The Hawaii Portal Hawaii (/həˈwaɪ.i/ hə-WY-ee; Hawaiian: Hawaiʻi [həˈvɐjʔi, həˈwɐjʔi]) is an island state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about 2,000 miles (3,200 km) southwest of the U.S. mainland. One of the two non-contiguous U.S. states (alongside Alaska), it is the only state not on the North American mainland, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only state in the tropics. Hawaii consists of 137 volcanic islands that comprise almost the entire Hawaiian archipelago (the exception, which is outside the state, is Midway Atoll). Spanning 1,500 miles (2,400 km), the state is physiographically and ethnologically part of the Polynesian subregion of Oceania. Hawaii's ocean coastline is consequently the fourth-longest in the U.S., at about 750 miles (1,210 km). The eight main islands, from northwest to southeast, are Niʻihau, Kauaʻi, Oʻahu, Molokaʻi, Lānaʻi, Kahoʻolawe, Maui, and Hawaiʻi, after which the state is named; the latter is often called the "Big Island" or "Hawaii Island" to avoid confusion with the state or archipelago. The uninhabited Northwestern Hawaiian Islands make up most of the Papahānaumokuākea Marine National Monument, the largest protected area in the U.S. and the fourth-largest in the world. Of the 50 U.S. states, Hawaii is the eighth-smallest in land area and the 11th-least populous; but with 1.4 million residents, it ranks 13th in population density. Two-thirds of Hawaii residents live on O'ahu, home to the state's capital and largest city, Honolulu. Hawaii is among the country's most demographically diverse states, owing to its central location in the Pacific and over two centuries of migration. As one of only seven majority-minority states, it has the only Asian American plurality, the largest Buddhist community, and largest proportion of multiracial people in the U.S. Consequently, Hawaii is a unique melting pot of North American and East Asian cultures, in addition to its indigenous Hawaiian heritage. Settled by Polynesians sometime between 1000 and 1200 CE, Hawaii was home to numerous independent chiefdoms. In 1778, British explorer James Cook was the first known non-Polynesian to arrive at the archipelago; early British influence is reflected in the state flag, which bears a Union Jack. An influx of European and American explorers, traders, and whalers soon arrived, leading to the decimation of the once-isolated indigenous community through the introduction of diseases such as syphilis, tuberculosis, smallpox, and measles; the native Hawaiian population declined from between 300,000 and one million to less than 40,000 by 1890. Hawaii became a unified, internationally recognized kingdom in 1810, remaining independent until American and European businessmen overthrew the monarchy in 1893; this led to annexation by the U.S. in 1898. As a strategically valuable U.S. territory, Hawaii was attacked by Japan on December 7, 1941, which brought it global and historical significance, and contributed to America's entry into World War II. Hawaii is the most recent state to join the union, on August 21, 1959. In 1993, the U.S. government formally apologized for its role in the overthrow of Hawaii's government, which had spurred the Hawaiian sovereignty movement and has led to ongoing efforts to obtain redress for the indigenous population. (Full article...) This is a Featured article, which represents some of the best content on English Wikipedia..
Mauna Kea (/ˌmɔːnə ˈkeɪə, ˌmaʊnə -/, Hawaiian: [ˈmɐwnə ˈkɛjə]; abbreviation for Mauna a Wākea) is a dormant shield volcano on the island of Hawaiʻi. Its peak is 4,207.3 m (13,803 ft) above sea level, making it the highest point in Hawaii and the island with the second highest high point, behind New Guinea, the world's largest tropical island with multiple peaks that are higher. The peak is about 38 m (125 ft) higher than Mauna Loa, its more massive neighbor. Mauna Kea is unusually topographically prominent for its height: its prominence from sea level is fifteenth in the world among mountains, at 4,207.3 m (13,803 ft); its prominence from under the ocean is 9,330 m (30,610 ft), rivaled only by Mount Everest. This dry prominence is greater than Everest's height above sea level of 8,848.86 m (29,032 ft), and some authorities have labeled Mauna Kea the tallest mountain in the world, from its underwater base. Mauna Kea is ranked 8th by topographic isolation. It is about one million years old and thus passed the most active shield stage of life hundreds of thousands of years ago. In its current post-shield state, its lava is more viscous, resulting in a steeper profile. Late volcanism has also given it a much rougher appearance than its neighboring volcanoes due to construction of cinder cones, decentralization of its rift zones, glaciation on its peak, and weathering by the prevailing trade winds. Mauna Kea last erupted 6,000 to 4,000 years ago and is now thought to be dormant. (Full article...) This is a Good article, an article that meets a core set of high editorial standards.
