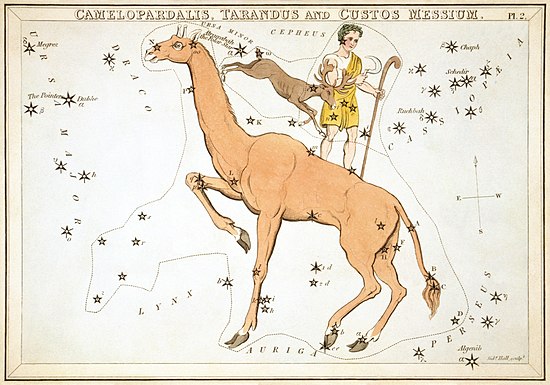
Camelopardalis is a large but faint constellation of the northern sky. Introduced in 1612 or 1613 by Petrus Plancius, it represents a giraffe. The brightest stars in Camelopardalis are β Cam, a double star 1,000 light-years from Earth with apparent magnitude 4.03; CS Cam, a 4.21-magnitude variable star; and α Cam, a blue-hued supergiant star of magnitude 4.3. At 5,000 light-years from Earth, α Cam is one of the most distant stars easily visible with the naked eye. The constellation is located in the part of the celestial sphere facing away from the galactic plane, which means it has many distant galaxies visible within its borders. This includes the NGC 2403 galaxy in the M81 Group, located approximately 12 million light-years from Earth.
This illustration was produced in around 1823 and comes from Urania's Mirror, a set of 32 astronomical star chart cards. Above the giraffe are the now-abandoned constellations of Tarandus and Custos Messium.Lithograph: Sidney Hall. Restoration: Adam Cuerden.