Template:Transclude list item excerpts as random slideshow/testcases/Portal:Lithuania
| This is the template test cases page for the sandbox of Template:Transclude list item excerpts as random slideshow/testcases. Purge this page to update the examples. If there are many examples of a complicated template, later ones may break due to limits in MediaWiki; see the HTML comment "NewPP limit report" in the rendered page. You can also use Special:ExpandTemplates to examine the results of template uses. You can test how this page looks in the different skins and parsers with these links: |
Portal maintenance status: (June 2018)
|
Introduction



Lithuania, officially the Republic of Lithuania, is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, bordered by Latvia to the north, Belarus to the east and south, Poland to the south, and the Russian semi-exclave of Kaliningrad Oblast to the southwest, with a maritime border with Sweden to the west. Lithuania covers an area of 65,300 km2 (25,200 sq mi), with a population of 2.88 million. Its capital and largest city is Vilnius. Other major cities are Kaunas, Klaipėda, Šiauliai and Panevėžys. Lithuanians belong to the ethnolinguistic group of the Balts and speak Lithuanian.
For millennia, the southeastern shores of the Baltic Sea were inhabited by various Baltic tribes. In the 1230s, Lithuanian lands were united for the first time by Mindaugas, who formed the Kingdom of Lithuania on 6 July 1253. Subsequent expansion and consolidation resulted in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, which by the 14th century was the largest country in Europe.
In 1386, the Grand Duchy entered into a de facto personal union with the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland. The two realms were united into the bi-confederal Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth in 1569, forming one of the largest and most prosperous states in Europe. The Commonwealth lasted more than two centuries, until neighbouring countries gradually dismantled it between 1772 and 1795, with the Russian Empire annexing most of Lithuania's territory. (Full article...)
Selected pictures
-
Image 1Vilnius University, one of the oldest universities in the region. It was established by Stephen Báthory, King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania, in 1579. (from Lithuania)
-
Image 2Physical map and geomorphological subdivision of Lithuania (from Lithuania)
-
Image 4Lithuanian counties by GDP per capita, 2022 (from Lithuania)
-
Image 5Statutes of Lithuania were the central piece of Lithuanian law in 1529–1795. (from Lithuania)
-
Image 6Lithuanian artist Jonas Mekas, regarded as godfather of American avant-garde cinema (from Culture of Lithuania)
-
Image 7Baltic amber was once a valuable trade resource. It was transported from the region of modern-day Lithuania to the Roman Empire through the Amber Road. (from Lithuania)
-
Image 8Lithuanian basketball clubs Žalgiris and Šiauliai playing a match (from Culture of Lithuania)
-
Image 10Rock band Antis, which under firm censorship actively mocked the Soviet Union regime by using metaphors in their lyrics, during an anti-Sovietism, anti-communism concert in 1987 (from Lithuania)
-
Image 12Lithuania's GDP per capita compared to rest of the world (2022) (from Lithuania)
-
Image 19Lithuania was a member of the United Nations Security Council. Its representatives are on the right side. (from Lithuania)
-
Image 20Cepelinai, a potato-based dumpling dish characteristic of Lithuanian cuisine with meat, curd or mushrooms (from Lithuania)
-
Image 23Panorama of Vilnius in 1600 (from Lithuania)
-
Image 24Traditional Lithuanian house from late 19th century (from Culture of Lithuania)
-
Image 28Members of the Council of Lithuania after signing the Act of Independence of Lithuania in 1918 (from Lithuania)
-
Image 29Stamp dedicated to Lithuania's presidency of the European Union. Post of Lithuania, 2013. (from Lithuania)
-
Image 30The white stork is the national bird of Lithuania, which has the highest-density stork population in Europe. (from Lithuania)
-
Image 31The first Lithuanian printed book, Catechism of Martynas Mažvydas (1547, Königsberg) (from Lithuania)
-
Image 32Population density of Lithuania (from Lithuania)
-
Image 36Guests of the 2023 Vilnius (NATO) summit in the Courtyard of the Presidential Palace in Vilnius (from Lithuania)
-
Image 38Commemoration of the Act of the Re-Establishment of the State of Lithuania in the historical Seimas hall where it was originally signed in 1990. The ceremony is attended by the Lithuanian President, Prime Minister, Chairman of the Seimas and other high-ranking officials. (from Lithuania)
-
Image 42The Great Courtyard of Vilnius University and the Church of St. Johns (from Culture of Lithuania)
-
Image 44Le Château — Conte de fées (Lithuanian: Pilis — Pasaka) by Mikalojus Konstantinas Čiurlionis (1909) (from Culture of Lithuania)
-
Image 47Lithuanian Army soldiers marching with their dress uniforms in Vilnius. An officer stands out with a sword. (from Lithuania)
-
Image 48Lithuania men's national basketball team is ranked eighth worldwide in FIBA Rankings. (from Lithuania)
