S-Adenosylmethioninamine is a substrate that is required for the biosynthesis of polyamines including spermidine, spermine, and thermospermine.[1] It is produced by decarboxylation of S-adenosyl methionine.
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
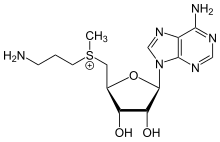
| IUPAC name
S-(3-Aminopropyl)-S-methyl-5′-thioadenosin-5′-ium
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(3-Aminopropyl){[(2S,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methyl}methylsulfanium | |
| Other names
S-Adenosyl-(5′)-3-methylthiopropylamine
decarboxylated S-adenosyl methionine decarboxy-S-adenosyl methionine (5-Deoxy-5-adenosyl)(3-aminopropyl)methylsulfonium cation | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| Abbreviations | dAdoMet, dc-SAM |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H23N6O3S+ | |
| Molar mass | 355.43582 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ Takahashi, Taku; Kakehi, Jun-Ichi (2009-10-13). "Polyamines: Ubiquitous polycations with unique roles in growth and stress responses". Annals of Botany. 105 (1): 1–6. doi:10.1093/aob/mcp259. PMC 2794062. PMID 19828463.