Macronovirus is the only genus of the family Sarthroviridae and only contains the species Macrobrachium satellite virus 1[1]
| Macronovirus | |
|---|---|
| |
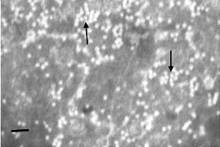
| Transmission electron micrographs of negatively-stained extra small virus species Macrobrachium satellite virus 1; bar = 50 nm | |
| Virus classification | |
| (unranked): | Virus |
| Realm: | Riboviria |
| Family: | Sarthroviridae |
| Genus: | Macronovirus |
| Species | |
| |
It is found in The French West Indies, Thailand, Taiwan, China, and India.[2]
Etymology
editThe genus name, Macronovirus, is a combination of Macro, from type species host Macrobrachium rosenbergii and no, from helper virus nodavirus.[2]
The family name, Sarthroviridae, is a combination of S, from Small and arthro, from host arthropoda.[3]
Hosts
editMacronovirus's cell tropism is muscle and connective cells of diseased animals, and its natural hosts are arthropods[3]
Structure
editThe virion Macrobrachium satellite virus 1 has a genome consisting of linear single-stranded RNA of positive polarity, 0.8kb in size, with two genes. This encodes two capsid proteins, CP-17 and CP-16. The virion is non-enveloped, spherical, with a capsid of about 15 nm with icosahedral symmetry. The virion is constructed from two capsid proteins CP-17 and CP-16. It has a Monopartite, linear, ssRNA(+) genome.[2]
Gene expression
editThe virion RNA is infectious and serves as both the genome and viral messenger RNA.[2]
Replication
editIts replication is cytoplasmic, and has 8 steps.[2]
- Attachement to host receptors mediates entry into the host cell.
- Uncoating, and release of the viral genomic RNA into the cytoplasm.
- Viral RNA is translated in a polyprotein to produce replication proteins.
- Replication by helper virus occurs in viral factories made of membrane vesicles derived from the ER. A dsRNA genome is synthesized from the genomic ssRNA(+).
- The dsRNA genome is transcribed/replicated thereby providing viral mRNAs/new ssRNA(+) genomes.
- Expression of the capsid proteins.
- Assembly of new virus particles.
- Virus release.
Disease
editWhitish muscle disease, which develops in post-larvae of freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii and is caused by Macrobrachium rosenbergii nodavirus (MrNV) and its associate Macrobrachium satellite virus 1. Main symptom is a whitish appearance of the muscles, particularly noticeable in the abdomen. Mortalities can reach 100%.[2]
References
edit- ^ "Virus Taxonomy: 2022 Release". International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV). Retrieved 12 August 2023.
- ^ a b c d e f "Macronovirus ~ ViralZone report". ViralZone. Retrieved 12 August 2023. This article incorporates text from this source, which is available under the CC BY 4.0 license.
- ^ a b "Sarthroviridae ~ ViralZone report". ViralZone. Retrieved 12 August 2023. This article incorporates text from this source, which is available under the CC BY 4.0 license.