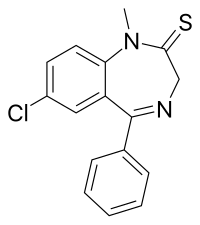
Sulazepam is a benzodiazepine derivative. It is the thioamide derivative of diazepam. It is metabolised into diazepam, desmethyldiazepam and oxydiazepam[citation needed]. It has sedative, muscle relaxant, hypnotic, anticonvulsant and anxiolytic properties like those of other benzodiazepines.[1][2] It was never marketed.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C16H13ClN2S |
| Molar mass | 300.80 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Synthesis
editTreatment of diazepam with phosphorus pentasulfide produces the corresponding thionamide, sulazepam.
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ "sulazepam". psychotropics.dk. 2003. Retrieved 29 December 2008.
- ^ Golovenko NI, Zin'kovskii VG (September 1976). "[Analysis of the structure of the components of the convulsive action of corazole following administration of sulazepam and its metabolites to mice]" [Analysis of the structure of the components of the convulsive action of corazole following administration of sulazepam and its metabolites to mice]. Biulleten' Eksperimental'noi Biologii I Meditsiny (in Russian). 82 (9): 1078–81. PMID 11012.
- ^ Archer GA, Sternbach LH (1964). "Quinazolines and 1,4-Benzodiazepines. XVI. Synthesis and Transformations of 5-Phenyl-1,4-benzodiazepine-2-thiones". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 29: 231. doi:10.1021/jo01024a511.