Introduction   Alaska (/əˈlæskə/ ə-LASS-kə) is a non-contiguous U.S. state on the northwest extremity of North America. Part of the Western United States region, it is one of the two non-contiguous U.S. states, alongside Hawaii. Alaska is also considered to be the northernmost, westernmost, and easternmost (the Aleutian Islands cross the 180th meridian into the eastern hemisphere) state in the United States. It borders the Canadian territory of Yukon and the province of British Columbia to the east. It shares a western maritime border, in the Bering Strait, with Russia's Chukotka Autonomous Okrug. The Chukchi and Beaufort Seas of the Arctic Ocean lie to the north, and the Pacific Ocean lies to the south. Technically, it is a semi-exclave of the U.S., and is the largest exclave in the world. Alaska is the largest U.S. state by area, comprising more total area than the following three largest states of Texas, California, and Montana combined, and is the sixth-largest subnational division in the world. It is the third-least populous and most sparsely populated U.S. state, but is, with a population of 736,081 as of 2020, the continent's most populous territory located mostly north of the 60th parallel, with more than quadruple the combined populations of Northern Canada and Greenland. The state contains the four largest cities in the United States by area, including the state capital of Juneau. The state's most populous city is Anchorage, and approximately half of Alaska's residents live within its metropolitan area. Indigenous people have lived in Alaska for thousands of years, and it is widely believed that the region served as the entry point for the initial settlement of North America by way of the Bering land bridge. The Russian Empire was the first to actively colonize the area beginning in the 18th century, eventually establishing Russian America, which spanned most of the current state and promoted and maintained a native Alaskan Creole population. The expense and logistical difficulty of maintaining this distant possession prompted its sale to the U.S. in 1867 for US$7.2 million (equivalent to $157 million in 2023). The area went through several administrative changes before becoming organized as a territory on May 11, 1912. It was admitted as the 49th state of the U.S. on January 3, 1959. Abundant natural resources have enabled Alaska— with one of the smallest state economies—to have one of the highest per capita incomes, with commercial fishing, and the extraction of natural gas and oil, dominating Alaska's economy. U.S. Armed Forces bases and tourism also contribute to the economy; more than half of the state is federally-owned land containing national forests, national parks, and wildlife refuges. It is among the most irreligious states, one of the first to legalize recreational marijuana, and is known for its libertarian-leaning political culture, generally supporting the Republican Party in national elections. The Indigenous population of Alaska is proportionally the second highest of any U.S. state, at over 15 percent, after only Hawaii. (Full article...) Entries here consist of Good and Featured articles, which meet a core set of high editorial standards.
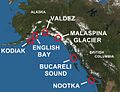
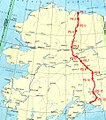
Wyatt Berry Stapp Earp (March 19, 1848 – January 13, 1929) was an American lawman in the American West, including Dodge City, Deadwood, and Tombstone. Earp was involved in the gunfight at the O.K. Corral, during which lawmen killed three outlaw Cochise County Cowboys. While Wyatt is often depicted as the key figure in the shootout, his brother Virgil was both Deputy U.S. Marshal and Tombstone City Marshal that day and had considerably more experience in law enforcement as a sheriff, constable, and marshal than did Wyatt. Virgil made the decision to enforce a city ordinance prohibiting carrying weapons in town and to disarm the Cowboys. Wyatt was only a temporary assistant marshal to his brother. In 1874, Earp arrived in the boomtown of Wichita, Kansas, where his reputed wife opened a brothel. Wyatt was arrested more than once for his presence in a brothel where he may have been a pimp. He was later appointed to the Wichita police force and developed a solid reputation as a lawman but was fined and "not rehired as a police officer" after getting into a physical altercation with a political opponent of his boss. Earp immediately left Wichita, following his brother James to Dodge City, Kansas where his brother's wife Bessie and Earp's common-law wife Sally operated a brothel. He later became an assistant city marshal. In late 1878, he went to Texas to track down an outlaw, Dave Rudabaugh, and met John "Doc" Holliday, whom Earp credited with saving his life. Throughout his life, Earp moved between boom towns. He left Dodge in 1879 and moved with his brothers James and Virgil to Tombstone where a silver boom was underway. The Earps clashed with a group of outlaws known as the "Cowboys". Wyatt, Virgil, and younger brother Morgan held various law enforcement positions that put them in conflict with Tom McLaury, Frank McLaury, Ike Clanton, and Billy Clanton, who threatened to kill the Earps on several occasions. The conflict escalated, culminating in the shootout at the O.K. Corral on October 26, 1881, where the Earps and Doc Holliday killed three Cowboys. During the next five months, Virgil was ambushed and maimed, and Morgan was murdered. Wyatt, Warren Earp, Doc Holliday, and others formed a federal posse that killed three more Cowboys whom they thought responsible. Wyatt was never wounded in any of the gunfights, unlike his brothers Virgil and Morgan or Doc Holliday, which added to his mystique after his death. (Full article...) TopicsCategoriesSelected article - The Inuit languages are a closely related group of indigenous American languages traditionally spoken across the North American Arctic and the adjacent subarctic regions as far south as Labrador. The Inuit languages are one of the two branches of the Eskimoan language family, the other being the Yupik languages, which are spoken in Alaska and the Russian Far East. Most Inuit people live in one of three countries: Greenland, a self-governing territory within the Kingdom of Denmark; Canada, specifically in Nunavut, the Inuvialuit Settlement Region of the Northwest Territories, the Nunavik region of Quebec, and the Nunatsiavut and NunatuKavut regions of Labrador; and the United States, specifically in northern and western Alaska. The total population of Inuit speaking their traditional languages is difficult to assess with precision, since most counts rely on self-reported census data that may not accurately reflect usage or competence. Greenland census estimates place the number of Inuit language speakers there at roughly 50,000. According to the 2021 Canadian census, the Inuit population of Canada is 70,540, of which 33,790 report Inuit as their first language. Greenland and Canada account for the bulk of Inuit speakers, although about 7,500 Alaskans speak some variety of an Inuit language out of a total population of over 13,000 Inuit. An estimated 7,000 Greenlandic Inuit live in Denmark, the largest group outside of North America. Thus, the total population of Inuit speakers is about 100,000 people. (Full article...) Selected picture -General imagesThe following are images from various Alaska-related articles on Wikipedia.
Recognized content
Featured articlesGood articles
Featured pictures
Former featured pictures
Related Portals
Related WikiProjectsState facts
State symbols:
Tasks
Associated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Discover Wikipedia using portals |