-
Image 49Real GDP per capita development of Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania (from Lithuania)
-
Image 50Changes in the territory of Lithuania from the 13th to 15th century. At its peak, Lithuania was the largest state in Europe. (from Lithuania)
-
Image 52Trakai Island Castle, the former residence of the Grand Dukes. Trakai was the capital of the medieval state. (from Lithuania)
-
Image 53Lithuania's name in writing (Litua, on line 7), 1009 (from Lithuania)
-
Image 56Major highways in Lithuania (from Lithuania)
-
Image 57A ceremony of Lithuanian modern pagans. (from Culture of Lithuania)
-
Image 61Cepelinai served with sour cream (from Culture of Lithuania)
-
Image 68The earliest known Lithuanian glosses (between 1520 and 1530) written in the margins of Johann Herolt book Liber Discipuli de eruditione Christifidelium. Words: teprÿdav[ſ]ʒÿ (let it strike), vbagÿſte (indigence). (from Lithuania)
-
Image 70Lithuanian cemetery at All Souls night (from Culture of Lithuania)
-
Image 74Gryčia (traditional dwelling house, built in the 19th century) (from Lithuania)
-
Image 81Simple Words of Catechism by Martynas Mažvydas was the first Lithuanian book and was published in 1547. (from Culture of Lithuania)
-
Image 84The title page of Radivilias (1592, Vilnius). The poem celebrating commander Mikalojus Radvila Rudasis (1512–1584) and recounts the famous victory of Lithuanian Armed Forces over Moscow troops (1564). (from Lithuania)
Selected county
-
Image 1
Kaunas County (Lithuanian: Kauno apskritis) is one of ten counties of Lithuania. It is in the centre of the country, and its capital is Kaunas. On 1 July 2010, the county administration was abolished. (Full article...) -
Image 2
Utena County (Lithuanian: Utenos Apskritis) is one of ten counties in Lithuania. It is the country's most sparsely populated county. The capital and the largest city in the county is Utena, which is 95 km (59 mi) from Vilnius, the capital of Lithuania. On 1 July 2010, the county administration was abolished. Since that date, Utena County remains as the territorial and statistical unit. It borders Latvia. (Full article...) -
Image 3
Klaipėda County (Lithuanian: Klaipėdos apskritis) is one of ten counties in Lithuania, bordering Tauragė County to the southeast, Telšiai County to the northeast, Kurzeme in Latvia to the north, and Kaliningrad Oblast in Russia to the south. To the west is the Baltic Sea. It lies in the west of the country and is the only county to have a coastline and not be landlocked. Its capital is Klaipėda. On 1 July 2010, the county administration was abolished, and since that date, Klaipėda County remains as the territorial and statistical unit. (Full article...) -
Image 4
Alytus County (Lithuanian: Alytaus apskritis) is one of ten counties in Lithuania. It is the southernmost county, and its capital is the city of Alytus. Its territory lies within the ethnographic region of Dzūkija. On 1 July 2010, the county administration was abolished, and since that date, Alytus County remains as the territorial and statistical unit.
It borders the Vilnius County in the east, Marijampolė County and Kaunas County in the north, Podlaskie Voivodeship of Poland in the west, and Grodno Region of Belarus in the south. (Full article...) -
Image 5Vilnius skyline
Vilnius County (Lithuanian: Vilniaus apskritis) is the largest of the 10 counties of Lithuania, located in the east of the country around the city Vilnius and is also known as Capital Region or Sostinės regionas by the Lithuanian statistics department and Eurostat. On 1 July 2010, the county administration was abolished, and since that date, Vilnius County remains as the territorial and statistical unit. (Full article...) -
Image 6
Šiauliai County (Lithuanian: Šiaulių apskritis) is one of ten counties in Lithuania. It is in the north of the country, and its capital is Šiauliai. On 1 July 2010, the county administration was abolished, and since that date, Šiauliai County remains as the territorial and statistical unit. It borders Latvia. (Full article...) -
Image 7
Panevėžys County (Lithuanian: Panevėžio apskritis) is one of ten counties in Lithuania. It is in the north-east of the country, and its capital is Panevėžys. On 1 July 2010, the county administration was abolished, and since that date, Panevėžys County remains as the territorial and statistical unit. (Full article...) -
Image 8
Telšiai County (Lithuanian: Telšių apskritis) is one of ten counties in Lithuania. It is in the west of the country, and its capital is Telšiai. There are Lithuanians (98.7%), Latvians (0.1%), Russians (0.9%), and others (0.3%). On 1 July 2010, the county administration was abolished, and since that date, Telšiai County remains as the territorial and statistical unit. It borders Latvia. (Full article...) -
Image 9
Tauragė County (Lithuanian: Tauragės apskritis) is one of ten counties in Lithuania. It is in the west of the country, and its capital is Tauragė. On 1 July 2010, the county administration was abolished, and since that date, Tauragė County remains as the territorial and statistical unit.
