| Main conditions[1] |
Characteristics |
Micrograph |
Photograph
|
| Generally/Not otherwise specified
|
Typical findings, called "vacuolar interface dermatitis":[1]
- Mild inflammatory cell infiltrate along the dermoepidermal junction (black arrow in image)
- Vacuolization within the basal keratinocytes (white arrow in image)
- Often necrotic, predominantly basal, individual keratinocytes, manifesting as colloid or Civatte bodies
|

|
|
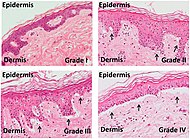
| Acute graft-versus-host-disease
|
- Vacuolar alteration of various severity, from focal or diffuse vacuolation of the basal keratinocytes (grade I), to separation at the dermoepidermal junction (grade III)
- Involvement of the hair follicle[1]
- Rarely eosinophils[1]
|
|
|
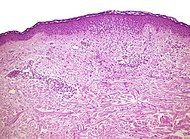
| Allergic drug reaction
|
- Rarely involvement of hair follicles.[1]
- Frequently eosinophils[1]
|
|
|
| Lichen sclerosus
|
Hyperkeratosis, atrophic epidermis, sclerosis of dermis and dermal lymphocytes.[2]
|

|
| Erythema multiforme
|
|
|
|
|
| Lupus erythematosis
|
Typical findings in systemic lupus erythematosus:[3]
- Fibrinoid necrosis at the dermoepidermal junction
- Liquefactive degeneration and atrophy of the epidermis
- Mucin deposition in the reticular dermis
- Edema, small hemorrhages
- Mild and mainly lymphocytic infiltrate in the upper dermis
- Fibrinoid material in the dermis around capillary blood vessels, on collagen and in the interstitium
- In non-bullous cases, perivascular and interstitial neutrophils are sometimes present in the upper dermis, with damage to blood vessels
|

|

|





