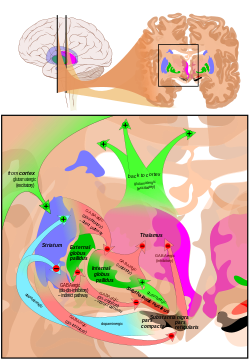
The main circuits of the basal ganglia, a group of nuclei in the brains of vertebrates that act as a cohesive functional unit. Shown here are two coronal slices that have been superimposed to include the involved basal ganglia structures. + and − signs at the point of the arrows indicate respectively whether the pathway is excitatory or inhibitory in effect.
Image: Mikael Häggström
Excitatory glutamatergic pathways
Inhibitory GABAergic pathways
Dopaminergic pathways that are excitatory on the direct pathway and inhibitory on the indirect pathway