Famous landmarks include Tauragė Castle and Panemunė Castle. (Full article...) -
Image 10
Marijampolė County (Lithuanian: Marijampolės apskritis) is one of the ten counties in Lithuania. It is in the southwest of the country and roughly corresponds to the historical region of Sudovia. Its capital and the largest town is Marijampolė. On 1 July 2010, the county administration was abolished, and since that date, Marijampolė County remains as the territorial and statistical unit.
It borders the Tauragė County in the north, Kaunas County and Alytus County in the east, Podlaskie Voivodeship of Poland in the south and Kaliningrad Oblast of Russia in the west. (Full article...)
Selected municipality
-
Image 1Landscape near Marškonė
Mažeikiai District Municipality (Lithuanian: Mažeikių rajono savivaldybė, Samogitian: Mažėikiu rajuona savivaldībė) is located in the north-west of Lithuania, on the River Venta in Telšiai County. The administrative center of Mažeikiai District is the city of Mažeikiai. Its territory of 1,220.2 km2 (471.1 sq mi) is composed of 32 km2 (12 sq mi) of towns and settlements, 22 km2 (8.5 sq mi) of industrial enterprises and roads, 614 km2 (237 sq mi) of agricultural lands, 273 km2 (105 sq mi) of forests, and 68 km2 (26 sq mi) of tracts of other designation. There is one urban and 8 rural elderates. In 2003, the population was 67,393. Of this number, 46,223 live in towns and 21,170 in villages.
It is situated in northern Samogitia. Mažeikiai District borders with the Republic of Latvia in the north, with Akmenė District Municipality in the east, with Telšiai District Municipality in the southeast, with Plungė District Municipality in the southwest and with Skuodas District Municipality in the west. Mažeikiai District stretches for 43.5 km (27.0 mi) east-to-west and 38 km (24 mi) north-to-south. Petraičiai village is the westernmost settlement, with Kalniškiai and Pakliaupė villages being the easternmost settlements. The northernmost is Giniočiai, while the southernmost is Pasruojė. (Full article...) -
Image 2
Lazdijai District Municipality (Lithuanian: Lazdijų rajono savivaldybė) is a municipality in Alytus County, Lithuania. (Full article...) -
Image 3
Alytus (Lithuanian: [ɐlʲiːˈtʊs] ⓘ) is a city with municipal rights in southern Lithuania. It is the capital of Alytus County. The population as of July 2024 was 50,996. Alytus is the historical centre of the Dzūkija region. The city lies on the banks of the Nemunas river. The major roads linking Vilnius, Kaunas, Lazdijai (border with Poland), and Grodno in Belarus pass through Alytus.
Divided onto two separate entities for centuries, it consists of two parts still frequently referred to as Alytus I and Alytus II, the earlier being a smaller town and the latter forming the city centre with parks, microdistricts and industrial areas. (Full article...) -
Image 4
Biržai District Municipality is a Lithuanian municipality, located in northern Lithuania, Aukštaitija ethnographic region, Panevėžys County.
The towns of Biržai and Vabalninkas lie within the district. About 64% of its land is agricultural, including a number of organic farms. Portions are protected in Biržai Regional Park and as botanical and geological reserves. (Full article...) -
Image 5

Akmenė District Municipality (Lithuanian: Akmenės rajono savivaldybė) is one of 60 municipalities in Lithuania. It lies in the Northwest of the country, with the administrative center in Naujoji Akmenė and borders Latvia in the north, Joniškis District in the east, Šiauliai District in the southeast, Telšiai District in the southwest, and Mažeikiai District in the west. The area of the municipality covers ca. 844 km2 and is the 43rd largest municipality by total area in the country. Its population shrank from some 30,300 (2001 census) to 18,500 (2021 census) which is around 39% in decline. (Full article...) -
Image 6

Radviliškis District Municipality (Lithuanian: Radviliškio rajono savivaldybė) is one of the seven municipalities of Šiauliai County (Šiaulių apskritis) in Lithuania. Radviliškis town has been its center since 1950.
