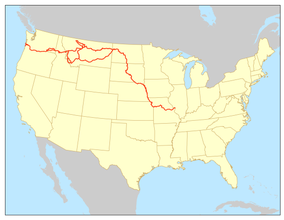
The Lewis and Clark National Historic Trail is a route across the United States commemorating the Lewis and Clark Expedition of 1804 to 1806. It is part of the National Trails System of the United States. It extends for some 4,900 miles (7,900 km) from Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, to the mouth of the Columbia River in Oregon.
| Lewis and Clark National Historic Trail | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Location | Ohio, Illinois, Missouri, Kansas, Iowa, Nebraska, South Dakota, North Dakota, Montana, Idaho, Oregon, and Washington in the United States |
| Coordinates | 41°0′0″N 96°0′0″W / 41.00000°N 96.00000°W |
| Established | November 10, 1978 |
| Visitors | 250,000 (in 2004) |
| Administrator | National Park Service |
| Website | www |
| Location | |
|---|---|
| Country | United States |
| Highway system | |
The trail is administered by the National Park Service, but sites along the trail are managed by federal land management agencies, state, local, tribal, and private organizations. The trail is not a hiking trail, but provides opportunities for hiking, boating and horseback riding at many locations along the route. The trail is the continuously longest of the 30 National Scenic and National Historic Trails.
The Lewis and Clark National Historic Trail is approximately 4,900 miles (7,900 km) long, extending from Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania to the mouth of the Columbia River, near present-day Astoria, Oregon. It follows the historic outbound and inbound routes of the Lewis and Clark Expedition as well as the preparatory section from Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania to Camp Dubois at Wood River, Illinois. The Trail connects 16 states (Pennsylvania, Ohio, West Virginia, Kentucky, Indiana, Illinois, Missouri, Kansas, Nebraska, Iowa, South Dakota, North Dakota, Montana, Idaho, Washington, and Oregon) and many tribal lands. It is administered by the National Park Service.[1]
Features
editThe official headquarters for the trail is located at the National Park Service Midwest Regional Headquarters, in Omaha, Nebraska. The visitor center features exhibits about the explorers and their historic trip, as well as information about sites along the trail.
A highway driving route approximates the path taken by the Lewis and Clark Expedition in 1804–06, between St. Louis, Missouri and the Pacific Ocean at Astoria, Oregon. Like the Great River Road, it is marked along existing roadways, in this case mostly paralleling the Missouri and Columbia rivers. Roads followed include Interstate 29 in Iowa, the appropriately-numbered SD 1804, ND 1804, SD 1806, and ND 1806, and Washington State Route 14. Two separate routes of the trail are signed between St. Louis and East Fairview, North Dakota, one on each side of the Missouri. In Washington, it is called the Lewis and Clark Trail Highway and is a state scenic byway.[2] The Washington State Legislature designated it as a named highway corridor in 1955, originally from Vancouver to Clarkston, and later expanded it to include most state highways along the Columbia River from Cape Disappointment to Clarkston.[3]
History
editIn 1948 the National Park Service proposed a "Lewis and Clark Tour-way" along the Missouri River from St. Louis to Three Forks, Montana. Later, Jay "Ding" Darling proposed the development of the expedition route as a recreational trail. Following a 1966 report by the Bureau of Outdoor Recreation, the National Trails System Act of 1968 listed the route for study as a possible National Scenic Trail. The Lewis and Clark Trail Commission published its report in 1969 and identified the route and recreation opportunities.[4]
In 1978 the law was amended by the National Parks and Recreation Act to provide for a new category of trail, National Historic Trails, one of which was to be the Lewis and Clark trail.[5]
From 2003 to 2006, the National Park Service commemorated the bicentennial of the Lewis and Clark Expedition with the Corps of Discovery II traveling exhibit.[6]
The 2019 John D. Dingell, Jr. Conservation, Management, and Recreation Act extended the Trail an additional 1,200 miles (1,900 km) along the Ohio and Mississippi Rivers from Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania to Wood River, Illinois.[1]
References
edit- ^ a b "Frequently Asked Questions - Lewis & Clark National Historic Trail (U.S. National Park Service)". www.nps.gov. National Park Service. Retrieved 18 May 2019. This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ "Washington Scenic Byways Map" (PDF). Washington State Department of Transportation. Retrieved June 11, 2018.
- ^ "RCW 47.22.020: Lewis and Clark Highway". Revised Code of Washington. Washington State Legislature. Retrieved October 4, 2021.
- ^ Lewis and Clark Trail Commission (October 1969). Final Report of the Lewis and Clark Trail Commission (Report). OCLC 129076.
- ^ Lewis and Clark Trail Foundation Document
- ^ NPS: Summary History of Corps II
- Bassman, John H. (2009). A navigation companion for the Lewis & Clark Trail. Volume 1, History, camp locations and daily summaries of expedition activities. United States: John H. Bassman.
- National Park Service (1978). Lewis and Clark National Historic Trail Comprehensive Plan for Management and Use. United States: United States Department of the Interior.
