The Koszalin Voivodeship[a] was a voivodeship (province) of the Polish People's Republic, with capital in Koszalin, that existed from 1950 to 1975. It was established on 6 July 1950, from the eastern half of the Szczecin Voivodeship,[1] and existed until 31 May 1975, when it was partitioned between then-established voivodeships of Koszalin, Słupsk, and Piła.[2]
| Koszalin Voivodeship | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voivodeship of Poland | |||||||||||||
| 1950–1975 | |||||||||||||
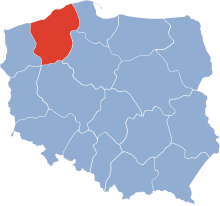 The Koszalin Voivodeship within Poland, between 1950 and 1975. | |||||||||||||
| Capital | Koszalin | ||||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||||
• 1956 | 17,914 km2 (6,917 sq mi) | ||||||||||||
• 1974 | 18,104 km2 (6,990 sq mi) | ||||||||||||
| Population | |||||||||||||
• 1950 | 518 354 | ||||||||||||
• 1974 | 837 000 | ||||||||||||
| • Type | Voivodeship | ||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||
• Established | 6 July 1950 | ||||||||||||
• Disestablished | 31 May 1975 | ||||||||||||
| Contained within | |||||||||||||
| • Country | |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
History
editThe Koszalin Voivodeship was established on 6 July 1950, as one of the voivodeships (provinces) of the Polish People's Republic. It was formed from the eastern half of the Szczecin Voivodeship. It included the counties of Białogard, Bytów, Człuchów, Drawsko, Kołobrzeg, Koszalin, Miastko, Sławno, Słupsk, Szczecinek, Wałcz, and Złotów, and the city county of Słupsk.[1][3] Additionally on that day, the capital on then-established voivodeship, Koszalin, became the city county.[4] In 1950, it was inhabited by 518 354 people,[5] and in 1956, it had an area of 17 914 km2.[6]
On 1 October 1954 was established the Świdwin County, from parts of the counties of Białogard, and Kołobrzeg.[7] In 1974, it had an area of 18 104 km2,[8] and was inhabited by 837 000 people.[9]
The voivodeship existed until 31 May 1975, when it was partitioned between then-established voivodeships of Koszalin, Słupsk, and Piła.[2]
Subdivisions
editThe voivodeship was divided into counties: Those were:
- Białogard County (seat: Białogard);
- Bytów County (seat: Bytów);
- Choszczno County (seat: Choszczno);
- Człuchów County (seat: Człuchów);
- Drawsko County (seat: Drawsko Pomorskie);
- Kołobrzeg County (seat: Kołobrzeg);
- Koszalin (city county);
- Koszalin County (seat: Koszalin);
- Miastko County (seat: Miastko);
- Sławno County (seat: Sławno);
- Słupsk (city county);
- Słupsk County (seat: Słupsk);
- Świdwin County (seat: Świdwin; 1954–1975);
- Szczecinek County (seat: Szczecinek);
- Wałcz County (seat: Wałcz);
- Złotów County (seat: Złotów).
Demographics
edit| Year | Population | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Urban (%) | Rural (%) | |
| 1950[5] | 518 354 | 176 722 (34.09%) | 341 632 (65.91%) |
| 1956[6] | 648 000 | 263 000 (40.5%) | 385 000 (59.5%) |
| 1960[10] | 687 915 | 306 967 (44.62%) | 380 948 (55.38%) |
| 1963[11] | 730 000 | 337 000 (46.2%) | 393 000 (53.8%) |
| 1965[12] | 755 100 | no data | no data |
| 1970[13] | 795 392 | 393 787 (49.51%) | 401 605 (50.49%) |
| 1971[14] | 803 200 | 401 900 (50%) | 401 300 (50%) |
| 1972[15] | 815 400 | 409 700 (50.2%) | 405 700 (49.8%) |
| 1973[16] | 826 000 | 423 000 (51.2%) | 403 000 (48.8%) |
| 1974[9] | 837 000 | 433 000 (51.7%) | 404 000 (48.%) |
Leaders
editFrom 1950, to 1973, the leader of the voivodeship was the chairperson of the Voivodeship National Council.[17] In 1973 was established the office of the voivode, however it remained vacant until the disestablishment of the voivodeship in 1975.[18]
The people in the office of the chairperson of the Voivodeship National Council, from 1950 to 1973, were:[19]
- 11 July 1950 – 25 May 1951: Henryk Kołodziejczyk;
- 25 May 1951 – 26 July 1953: Jan Musiał;
- 27 July 1953 – 21 April 1955: Józef Szczęśniak;
- 22 April 1955 – 14 March 1956: Franciszek Grochalski;
- 15 March 1956 – 11 December 1957: Jan Kawiak;
- 12 November 1957 – 26 July 1966: Zdzisław Tomal;
- 26 July 1966 – 19 September 1968: Tadeusz Makowski;
- 20 September 1968 – 24 November 1972: Wacław Gelger;
- 25 November 1972 – 24 November 1973: Stanisław Mach.
