Leucofisetinidin is a flavan-3,4-diol (leucoanthocyanidin), a type of natural phenolic substance. It is the monomer of condensed tannins called profisetinidins. Those tannins can be extracted from the heartwood of Acacia mearnsii [2] or from the heartwoods of Schinopsis balansae, Schinopsis quebrachocolorado and from commercial quebracho extract.[3]
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
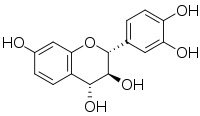
| IUPAC name
(2R,3S,4R)-Flavan-3,3′,4,4′,7-pentol
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2R,3S,4R)-2-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-1-benzopyran-3,4,7-triol | |
| Other names
(+)-Leucofisetinidin
(+)-Mollisacacidin (+)-7:3':4'-Trihydroxyflavan-3:4-diol Fisetinidol-4alpha-ol Leuco-fisetinidin | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H14O6 | |
| Molar mass | 290.271 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ Chemical Book
- ^ Roux, D. G.; Paulus, E. (1962). "Condensed tannis. 12. Polymeric leucofisetinidin tannins from the heartwood of Acacia mearnsii". The Biochemical Journal. 82 (2): 320–324. doi:10.1042/bj0820320. PMC 1243455. PMID 14494576.
- ^ Roux, D. G.; Evelyn, S. R. (1958). "Condensed tannins. 2. Biogenesis of condensed tannins based on leucoanthocyanins". The Biochemical Journal. 70 (2): 344–349. doi:10.1042/bj0700344. PMC 1196676. PMID 16748787.