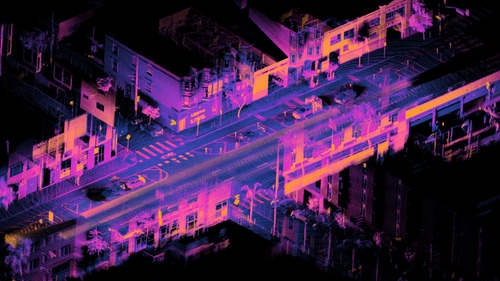
Lidar is a method for determining ranges by targeting an object with a laser and measuring the time taken by the reflected light to return to the receiver. Lidar can also be used to make digital 3-D representations of areas on the Earth's surface and ocean floor, due to differences in laser return times, and by varying laser wavelengths. It has terrestrial, airborne, and mobile applications. This image shows an orthographic projection of a registered point cloud depicting the intersection of Folsom Street and Dore Street in San Francisco, California. The point cloud was captured over 18 seconds and registered in real time using an Ouster OS1 lidar unit mounted on a moving car. The points are coloured by a function based on raw lidar intensity multiplied by range, with orange signifying brighter regions and dark blue for darker regions. Lidar is a popular sensor for self-driving cars.Image credit: Daniel L. Lu