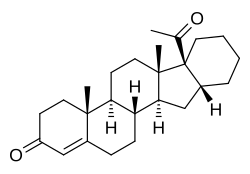
Pentarane A, also known as D'6-pentarane or pregna-D'6-pentarane, as well as 16α,17α-cyclohexanoprogesterone, 16α,17α-tetramethylenepregn-4-ene-3,20-dione, or 17α-acetyl-16β,24-cyclo-21-norchol-4-en-3-one, is a steroidal progestin that was developed by the Zelinskii Institute of Organic Chemistry of the Russian Academy of Sciences and was never marketed.[1][2] The 6α-methylated analogue of pentarane A is known as mecigestone or as pentarane B.[2]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | D'6-Pentarane; Pregna-D'6-pentarane; 16α,17α-Cyclohexanoprogesterone; 16α,17α-Tetramethylenepregn-4-ene-3,20-dione; 17α-Acetyl-16β,24-cyclo-21-norchol-4-en-3-one |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C25H36O2 |
| Molar mass | 368.561 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ Kamernitzky AV, Levina IS, Kulikova LE, Ignatov VN, Korkhov VV, Nikitina GV, Terekhina AI (January 1982). "Pregna-D'-pentaranes - a new class of active gestagenes". Journal of Steroid Biochemistry. 16 (1): 61–67. doi:10.1016/0022-4731(82)90144-3. PMID 7062740.
- ^ a b Bhakta A, Herman M, Levina IS, Moudgil VK (August 1993). "Interaction of cycloalkanoprogesterones with mammalian progesterone receptor: binding of pregna-D'-pentaranes in the calf uterine cytosol". Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry. 125 (2): 153–161. doi:10.1007/BF00936444. PMID 8283970. S2CID 20319611.