Phosphatocopina (alternatively Phosphatocopida) is an extinct group of bivalved arthropods known from the Cambrian period. They are generally sub-milimetric to a few millimetres in size. They are typically only known from isolated carapaces, but some found in Orsten-type phosphatized preservation have their bodies preserved in high fidelity in three dimensions.
| Phosphatocopina Temporal range:
| |
|---|---|
| |
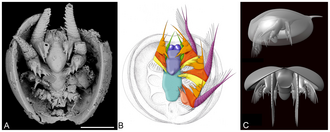
| Hesslandona (left), Klausmuelleria (centre), Vestrogothia (right) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Clade: | †Phosphatocopina Müller, 1964 |
| Genera | |
Description
editThe phosphatized bivalved carapace covered the entire body.[1] Members typically grew to a maximum of 1–3 millimetres (3⁄64–1⁄8 in) in length, though Cyclotron grew up to 6 mm (1⁄4 inch).[2] In some species, spines were present on the carapace.[3] The head either bore a pair of stalked eyes or a pair of dome-shaped medial eyes.[4] The first appendage pair, dubbed the "antennulae", were uniramous, with the remaining appendage pairs being biramous. The basipods and endopods of the biramous limbs had prominently developed endites, while the exopods were typically annulated, and bore setae.[3] The earliest larval stages of phosphatocopines are known as "head larva", due to them only having the four pairs of cephalic appendages, a feature that is a shared groundplan with most other arthropod groups.[1][3] Fossilised eggs likely to belong to phosphatocopids have been found in Furongian deposits in Poland.[5]
Ecology
editPhosphatocopines are generally thought to have been nektobenthic (swimming close to the sediment), and have been suggested to have fed on small particulate organic matter, using the endites and spines on their limbs to trap particles.[6] They are thought to have been tolerant of hypoxic environments, which was probably their preferred habitat.[2]
Taxonomy
editWhen phosphatocopines were first described, they were suggested to be ostracods, but this was rejected after their soft tissue was described.[7] They have often been suggested to be close relatives of crustaceans, with the proposed clade containing the two groups dubbed Labrophora.[4] However, their mandibles and maxillae are not strongly morphologically differentiated from the other trunk limbs, with differentiated mandibles and maxillae characterising most crown-group mandibulates, including crustaceans, and as such have been alternatively suggested to be stem-group mandibulates.[8] The fact that specimens with preserved soft tissue all appear to be larval instars makes their exact placement uncertain.[9] Several subgroups have been proposed, such as Hesslandonidae and Vestrogothiidae.[1]
Genera
edit- Hesslandona Müller, 1964 Orsten, Sweden, China Upper Cambrian (Furongian)
- Trapezilites Hinz-Schallreuter, 1993 Orsten, Sweden, Upper Cambrian (Furongian)
- Cyclotron Rushton, 1969 England, Poland, Upper Cambrian (Furongian)
- Waldoria Gründel, 1981 Orsten, Sweden, Upper Cambrian (Furongian)
- Veldotron Gründel, 1981 Orsten, Sweden, Upper Cambrian (Furongian)
- Klausmuelleria Siveter et al., 2003 Comley Limestone, England, Cambrian Series 2
- Vestrogothia Müller, 1964 Orsten, Sweden, China Upper Cambrian (Furongian)
- Falites Müller, 1964 Orsten, Sweden, Upper Cambrian (Furongian)
- Dabashanella Huo et al., 1983 China, Cambrian Stage 3
- Comleyopsis Hinz, 1993 Comley limestone, England, Cambrian Series 2
- Bidimorpha Hinz-Schallreuter, 1993 Sweden, Denmark, Middle Cambrian
References
edit- ^ a b c Olempska, Ewa; Maas, Andreas; Waloszek, Dieter; Eriksson, Mats (2019). "Exceptionally well-preserved Orsten-type phosphatocopid crustaceans from the Cambrian of Poland". Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 64. doi:10.4202/app.00553.2018.
- ^ a b Williams, Mark; Vannier, Jean; Corbari, Laure; Massabuau, Jean-Charles (2011-12-02). Stepanova, Anna (ed.). "Oxygen as a Driver of Early Arthropod Micro-Benthos Evolution". PLOS ONE. 6 (12): e28183. Bibcode:2011PLoSO...628183W. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0028183. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 3229522. PMID 22164241.
- ^ a b c Maas, Andreas; Waloszek, Dieter (2005). "Phosphatocopina – ostracode-like sister group of Eucrustacea". Hydrobiologia. 538 (1–3): 139–152. doi:10.1007/PL00021866. ISSN 0018-8158. S2CID 39987017.
- ^ a b Zhang, Xi-guang; Pratt, Brian R. (November 2012). "The First Stalk-Eyed Phosphatocopine Crustacean from the Lower Cambrian of China". Current Biology. 22 (22): 2149–2154. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2012.09.027. PMID 23084994.
- ^ Olempska, Ewa; Błażejowski, Błażej; Waloszek, Dieter; Maas, Andreas (15 January 2023). "Phosphatic bromalites and microfossils from the Furongian (Cambrian) of northern Poland (Baltica) and palaeobiological implications". Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology. 610: 111350. doi:10.1016/j.palaeo.2022.111350. ISSN 0031-0182. S2CID 254342747. Retrieved 26 September 2023.
- ^ Eriksson, Mats E.; Terfelt, Fredrik; Elofsson, Rolf; Maas, Andreas; Marone, Federica; Lindskog, Anders; Waloszek, Dieter; Schmitz, Birger; Stampanoni, Marco (2016). "Baring it all: undressing Cambrian 'Orsten' phosphatocopine crustaceans using synchrotron radiation X-ray tomographic microscopy". Lethaia. 49 (3): 312–326. doi:10.1111/let.12149.
- ^ Zhang, Hua-Qiao (June 2022). "A new assemblage of dabashanellids (Crustacea: Phosphatocopida) from Cambrian Stage 3 of western Hubei Province, South China". Palaeoworld. 32 (in press): 14–26. doi:10.1016/j.palwor.2022.06.004. S2CID 250080273.
- ^ Hegna, Thomas A.; Luque, Javier; Wolfe, Joanna M. (2020-09-10), "The Fossil Record of the Pancrustacea", Evolution and Biogeography, Oxford University Press, pp. 21–52, doi:10.1093/oso/9780190637842.003.0002, ISBN 978-0-19-063784-2, retrieved 2022-12-21
- ^ Schram, Frederick R.; Koenemann, Stefan (2022-03-31), "Bradoriida and Phosphatocopida", Evolution and Phylogeny of Pancrustacea (1 ed.), Oxford University PressNew York, pp. 63–C5.P113, doi:10.1093/oso/9780195365764.003.0005, ISBN 978-0-19-536576-4, retrieved 2023-06-03