Radviliškis district has 13 subdivisions or elderships (Seniūnija). (Full article...) -
Image 7Svobiškėlis mound
The Molėtai District Municipality is one of 60 municipalities in Lithuania.
Molėtai is known for its many lakes. There are about 220 lakes in the district and they cover about 7% of the total territory. Since it is only about 60 km north of Vilnius, many Vilnians own summer homes there. The area offers many recreational opportunities. It is easy to reach Molėtai because there is a highway connecting Vilnius and Utena which divides the district into two almost equal parts. Since there is little industry, the district is proud of its lack of pollution. The land is not very fertile, therefore the district's government is focused on developing tourism. (Full article...) -
Image 8
Kėdainiai District Municipality (Lithuanian: Kėdainių rajono savivaldybė) is one of 60 municipalities in Lithuania, located in the central part of the country. (Full article...) -
Image 9
-
Image 10
-
Image 11Landscape near Rūdaičiai
Kretinga District Municipality is one of 60 municipalities in Lithuania. (Full article...) -
Image 12

Klaipėda District Municipality (Lithuanian: Klaipėdos rajono savivaldybė) is a municipality in western Lithuania, east of the city of Klaipėda, by the Curonian Lagoon and the Baltic Sea. Its administrative centre is the town of Gargždai (unlike other Lithuanian municipalities, the name of this municipality does not correspond to its administrative centre). It covers an area of 1336 km² (2% of the total area of Lithuania). The municipality owns most of the Seaside Regional Park. It is home to the famous The Dutchman's Cap Hill, the highest cliff on the Lithuanian coast. (Full article...) -
Image 13
-
Image 14

Kaunas District Municipality (Kauno rajono savivaldybė) is one of 60 municipalities in Lithuania. The seat of the municipality is the city of Kaunas, which does not belong to the municipality but is a separate administrative unit. It surrounds the Kaunas City Municipality from the north, west and south, while in the east Kaunas district municipality borders Kaišiadorys District Municipality. Kaunas District Municipality has the second largest international airport in Lithuania (Kaunas International Airport), and is well connected by major roads (A1 highway and Via Baltica), as well as railways with other cities of Lithuania. (Full article...) -
Image 15
Šiauliai (/ʃaʊˈleɪ/ show-LAY; Lithuanian: [ɕɛʊ̯ˈlʲɛɪ̯ˑ] ⓘ) is a city in northern Lithuania, the country's fourth largest city and the sixth largest city in the Baltic States, with a population of 112 581 in 2024. From 1994 to 2010 it was the capital of Šiauliai County. (Full article...)
Selected World Heritage Site
-
Image 1
The Old Town of Vilnius (Lithuanian: Vilniaus senamiestis), one of the largest surviving medieval old towns in Northern Europe, has an area of 3.59 square kilometres (887 acres). It encompasses 74 quarters, with 70 streets and lanes numbering 1487 buildings with a total floor area of 1,497,000 square meters. It was founded by the Lithuanian Grand Duke and King of Poland Jogaila in 1387 on the Magdeburg rights the oldest part of the Lithuanian capital of Vilnius, it had been developed over the course of many centuries, and has been shaped by the city's history and a constantly changing cultural influence. It is a place where some of Europe's greatest architectural styles—gothic, renaissance, baroque and neoclassical—stand side by side and complement each other. There are many Catholic, Lutheran and Orthodox churches, residential houses, cultural and architectural monuments, museums in the Old Town.
Pilies Street is the Old Town's main artery and the hub of cafe and street market life. The main street of Vilnius, Gediminas Avenue, is partially located in the Old Town. The central squares in the Old Town are the Cathedral Square and the Town Hall Square. (Full article...) -
Image 2The Valley of Death looking from the Parnidis Dune in Neringa Municipality, Lithuania in October 2022.
