The middle pharyngeal constrictor is a fan-shaped muscle located in the neck. It is one of three pharyngeal constrictor muscles. It is smaller than the inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscle.
| Middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle | |
|---|---|
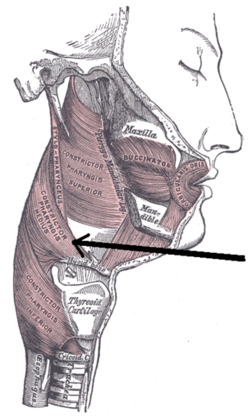 | |
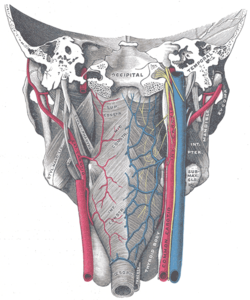 Muscles of the pharynx, viewed from behind, together with the associated vessels and nerves (middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle labeled as Mid. constr. at center) | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Hyoid bone |
| Insertion | Pharyngeal raphe |
| Artery | Ascending pharyngeal artery |
| Nerve | Pharyngeal plexus of vagus nerve |
| Actions | Swallowing |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus constrictor pharyngis medius |
| TA98 | A05.3.01.108 |
| TA2 | 2184 |
| FMA | 46622 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The middle pharyngeal constrictor originates from the greater cornu and lesser cornu of the hyoid bone, and the stylohyoid ligament. It inserts onto the pharyngeal raphe. It is innervated by a branch of the vagus nerve through the pharyngeal plexus. It acts to propel a bolus downwards along the pharynx towards the esophagus, facilitating swallowing.
Structure
editThe middle pharyngeal constrictor is a sheet-like, fan-shaped muscle.[1]
The muscle's fibers diverge from their origin: the more inferior fibres descend deep to the inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscle; the middle portion of fibres pass transversely; the more superior fibers ascend and overlap the superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle.[1]
Origin
editTwo parts of the middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle are distinguished according to its sites of origin:
- Ceratopharyngeal part - arises (the entire superior margin of) the greater cornu of the hyoid bone.[1]
- Chondropharyngeal part - arises from the lesser cornu of the hyoid bone, and (the inferior portion of) the stylohyoid ligament. The chondropharyngeal part represents the muscle's anterior origin.[1]
Insertion
editThe muscle inserts (posteriorly) into the pharyngeal raphe,[1] blending with its contralateral partner at the midline.[citation needed]
Innervation
editSimilarly to the superior and inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscles, it is innervated by a branch of the vagus nerve through the pharyngeal plexus.[citation needed]
Actions/movements
editThe contraction of the muscle constricts the middle portion of the pharynx.[1]
Function
editThe muscle contracts during swallowing:[1] as soon as the bolus of food is received in the pharynx, the elevator muscles relax, the pharynx descends, and the constrictors contract upon the bolus, and convey it downward towards the esophagus.[2][3]
They also have respiratory mechanical effects.[4]
Additional images
edit-
Hyoid bone. Anterior surface. Enlarged.
-
Muscles of the neck. Lateral view.
-
Middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle
-
Middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle
-
Deep dissection of larynx, pharynx and tongue seen from behind
-
Deep dissection of larynx, pharynx and tongue seen from behind
-
Deep dissection of larynx, pharynx and tongue seen from behind
References
editThis article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1143 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ a b c d e f g Standring, Susan (2020). Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice (42th ed.). New York. pp. 712–713. ISBN 978-0-7020-7707-4. OCLC 1201341621.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Rowe LD, Miller AJ, Chierici G, Clendenning D (August 1984). "Adaptation in the function of pharyngeal constrictor muscles". Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery. 92 (4): 392–401. doi:10.1177/019459988409200404. PMID 6435057. S2CID 32361287.
- ^ Donner, Martin W.; Bosnia, James F.; Robertson, Diane L. (1985). "Anatomy and physiology of the pharynx". Gastrointestinal Radiology. 10 (1): 197–212. doi:10.1007/BF01893103. ISSN 0364-2356. PMID 4029536. S2CID 37515662.
- ^ Kuna, Samuel T (2000). "Respiratory-related activation and mechanical effects of the pharyngeal constrictor muscles". Respiration Physiology. 119 (2–3): 155–161. doi:10.1016/S0034-5687(99)00110-3. ISSN 0034-5687. PMID 10722858.
Further reading
edit- Its role in speech: Hamaker, Ronald C.; Blom, Eric D. (2003). "Botulinum Neurotoxin for Pharyngeal Constrictor Muscle Spasm in Tracheoesophageal Voice Restoration". The Laryngoscope. 113 (9): 1479–1482. doi:10.1097/00005537-200309000-00010. ISSN 0023-852X. PMID 12972919. S2CID 12251825.
- Its role in Hyoid bone syndrome: Ernest, Edwin A.; Salter, E. George (1991). "Hyoid bone syndrome: A degenerative injury of the middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle with photomicroscopic evidence of insertion tendinosis". The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry. 66 (1): 78–83. doi:10.1016/0022-3913(91)90357-3. ISSN 0022-3913. PMID 1941681.
External links
edit- lesson8 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (latpharyngealitems3)