Partitiviridae is a family of double-stranded RNA viruses.[2] Plants, fungi, and protozoa serve as natural hosts. It has been suggested that they can also infect bacteria.[3] The name comes from the Latin partitius, which means divided, and refers to the segmented genome of partitiviruses. There are five genera and 60 species in the family, 15 of which are unassigned to a genus.[4][5]
| Partitiviridae | |
|---|---|
| |
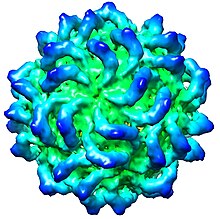
| CryoEM of Penicillium stoloniferum virus S capsid, EMD-5161[1] | |
| |
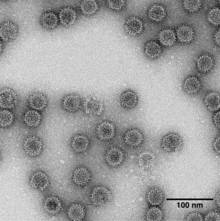
| TEM of Penicillium stoloniferum virus S | |
| Virus classification | |
| (unranked): | Virus |
| Realm: | Riboviria |
| Kingdom: | Orthornavirae |
| Phylum: | Pisuviricota |
| Class: | Duplopiviricetes |
| Order: | Durnavirales |
| Family: | Partitiviridae |
Structure
editViruses in the family Partitiviridae are non-enveloped with icosahedral geometries and T=1 symmetry.[6] The diameter of partitiviruses is around 25–43 nm.[4]
Genome
editPartitiviruses have double-stranded RNA genomes divided into two genomic segments, and there may be additional subgenomic segments. The two genome segments are packaged in separate virus particles. They code for two separate proteins. The first segment codes for the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp), and the second segment codes for the coat protein. The segments are around 1.4–3.0 kbp in length, while the total genome length is around 3.0–4.8 kbp.[4][6]
Life cycle
editViral replication is cytoplasmic. Entry into the host cell is achieved by penetration into the host cell. Replication follows the double-stranded RNA virus replication model. Double-stranded RNA virus transcription is the method of transcription. The virus exits the host cell by cell-to-cell movement. Fungi and plants serve as the natural host.[4][6] Cryspoviruses infect apicomplexian protozoa of the genus Cryptosporidium,[7] while viruses of the other genera infect plants and fungi. It has been suggested that they can also infect bacteria.
| Genus | Host details | Tissue tropism | Entry details | Release details | Replication site | Assembly site | Transmission |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cryspovirus | Protists | None | Cell division; sporogenesis; hyphal anastomosis | Cell division; sporogenesis; hyphal anastomosis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Cell division; sporogenesis; hyphal anastomosis |
| Alphapartitivirus | None | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Cell division | |||
| Deltapartitivirus | Plants | None | Viral movement; mechanical inoculation | Cell division | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Cell division |
| Betapartitivirus | None | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Cell division | |||
| Gammapartitivirus | Fungi | None | Cytoplasmic exchange; hyphal anastomosis | Cytoplasmic exchange; hyphal anastomosis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasmic exchange; hyphal anastomosis |
Phylogenetics
editBased on the RNA polymerase gene this group can be divided into four clades (I-IV).[8] Four isolates from animals and protozoans form a fifth clade. Clades I–IV consist of mixtures of partitivirus-like sequences from plants and fungi.[citation needed]
Taxonomy
editThere are five recognized genera within the Partitiviridae family. There are an additional fifteen species in the family unassigned to a genus:[4][5]
- Beet cryptic virus 1