Citations
editNotes
editReferences
edit- ^ a b Ustawa z dnia 28 czerwca 1950 r. o zmianach podziału administracyjnego Państwa (Dz.U. z 1950 r. nr 28, poz. 255).
- ^ a b Ustawa z dnia 28 maja 1975 r. o dwustopniowym podziale administracyjnym Państwa oraz o zmianie ustawy o radach narodowych. (Dz.U. 1975 nr 16 poz. 91).
- ^ Zarządzenie Ministra Ziem Odzyskanych w sprawie wykonywania przez prezydentów miast funkcji władz powiatowych rządowej administracji ogólnej.
- ^ Rozporządzenie Rady Ministrów z dnia 21 czerwca 1950 r. w sprawie utworzenia powiatów miejskich z miast: Zielona Góra w województwie poznańskim, Rzeszów w województwie rzeszowskim i Koszalin w województwie szczecińskim.
- ^ a b Narodowy Spis Powszechny z dnia 3 grudnia 1950 r. Struktura zawodowa i demograficzna ludności. Indywidualne gospodarstwa rolne. Polska, Warsaw: Central Statistical Office, 1954, p. 3 (p. 8 of the PDF document).
- ^ a b Rocznik statystyczny 1957, Warsaw: Central Statistical Office, 1957, p. 9 (p. 48 of the PDF document).
- ^ Rozporządzenie Rady Ministrów z dnia 11 sierpnia 1954 r. w sprawie utworzenia powiatu świdwińskiego w województwie koszalińskim.
- ^ Polska. Zarys encyklopedyczny, Warsaw: Polish Scientific Publishers PWN, 1974, p. 700.
- ^ a b Encyklopedia powszechna PWN, vol. 3, Warsaw: Polish Scientific Publishers PWN, 1975, p. 577.
- ^ Spis Powszechny z dnia 6 grudnia 1960 r. Wyniki ostateczne. Ludność, gospodarstwa domowe. Polska, Warsaw: Central Statistical Office, 1965, p. 6-7 (p. 5-7 of the PDF document).
- ^ Rocznik polityczny i gospodarczy 1964, Polskie Wydawnictwo Ekonomiczne, p. 32.
- ^ Wielka Encyklopedia Powszechna PWN, vol. 9, Warsaw: Polish Scientific Publishers PWN, 1967, p. 5.
- ^ Narodowy Spis Powszechny 8 XII 1970. Struktura demograficzna i zawodowa ludności, gospodarstwa domowe. Polska. Wyniki ostateczne, Warsaw: Central Statistical Office, 1965, p. 4-6 (p. 60-62 of the PDF document).
- ^ Rocznik statystyczny 1972, Warsaw: Central Statistical Office, p. 76.
- ^ Rocznik polityczny i gospodarczy 1973, Państwowe Wydawnictwo Ekonomiczne, p. 37.
- ^ Rocznik polityczny i gospodarczy 1974, Warsaw: Państwowe Wydawnictwo Ekonomiczne, 1975, p. 85.
- ^ Ustawa z dnia 20 marca 1950 r. o terenowych organach jednolitej władzy państwowej.
- ^ "Ustawa z dnia 22 listopada 1973 r. o zmianie ustawy o radach narodowych" (in Polish). Retrieved 15 May 2022.
- ^ "Voivodeships of Poland 1945-1975 and 1999-". worldleadersindex.org. Archived from the original on 4 August 2014.