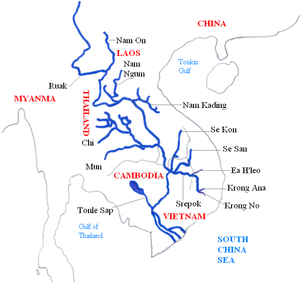
Nam Ngum (Laotian: ນໍ້າງືມ [nâːm ŋɯ́ːm]) is a 354 km long river in Laos. It is a major tributary of the Mekong River.[1]
Geography
editThe Nam Ngum originates from the northern mountainous region of Xiangkhoang Province and flows south through Vientiane Province joining the Mekong at the capital of Laos, Vientiane.
The Nam Ngum river basin is home to about one million people in Laos. The current largest dam on Nam Ngum, Nam Ngum Dam (Nam Ngum 1 Hydropower Project) was originally constructed between 1968 and 1971. There are also four other hydropower projects under construction or planned for construction on the Nam Ngum River. Tourism destinations along Nam Ngum include the Nam Ngum Lake, Dansavanh Nam Ngum Resort, and Vang Vieng.
The Nam Ngum river basin covers 16,906 square kilometers, including 8,297 km2 of watershed area. The Nam Ngum river basin covers 2.73 percent of the lower Mekong river basin. The water flow of the Nam Ngum River to the Mekong River is 700 m3/s. Thirty percent of the river basin is covered by forest. Various international organizations and financial institutions assist in watershed management, water resource management, establishment of water regulation, and river basin organizations for optimum use of water resources and watershed protection. One such project, the Nam Ngum River Basin Development Sector Projects, has operated since 2002.
Wildlife
editThe hemimyzon confluens, a type of ray-finned fish, is known to live only in the Nam Ngum drainage area. It is threatened by mining, pollution, and hydro-power development.[2]
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ "Laos in brief". www.un.int. Archived from the original on 9 April 2008.
- ^ Kottelat, M. (2012). "Hemimyzon confluens". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2012: e.T181035A1691255. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2012-1.RLTS.T181035A1691255.en. Retrieved 15 January 2018.