Oxanamide (Quiactin) is an anxiolytic and muscle relaxant which can produce sedative and hypnotic effects in sufficiently high doses.[1] An uncontrolled trial on patients treated in a clinical gynecology practice published in 1959 found that oxanamide was efficacious in the treatment of anxiety resulting from premenstrual syndrome, menopause, and various other causes, with minimal sedation or other side effects.[2]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
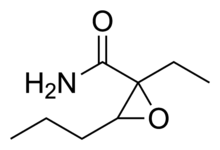
| Formula | C8H15NO2 |
| Molar mass | 157.213 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
References
edit- ^ Kuhn WL, Ketteler HJ, Van Maanen EF (January 1960). "Effects of oxanamide on the central nervous system". Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine. 103: 101–3. doi:10.3181/00379727-103-25425. PMID 14412594. S2CID 40927309.
- ^ Woodhull RB (April 1959). "Oxanamide; adjunctive use of a new tranquilizer in gynecology". California Medicine. 90 (4): 275–7. PMC 1577644. PMID 13638840.