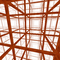
In geometry, there are a sequence of regular polytopes and honeycombs, {4,3,p}, with cubic cells. The first is the finite tesseract in 4-dimensional space. The second is the cubic honeycomb that tessellates Euclidean 3-space. The next two tessellate hyperbolic 3-space.
| {4,3,p} regular honeycombs | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Space | S3 | E3 | H3 | ||||||||
| Form | Finite | Affine | Compact | Paracompact | Noncompact | ||||||
| Name |
{4,3,3} |
{4,3,4} |
{4,3,5} |
{4,3,6} |
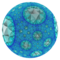
{4,3,7} |
{4,3,8} |
... {4,3,∞} | ||||
| Image | 
|
|

|

|

|
|

| ||||
| Vertex figure |
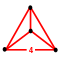 {3,3} |
 {3,4} |
 {3,5} |
 {3,6} |
 {3,7} |
 {3,8} |
 {3,∞} | ||||
References
edit- Coxeter, Regular Polytopes, 3rd. ed., Dover Publications, 1973. ISBN 0-486-61480-8. (Tables I and II: Regular polytopes and honeycombs, pp. 294–296)
- The Beauty of Geometry: Twelve Essays (1999), Dover Publications, LCCN 99-35678, ISBN 0-486-40919-8 (Chapter 10, Regular Honeycombs in Hyperbolic Space Archived 2015-04-02 at the Wayback Machine) Table III
- N. W. Johnson, R. Kellerhals, J. G. Ratcliffe, S. T. Tschantz, Commensurability classes of hyperbolic Coxeter groups, (2002) H3: p130. [1]