In human anatomy, the sacral plexus is a nerve plexus which provides motor and sensory nerves for the posterior thigh, most of the lower leg and foot, and part of the pelvis. It is part of the lumbosacral plexus and emerges from the lumbar vertebrae and sacral vertebrae (L4-S4).[1] A sacral plexopathy is a disorder affecting the nerves of the sacral plexus, usually caused by trauma, nerve compression, vascular disease, or infection. Symptoms may include pain, loss of motor control, and sensory deficits.
| Sacral plexus | |
|---|---|
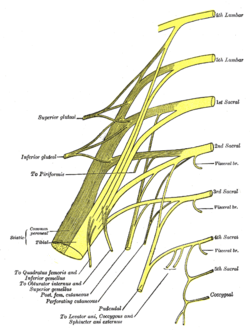 Plan of sacral and pudendal plexuses. | |
 Relations of the sacral plexus. Dissection of side wall of pelvis showing sacral and pudendal plexuses. | |
| Details | |
| From | L4-L5, S1-S4 |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | plexus sacralis |
| TA98 | A14.2.07.027 |
| TA2 | 6539 |
| FMA | 5909 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
Structure
editThe sacral plexus is formed by:
- the lumbosacral trunk
- the anterior division of the first sacral nerve
- portions of the anterior divisions of the second and third sacral nerves
The nerves forming the sacral plexus converge toward the lower part of the greater sciatic foramen, and unite to form a flattened band, from the anterior and posterior surfaces of which several branches arise. The band itself is continued as the sciatic nerve, which splits on the back of the thigh into the tibial nerve and common fibular nerve; these two nerves sometimes arise separately from the plexus, and in all cases their independence can be shown by dissection. Often, the sacral plexus and the lumbar plexus are considered to be one large nerve plexus, the lumbosacral plexus. The lumbosacral trunk connects the two plexuses.
Relations
editThe sacral plexus lies on the back of the pelvis in front of the piriformis muscle and the pelvic fascia. In front of it are the internal iliac artery, internal iliac vein, the ureter, and the sigmoid colon. The superior gluteal artery and vein run between the lumbosacral trunk and the first sacral nerve, and the inferior gluteal artery and vein between the second and third sacral nerves.
Nerves formed
editAll the nerves entering the plexus, with the exception of the third sacral, split into ventral and dorsal divisions, and the nerves arising from these are as follows of the table below:
Additional images
edit-
The right sympathetic chain and its connections with the thoracic, abdominal, and pelvic plexuses.
-
A schematic depiction.
-
Diagram of the sacral plexus
See also
editNotes
editReferences
editThis article relies largely or entirely on a single source. (January 2009) |
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 957 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- Thieme Atlas of Anatomy: General Anatomy and Musculoskeletal System. Thieme. 2006. ISBN 1-58890-419-9.
External links
edit- Lumbosacral+Plexus at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Cross section image: pembody/body15a—Plastination Laboratory at the Medical University of Vienna
- MedicalMnemonics.com: 3544 2382