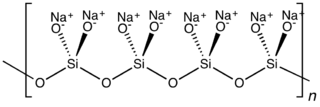
Metasilicates are silicates containing ions of empirical formula SiO2−
3. Common stoichiometries include MI
2SiO3 and MIISiO3. Metasilicates can be cyclic, usually the hexamer (SiO3)12−6 or chains (SiO3)n2−.[1]
Common compounds containing metasilicate anion are:

References
edit- ^ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.