The North Hungarian Mountains (Hungarian: Északi-középhegység), sometimes also referred to as the Northeast Hungarian Mountains, Northeast Mountains, North Hungarian Highlands, North Hungarian Mid-Mountains or North Hungarian Range,[1][2] is the northern, mountainous part of Hungary. It forms a geographical unity with the Mátra-Slanec Area, the adjacent parts of Slovakia. It is a separate geomorphological area within the Western Carpathians.
| North Hungarian Mountains | |
|---|---|
 The view of the valley of Lillafüred in the Bükk mountains. Although this is not the highest part of the county, the landscape is typical of Hungarian mountains. | |
| Location | Northern Hungary, southern Slovakia |
| Territory | 13,000 km2 (in Hungary) |
| Highest point | Kékes (Hungary) 1014 m Šimonka (Slovakia) 1092 m |
| Terrain | lower and moderately high mountains |
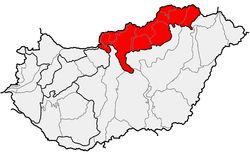
The mountains run along the northeastern border of Hungary as well as eastern parts of the Hungarian–Slovak border in broadband from the Danube Bend to the town of Prešov.
Subdivisions
editThe area consists of the following geomorphological units:
- Börzsöny [3] (Hungarian: Börzsöny + Burda (SK)
- Gödöllő Hills (Hungarian: Gödöllői-dombság)
- Cserhát[3]
- Karancs-Medves area + Cerová Highlands (SK)
- Mátra[3] (Hungarian: Mátra)
- Bükk[3] (Hungarian: Bükk or "Bükk hegység" – literally Beech (Mountains))
- Zemplén Mountains or Tokaj Mountains (Hungarian: Zempléni-hegység, Tokaji-hegység)
Ranges of the adjacent Mátra-Slanec Area in Slovakia:
- Slanec Mountains (Slovak: Slanské vrchy)
- Zemplín Mountains (Slovak: Zemplínske vrchy)
Description
editThe North Hungarian Mountains begin with the mountain range of Börzsöny, adjacent to the Danube Bend, where it meets the Transdanubian Mountains.
The Börzsöny range is about 600 km2 in area, and mainly of volcanic origin. The highest peak is the Csóványos (938 m).
The next range towards the east is the Cserhát, with the same geological composition as the Börzsöny. Erosion here was more severe: these are mere hills and comprise the lowest part of the North Hungarian Mountains. The highest point is Naszály (654 m).
Kékes, the country's highest peak at 1014 meters, is located in the next range, Mátra. However, the range's average height is only 600 meters, less than that of the neighboring Bükk. Mátra is also of volcanic origin.
The Bükk is a limestone range; it has the highest average height in Hungary. It is rich in caves, some of which were inhabited in ancient times.
The Aggtelek Karst area is a geologic formation spanning the Hungarian-Slovakian border, and the reason for the Caves of Aggtelek Karst and Slovak Karst World Heritage Site, and the Hungarian Aggtelek National Park. Hungary's a most popular cave, the Baradla, is located there.
The Zemplén Mountains are again of volcanic origin; the soil's high-quality favors viticulture.
Natural resources
editNational parks
edit- Aggtelek National Park (established in 1985)
- Bükk National Park (established in 1976)
- Danube-Ipoly National Park (established in 1997)
Protected areas
edit- Hollókő (since 1977)
- East Cserhát (since 1989)
- Karancs-Medves (since 1989)
- Mátra (since 1985)
- Tarnavidék (since 1993)
- Lázbérc (since 1975)
- Tokaj-Bodrogzug (since 1986)
- Zemplén (since 1984)
Images
edit-
Mátra mountains
-
Aggtelek National Park – Baradla Cave
-
The highest peak, Kékes
See also
edit- Bükk
- Carpathians
- Geography of Hungary
- Mátra
- Tokaj-Hegyalja (part of Zemplén Mountains)
References
edit- ^ Gábor Gercsák (2002). "Hungarian geographical names in English language publications" (PDF). Studia Cartologica. Eötvös Loránd University. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 March 2012. Retrieved 30 April 2011.
- ^ Gábor Gercsák (2005). "Magyar tájnevek Angol fordítása" (PDF). Fasciculi Linguistici / Series Lexicographica (in Hungarian). Eötvös Loránd University. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 March 2012. Retrieved 30 April 2011.
- ^ a b c d Regional Map Series of Hungary Archived 2007-10-07 at the Wayback Machine