The Curonian (Courish) Spit (Lithuanian: Kuršių nerija; Russian: Ку́ршская коса́) is a 98-kilometre (61 mi) long, thin, curved sand-dune spit that separates the Curonian Lagoon from the Baltic Sea. It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site shared by Lithuania and Russia. Its southern portion lies within Kaliningrad Oblast of Russia, and its northern within southwestern Klaipėda County of Lithuania. (Full article...) -
Image 3
Kaunas (/ˈkaʊnəs/; Lithuanian: [ˈkɐʊ̯ˑnˠɐs] ⓘ; previously known in English as Kovno /ˈkɒvnoʊ/) is the second-largest city in Lithuania after Vilnius, the fourth largest city in the Baltic States and an important centre of Lithuanian economic, academic, and cultural life. Kaunas was the largest city and the centre of a county [pl] in the Duchy of Trakai of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and Trakai Palatinate since 1413. In the Russian Empire, it was the capital of the Kaunas Governorate from 1843 to 1915.
During the interwar period, it served as the temporary capital of Lithuania, when Vilnius was seized and controlled by Poland between 1920 and 1939. During that period Kaunas was celebrated for its rich cultural and academic life, fashion, construction of countless Art Deco and Lithuanian National Revival architectural-style buildings as well as popular furniture, interior design of the time, and a widespread café culture. The city interwar architecture is regarded as among the finest examples of European Art Deco and has received the European Heritage Label. It contributed to Kaunas being designated as the first city in Central and Eastern Europe as a UNESCO City of Design, and also to becoming a World Heritage Site in 2023 as the only European city representing large scale urbanization during the interwar period and versatile modernism architecture. (Full article...) -
Image 4
Kernavė was a medieval capital of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and today is a tourist attraction and an archeological site (population 238, 2021). It is located in the Širvintos district municipality located in southeast Lithuania. A Lithuanian state cultural reserve was established in Kernavė in 1989. In 2004 Kernavė Archaeological Site was included into UNESCO World Heritage list. (Full article...) -
Image 5The northernmost station of the Struve Geodetic Arc is located in Fuglenes, Norway.
The Struve Geodetic Arc is a chain of survey triangulations stretching from Hammerfest in Norway to the Black Sea, through ten countries and over 2,820 kilometres (1,750 mi), which yielded the first accurate measurement of a meridian arc.
The chain was established and used by the German-born Russian scientist Friedrich Georg Wilhelm von Struve in the years 1816 to 1855 to establish the exact size and shape of the earth. At that time, the chain passed merely through three countries: Norway, Sweden and the Russian Empire. The Arc's first point is located in Tartu Observatory in Estonia, where Struve conducted much of his research. Measurement of the triangulation chain comprises 258 main triangles and 265 geodetic vertices. The northernmost point is located near Hammerfest in Norway and the southernmost point near the Black Sea in Ukraine. (Full article...)
Selected history article
-
Image 1The history of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (1569–1648) covers a period in the history of Poland and Lithuania, before their joint state was subjected to devastating wars in the mid-17th century. The Union of Lublin of 1569 established the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, a more closely unified federal state, replacing the previously existing personal union of the two countries. The Union was largely run by the Polish and increasingly Polonized Lithuanian and Ruthenian nobility, through the system of the central parliament and local assemblies, but from 1573 led by elected kings. The formal rule of the nobility, which was a much greater proportion of the population than in other European countries, constituted a sophisticated early democratic system, in contrast to the absolute monarchies prevalent at that time in the rest of Europe.[a]
The Polish–Lithuanian Union had become an influential player in Europe and a significant cultural entity. In the second half of the 16th and the first half of the 17th century, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth was a huge state in central-eastern Europe, with an area approaching one million square kilometers. (Full article...) -
Image 2
The Act of Independence of Lithuania (Lithuanian: Lietuvos Nepriklausomybės Aktas) or the Act of February 16th, also the Lithuanian Resolution on Independence (Lithuanian: Lietuvos Nepriklausomybės Nutarimas), was signed by the Council of Lithuania on February 16, 1918, proclaiming the restoration of an independent State of Lithuania, governed by democratic principles, with Vilnius as its capital. The Act was signed by all twenty representatives of the Council, which was chaired by Jonas Basanavičius. The Act of February 16 was the result of a series of resolutions on the issue, including one issued by the Vilnius Conference and the Act of January 8. The path to the Act was long and complex because the German Empire exerted pressure on the Council to form an alliance. The Council had to carefully maneuver between the Germans, whose troops were present in Lithuania, and the demands of the Lithuanian people.