Charles Kanaʻina (Kanaʻina II c. May 4, 1798 – March 13, 1877), was an aliʻi (hereditary noble) of the Kingdom of Hawaii, prince consort of Kuhina Nui, Kaʻahumanu III and father of William Charles Lunalilo, the 6th monarch of the Kamehameha Dynasty. Kanaʻina was a descendant of several figures from ancient Hawaiian history, including Liloa, Hakau and Umi-a-Liloa of Hawaiʻi Island as well as Piilani of Maui. He served on both the Privy Counsel and in the House of Nobles. He was named after his uncle Kanaʻina, a name that means "The conquering" in the Hawaiian Language. This uncle greeted Captain James Cook in 1778 and confronted the navigator before he was killed. His wife Miriam Auhea Kekāuluohi was a widow and niece of Kamehameha I. She was also married to Kamehameha II before he converted to Christianity and gave up all but one wife. Kanaʻina and Kekāuluohi lived in a traditional aliʻi style home in a sacred neighborhood in Honolulu called Pohukaina near Kekūanaōʻa, Kaʻahumanu and their offspring. The compound would eventually become the Iolani Palace (the official Royal Residence of the Hawaiian Royal Family) and Palace Walk when Kekūanaōʻa built Hale Aliʻi in the center of the families estates as a gift to his daughter Victoria Kamāmalu. Kanaʻina kept his property at the palace until his death and would be the only original owner to do so while the Palace was in use, living there through five monarchs, from the 1820s to 1877. Kanaʻina's son, William Charles Lunalilo, was named by Kamehameha III as an heir to the throne of the kingdom and ascended in 1873 while his father still lived. Lunalilo died only a year later, three years before his father's death on March 13, 1877. Having not re-written his will, which left everything to his son who had predeceased, Kanaʻina died intestate. Probate hearings proceeded for 5 years. On final adjudication his property was auctioned with the proceeds going to several of Kanaʻina's cousins including Ruth Keelikōlani and Bernice Pauahi Bishop. (Full article...) Selected Picture -'Ōlelo (Language) -This section is here to highlight some of the most common words of the Hawaiian Language, ʻŌlelo, that are used in everyday conversation amongst locals.
Hauʻoli
Happy, glad, joyful Hauʻoli Makahiki Hou, Happy New Year; Hauʻoli lā hānau, happy birthday State Facts
State Symbols:
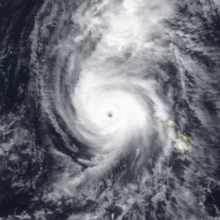
Selected article -Hurricane Iniki (/iːˈniːkiː/ ee-NEE-kee; Hawaiian: ʻiniki meaning "strong and piercing wind") was a hurricane that struck the island of Kauaʻi on September 11, 1992. It was the most powerful hurricane to strike Hawaiʻi in recorded history, and the only hurricane to directly affect the state during the 1992 Pacific hurricane season. Forming on September 5, 1992, during the strong 1990–1995 El Niño, Iniki was one of eleven Central Pacific tropical cyclones during that season. It attained tropical storm status on September 8 and intensified into a hurricane the next day. After abruptly turning north, Iniki struck Kauaʻi at peak intensity; it had winds of 145 mph and reached Category 4 status on the Saffir–Simpson hurricane scale. Winds gusted to 225 mph (362 km/h). It was the first hurricane to hit the state since Hurricane Iwa in the 1982 season, and the only known major hurricane to hit the state. Iniki dissipated on September 13, about halfway between Hawaii and Alaska. (Full article...) Did you know? -
Hawaii News
Wikinews Hawaii portal
Quotes - "E naʻi wale nō ʻoukou, i kuʻu pono ʻaʻole pau" — King Kamehameha I On this day...There are no anniversaries listed for this day. Related portalsTopicsCategoriesAssociated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
SourcesDiscover Wikipedia using portals |