Sulfur oxoacids are chemical compounds that contain sulfur, oxygen, and hydrogen. The best known and most important industrially used is sulfuric acid. Sulfur has several oxoacids; however, some of these are known only from their salts (these are shown in italics in the table below). The acids that have been characterised contain a variety of structural features, for example:
- tetrahedral sulfur when coordinated to oxygen
- terminal and bridging oxygen atoms
- terminal peroxo groups
- terminal S=S
- chains of (−S−)n
| Acid | Formula | Formal oxidation number | Structure | Related anions | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sulfuric acid | H2SO4 | +6 | 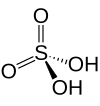
|
Sulfate, SO2− 4 and hydrogen sulfate commonly known as bisulfate, HSO− 4 |
Best known and industrially significant. |
| Polysulfuric acids including disulfuric acid (pyrosulfuric acid) | H2SO4·nSO3 | +6 | 
|
Disulfate (commonly known as pyrosulfate), S 2O2− 7 and trisulfate, S 3O2− 10 |
Pure disulfuric acid melts at 36 °C. Present in fuming sulfuric acid, oleum. Examples known for n = 1 and n = 2. |
| Peroxymonosulfuric acid | H2SO5 | +6 | 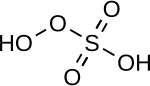
|
Peroxomonosulfate, OOSO2− 3 |
"Caro's acid", a solid melting at 45 °C |
| Peroxydisulfuric acid | H2S2O8 | +6 | 
|
Peroxydisulfate, O 3SOOSO2− 3 |
"Marshall's acid", a solid melting at 65 °C. |
| Dithionic acid | H2S2O6 | +5 | 
|
Dithionate, O 3SSO2− 3 |
Not isolated in pure form, only concentrated solutions have been prepared |
| Thiosulfuric acid | H2S2O3 | 0 (for the terminal sulfur), +4 (for the central atom) | 
|
Thiosulfate, S 2O2− 3 Hydrogenthiosulfate HS 2O− 3 (ammonium salt prepared in anhydrous methanol at −80 °C[1]) |
Aqueous solutions decompose. |
| Disulfurous acid or pyrosulfurous acid | H2S2O5 | +5 (of the sulfur atom bonded to 3 oxygen atoms), +3 (of other sulfur atom) | 
|
Disulfite commonly known as metabisulfite, S 2O2− 5 |
Not known. |
| Sulfurous acid | H2SO3 | +4 | 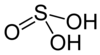
|
Bisulfite, HSO− 3 and sulfite, SO2− 3 |
Not known. |
| Dithionous acid | H2S2O4 | +3 | 
|
Dithionite, O 2SSO2− 2 |
Not known. |
| Sulfoxylic acid | H2SO2 | +2 | Sulfoxylate, SO2− 2 |
Free acid not known | |
| Polythionic acid | H2SxO6 | 0 (for the bridging S atoms), +5 (for the terminal central S atoms) | 
|
Polythionates, O 3S(S x−2)SO2− 3. Example trithionate, tetrathionate, pentathionate, hexathionate, heptathionate, octathionate, nonathionate, decathionate, undecathionate, dodecathionate, tridecathionate, and tetradecathionate. |
Examples known with x = 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 10, 12, 14. |
| Thiosulfurous acid | H2S2O2 | −1 (for the exterior sulfur atom ), +3 (for the central atom) | Thiosulfites | Not known | |
| Dihydroxydisulfane | H2S2O2 | +1 | Acid known |
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ Raman spectroscopic discovery of the hydrogenthiosulphate anion, HSSO−
3, in solid NH4HS2O3 Steudel Rr.; Prenzel A Zeitschrift für Naturforschung 1989,44, 12, 1499-1502
External links
edit- Sulfur+Acids at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) Sulfur oxoacids along with other acids containing sulfur