus 37, 156–181.
- ^ Raeburn, P. 1998. Uncovering the Secrets of the Red Planet Mars. National Geographic Society. Washington D.C.
- ^ Moore, P. et al. 1990. The Atlas of the Solar System. Mitchell Beazley Publishers NY, NY.
- ^ Carr, M. 1979. Formation of martian flood features by release of water from confined aquifers. J. Geophys. Res. 84: 2995-3007.
- ^ Hanna, J. and R. Phillips. 2005. Tectonic pressurization of aquifers in the formation of Mangala and Athabasca Valles on Mars. LPSC XXXVI. Abstract 2261.
- ^ Pye, Kenneth; Haim Tsoar (2008). Aeolian Sand and Sand Dunes. Springer. p. 138. ISBN 9783540859109.
- ^ "Barchan | sand dune".
- ^ Mellon, J. T.; Feldman, W. C.; Prettyman, T. H. (2003). "The presence and stability of ground ice in the southern hemisphere of Mars". Icarus. 169 (2): 324–340. Bibcode:2004Icar..169..324M. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2003.10.022.
- ^ Morton, Oliver (2002). Mapping Mars: Science, Imagination, and the Birth of a World. New York: Picador USA. p. 98. ISBN 0-312-24551-3.
- ^ "Online Atlas of Mars". Ralphaeschliman.com. Retrieved December 16, 2012.
- ^ "PIA03467: The MGS MOC Wide Angle Map of Mars". Photojournal. NASA / Jet Propulsion Laboratory. February 16, 2002. Retrieved December 16, 2012.