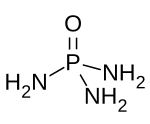
Phosphoramide is a chemical compound with the molecular formula O=P(NH2)3. It is a derivative of phosphoric acid in which each of the hydroxyl groups have been replaced with an amino group. In bulk, the compound is a white solid which is soluble in polar solvents.
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Phosphoric triamide
| |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| O=P(NH2)3 | |
| Molar mass | 95.042 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| good | |
| Acidity (pKa) | <3.6[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Chemical properties
editPhosphoramide arises from the reaction of phosphoryl chloride with ammonia. In moist air, it hydrolyzes to an ammonium salt:
- 2 H2O + O=P(NH2)3 → [NH4]+[PO2(OH)(NH2)]− + NH3
It reacts with sodium hydroxide with loss of ammonia:[2]
- NaOH + O=P(NH2)3 → Na+[PO2(NH2)2]− + NH3
The related thiophosphoryl triamide compound S=P(NH2)3 was made from the reaction of thiophosphoryl chloride with ammonia.
Phosphoramides
editPhosphoramide is also the parent compound for a range of derivatives called phosphoramides.[3] An example compound is the polar solvent hexamethylphosphoramide (HMPA).
References
edit- ^ Perrin, D. D., ed. (1982) [1969]. Ionisation Constants of Inorganic Acids and Bases in Aqueous Solution. IUPAC Chemical Data (2nd ed.). Oxford: Pergamon (published 1984). Entry 186. ISBN 0-08-029214-3. LCCN 82-16524.
- ^ Robert Klement; Otto Koch (1954). "Phosphoroxy‐triamid und Phosphorthio‐triamid". Chemische Berichte. 87 (3): 333–340. doi:10.1002/cber.19540870308.
- ^ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "phosphoramides". doi:10.1351/goldbook.A00484
External links
edit- Media related to phosphoramides at Wikimedia Commons
- The dictionary definition of phosphoramide at Wiktionary