Sercloremine (CGP-4718A), usually as the hydrochloride salt, is a drug which was developed in the 1980s and was formerly under investigation as an antidepressant, but was never marketed.[1][2] It acts as a selective, reversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase A (RIMA) and serotonin reuptake inhibitor.[1][3]
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
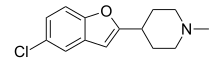
| Preferred IUPAC name
4-(5-Chloro-1-benzofuran-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H16ClNO | |
| Molar mass | 249.74 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
References
edit- ^ a b Luttinger D, Hlasta DJ (January 1987). "Antidepressant agents". In Hesp B, Bailey DM (eds.). Annual Reports in Medicinal Chemistry. Vol. 22. Academic Press. pp. 21–30 (25). ISBN 978-0-08-058366-2.
- ^ Ganellin CR, Triggle DJ (21 November 1996). Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents. CRC Press. pp. 1801–. ISBN 978-0-412-46630-4.
- ^ Delini-Stula A, Fischbach R, Gnirss F, Bures E, Pöldinger W (1985). "Early experience with CGP 4718 A (Sercloremine), a new selective and reversible MAO-A and 5-HT-uptake inhibitor, in the treatment of depressive patients". Drug Development Research. 6 (4): 371–384. doi:10.1002/ddr.430060409. ISSN 0272-4391. S2CID 85113482.