This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. (January 2013) |
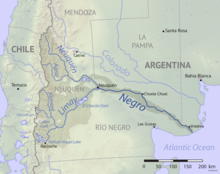
The Neuquén River (Spanish: Río Neuquén) is the second most important river of the province of Neuquén in the Argentine Patagonia, after the Limay River. Rocks of the Neuquén Basin are fossiliferous, and the basin hosts what may become important fields of tight oil and gas.


Overview
editThe river begins in the northwest of the province at an elevation of 2,300 metres (7,500 ft), to be fed by a number of streams through valleys of the lower Andes while advancing diagonally in southeast direction. Among these streams, some of them from draining of small lakes, are the Trocomán, Reñi Leuvü, Agrio and Nahueve. Further down, its main tributaries are the rivers Varvarco, and Agrio, who provides almost a third of the Neuquén flow. Along its way the river receives some sediments from volcanoes Copahue and Domuyo that might sometimes affect the clarity of the otherwise clean waters.
After meeting the Agrio, the Neuquén river has no natural lakes that could regulate its flow, which results in sharp raises of level during thawing and rainy periods. A derivative channel towards the Pellegrini Lake in Río Negro Province has been built to compensate for abrupt changes in the flow, as well as the Cerros Colorados Complex, also used to generate hydroelectricity.
The average flow of the river is of 308 cubic metres per second (10,900 cu ft/s) (measured at Paso de Indios), and its drainage basin covers about 50,774 square kilometres (19,604 sq mi). At its mouth at 38°59′34″S 68°00′06″W / 38.9927°S 68.0017°W, the Neuquén meets the Limay River near the city of Neuquén, to form the Río Negro, which continues its way east towards the Atlantic Ocean.
Although not as famous as other fishing rivers in Patagonia, the river is also visited by fly fishing and spinning enthusiasts, as well as the two artificial lakes named Los Barreales and Mari Menuco, located by the river near the border with Río Negro Province. The main catch are trouts and Patagonian pejerrey.
Geology of the Neuquén Basin
editIn the satellite image, the deep reds of the Candeleros Formation, a sequence of sandstones formed roughly 90 to 100 million years ago in a braided river system, dominate the landscape. These rocks are flanked in some areas, especially near the river, by a green-yellow sequence of rocks that are part of the younger Hunical Formation, formed during drier times.
Paleontologists have uncovered numerous fossils in the Candeleros rocks, including ancient species of fish, frogs, snakes, turtles, small mammals, and several types of dinosaurs. The best known dinosaur found here is Giganotosaurus carolinii, a carnivorous theropod thought to be larger and faster than Tyrannosaurus rex.[1]
The recent discovery of a large deposit of shale gas and oil in the deeper Vaca Muerta formation has made the Neuquén Basin one of the few regions outside of the United States where companies are pursuing horizontal drilling and hydraulic fracturing.[1]
References and external links
edit- ^ a b The Geologic Wonder of the Neuquén Basin, by NASA Earth Observatory, 2018
- Subsecretaría de Recursos Hídricos[permanent dead link] — "Cartografía Hídrica de Neuquén" - pdf
- Monografias.com — "Región patagónica"
- Ministry of Environment — Hydrological basins of Argentina.