Surotomycin was an investigational oral antibiotic. This macrolide antibiotic was under investigation by Merck & Co (who acquired Cubist Pharmaceuticals) for the treatment of life-threatening diarrhea, commonly caused by the bacterium Clostridioides difficile.[1] After reaching phase III in clinical trials, its production was discontinued in 2017 due to its non-superiority to current therapies.[2][3]
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
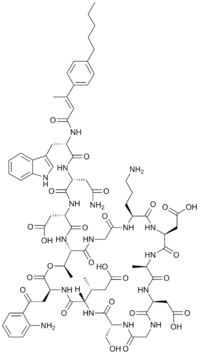
| IUPAC name
(3S)-3-{[(3S,6S,9R,15S,18R,21S,24S,30S,31R)-3-[2-(2-aminophenyl)-2-oxoethyl]-24-(3-aminopropyl)-15,21-bis(carboxymethyl)-6-[(2R)-1-carboxypropan-2-yl]-9-(hydroxymethyl)-18,31-dimethyl-2,5,8,11,14,17,20,23,26,29-decaoxo-1-oxa-4,7,10,13,16,19,22,25,28-nonaazacyclohentriacontan-30-yl]carbamoyl}-3-[(2R)-3-carbamoyl-2-[(2R)-3-(1H-indol-3-yl)-2-[(2E)-3-(4-pentylphenyl)but-2-enamido]propanamido]propanamido]propanoic acid
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C77H101N17O26 | |
| Molar mass | 1680.748 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ "Surotomycin Fact Sheet" (PDF). cubist.com.
- ^ P Daley; T Louie; J E Lutz; S Khanna; U Stoutenburgh; M Jin; A Adedoyin; L Chesnel; D Guris; K B Larson; Y Murata (December 2017). "Surotomycin versus vancomycin in adults with Clostridium difficile infection: primary clinical outcomes from the second pivotal, randomized, double-blind, Phase 3 trial". Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. 72 (12): 3462–3470. doi:10.1093/jac/dkx299. PMID 28961905.
- ^ Jenna Payesko. "Surotomycin Fails To Show Benefit Over Vancomycin in C. Difficile Treatment in Phase 3 Trial". MD magazines. Retrieved 24 September 2019.