This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. (May 2024) |
Moprolol is a beta-adrenergic antagonist, or beta blocker. It is typically prescribed to treat hypertension, high blood pressure, angina pectoris, arrhythmias, anxiety, and glaucoma.[1]
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
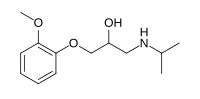
| IUPAC name
1-(2-Methoxyphenoxy)-3-(propan-2-ylamino)propan-2-ol
| |
| Other names
(±)-Moprolol
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.024.777 |
| EC Number |
|
| MeSH | C009976 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C13H21NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 239.315 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Moprolol is currently off the market, most likely due to the manufacturer being in violation of US good manufacturing practices.[1]
See also
edit- Levomoprolol, the (S)-enantiomer of moprolol
References
edit- ^ a b "MOPROLOL". National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences. Retrieved 11 October 2024.