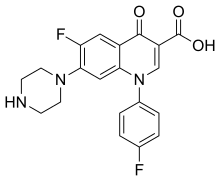
Sarafloxacin (INN) is a quinolone antibiotic drug,[1][2] which was removed from clinical use by its manufacturer Abbott Laboratories from April 30, 2001.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATCvet code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H17F2N3O3 |
| Molar mass | 385.371 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ "Evaluation of certain veterinary drug residues in food. Fiftieth report of the joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives". World Health Organization Technical Report Series. 888: i–vii, 1–95. 1999. PMID 10416362.
- ^ Gingerich WH, Stehly GR, Clark KJ, Hayton WL (1998). "Crop grouping: a proposal for public aquaculture". Veterinary and Human Toxicology. 40 (Suppl 2): 24–31. PMID 9823579.