- Carrot cryptic virus
- Cherry chlorotic rusty spot associated partitivirus
- Chondrostereum purpureum cryptic virus 1
- Flammulina velutipes browning virus
- Helicobasidium mompa partitivirus V70
- Heterobasidion partitivirus 1
- Heterobasidion partitivirus 3
- Heterobasidion partitivirus 12
- Heterobasidion partitivirus 13
- Heterobasidion partitivirus 15
- Rosellinia necatrix partitivirus 2
- Vicia cryptic virus
- White clover cryptic virus 1
- Atkinsonella hypoxylon virus
- Cannabis cryptic virus
- Ceratocystis resinifera virus 1
- Crimson clover cryptic virus 2
- Dill cryptic virus 2
- Fusarium poae virus 1
- Heterobasidion partitivirus 2
- Heterobasidion partitivirus 7
- Heterobasidion partitivirus 8
- Heterobasidion partitivirus P
- Hop trefoil cryptic virus 2
- Pleurotus ostreatus virus 1
- Primula malacoides virus 1
- Red clover cryptic virus 2
- Rhizoctonia solani virus 717
- Rosellinia necatrix virus 1
- White clover cryptic virus 2
- Beet cryptic virus 2
- Beet cryptic virus 3
- Fig cryptic virus
- Pepper cryptic virus 1
- Pepper cryptic virus 2
- Aspergillus ochraceous virus
- Discula destructiva virus 1
- Discula destructiva virus 2
- Fusarium solani virus 1
- Gremmeniella abietina RNA virus MS1
- Ophiostoma partitivirus 1
- Penicillium stoloniferum virus F
- Penicillium stoloniferum virus S
Unassigned to a genus:
- Agaricus bisporus virus 4
- Alfalfa cryptic virus 1
- Carnation cryptic virus 1
- Carrot temperate virus 1
- Carrot temperate virus 2
- Carrot temperate virus 3
- Carrot temperate virus 4
- Gaeumannomyces graminis virus 0196A
- Gaeumannomyces graminis virus T1A
- Hop trefoil cryptic virus 1
- Hop trefoil cryptic virus 3
- Radish yellow edge virus
- Ryegrass cryptic virus
- Spinach temperate virus
- White clover cryptic virus 3
References
edit- ^ Tang, J.; Pan, J.; Havens, W. M.; Ochoa, W. F.; Guu, T. S. Y.; Ghabrial, S. A.; Nibert, M. L.; Tao, Y. J.; Baker, T. S. (2010). "Backbone Trace of Partitivirus Capsid Protein from Electron Cryomicroscopy and Homology Modeling". Biophysical Journal. 99 (2): 685–694. Bibcode:2010BpJ....99..685T. doi:10.1016/j.bpj.2010.04.058. PMC 2905076. PMID 20643089.
- ^ Vainio, EJ; Chiba, S; Ghabrial, SA; Maiss, E; Roossinck, M; Sabanadzovic, S; Suzuki, N; Xie, J; Nibert, M; Ictv Report, Consortium (January 2018). "ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Partitiviridae". The Journal of General Virology. 99 (1): 17–18. doi:10.1099/jgv.0.000985. PMC 5882087. PMID 29214972.
- ^ Neri U, Wolf YI, Roux S, Camargo AP, Kazlauskas D, Min Chen I, Lee B, Ivanova N, Allen LZ, Paez-Espino D, Bryant DA, Bhaya D, Krupovic M, Dolja VV, Kyrpides NC, Koonin EV, Gophna U (17 February 2022). "A five-fold expansion of the global RNA virome reveals multiple new clades of RNA bacteriophages". bioRxiv 10.1101/2022.02.15.480533.
- ^ a b c d e "ICTV Online Report Partitiviridae".
- ^ a b "Virus Taxonomy: 2020 Release". International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV). March 2021. Retrieved 20 May 2021.
- ^ a b c "Viral Zone". ExPASy. Retrieved 15 June 2015.
- ^ Nibert ML, Woods KM, Upton SJ, Ghabrial SA (2009) Cryspovirus: a new genus of protozoan viruses in the family Partitiviridae. Arch Virol 154(12):1959–1965
- ^ Liu H, Fu Y, Xie J, Cheng J, Ghabrial SA, Li G, Yi X, Jiang D (2012) Discovery of Novel dsRNA Viral Sequences by In Silico Cloning and Implications for Viral Diversity, Host Range and Evolution. PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e42147.