The immediate effects of the announcement of Lithuania's re-establishment of independence were limited. Publication of the Act was prohibited by the German authorities, and the text was distributed and printed illegally. The work of the Council was hindered, and Germans remained in control over Lithuania. The situation changed only when Germany lost World War I in the fall of 1918. In November 1918 the first Cabinet of Lithuania was formed, and the Council of Lithuania gained control over the territory of Lithuania. Independent Lithuania, although it would soon be battling the Wars of Independence, became a reality. (Full article...) -
Image 3

The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a sovereign state in northeastern Europe that existed from the 13th century, succeeding the Kingdom of Lithuania, to the late 18th century, when the territory was suppressed during the 1795 partitions of Poland–Lithuania. The state was founded by Lithuanians, who were at the time a polytheistic nation of several united Baltic tribes from Aukštaitija. By 1440 the grand duchy had become the largest European state, controlling an area from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Black Sea in the south.
The grand duchy expanded to include large portions of the former Kievan Rus' and other neighbouring states, including what is now Belarus, Lithuania, most of Ukraine as well as parts of Latvia, Moldova, Poland and Russia. At its greatest extent, in the 15th century, it was the largest state in Europe. It was a multi-ethnic and multiconfessional state, with great diversity in languages, religion, and cultural heritage. (Full article...) -
Image 4
The Balts or Baltic peoples (Lithuanian: baltai, Latvian: balti) are a group of peoples inhabiting the eastern coast of the Baltic Sea who speak Baltic languages. Among the Baltic peoples are modern-day Lithuanians (including Samogitians) and Latvians (including Latgalians) — all East Balts — as well as the Old Prussians, Curonians, Sudovians, Skalvians, Yotvingians and Galindians — the West Balts — whose languages and cultures are now extinct.
The Balts are descended from a group of Proto-Indo-European tribes who settled the area between the lower Vistula and southeast shore of the Baltic Sea and upper Daugava and Dnieper rivers, and which over time became differentiated into West and East Balts. In the fifth century CE, parts of the eastern Baltic coast began to be settled by the ancestors of the Western Balts, whereas the East Balts lived in modern-day Belarus, Ukraine and Russia. In the first millennium CE, large migrations of the Balts occurred. By the 13th and 14th centuries, the East Balts shrank to the general area that the present-day Balts and Belarusians inhabit. (Full article...) -
Image 5

Lithuania, officially the Republic of Lithuania, is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, bordered by Latvia to the north, Belarus to the east and south, Poland to the south, and the Russian semi-exclave of Kaliningrad Oblast to the southwest, with a maritime border with Sweden to the west. Lithuania covers an area of 65,300 km2 (25,200 sq mi), with a population of 2.88 million. Its capital and largest city is Vilnius. Other major cities are Kaunas, Klaipėda, Šiauliai and Panevėžys. Lithuanians belong to the ethnolinguistic group of the Balts and speak Lithuanian.
For millennia, the southeastern shores of the Baltic Sea were inhabited by various Baltic tribes. In the 1230s, Lithuanian lands were united for the first time by Mindaugas, who formed the Kingdom of Lithuania on 6 July 1253. Subsequent expansion and consolidation resulted in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, which by the 14th century was the largest country in Europe. (Full article...) -
Image 6

The Lithuanian Soviet Socialist Republic (Lithuanian SSR; Lithuanian: Lietuvos Tarybų Socialistinė Respublika; Russian: Литовская Советская Социалистическая Республика, romanized: Litovskaya Sovetskaya Sotsialisticheskaya Respublika), also known as Soviet Lithuania or simply Lithuania, was de facto one of the constituent republics of the Soviet Union between 1940–1941 and 1944–1990. After 1946, its territory and borders mirrored those of today's Republic of Lithuania, with the exception of minor adjustments to its border with Belarus.
During World War II, the previously independent Republic of Lithuania was occupied by the Red Army on 16 June 1940, in conformity with the terms of the 23 August 1939 Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact, and established as a puppet state on 21 July. Between 1941 and 1944, the German invasion of the Soviet Union caused its de facto dissolution. However, with the retreat of the Germans in 1944–1945, Soviet hegemony was re-established and continued for forty-five years. As a result, many Western countries continued to recognize Lithuania as an independent, sovereign de jure state subject to international law, represented by the legations appointed by the pre-1940 Baltic states, which functioned in various places through the Lithuanian Diplomatic Service. (Full article...) -
Image 7
The monarchy of Lithuania concerned the monarchical head of state of Lithuania, which was established as an absolute and hereditary monarchy. Throughout Lithuania's history there were three ducal dynasties—the House of Mindaugas, the House of Gediminas, and the House of Jagiellon. Despite this, the one and only crowned king of Lithuania was King Mindaugas I. In two more instances, royal nobles were not crowned due to political circumstances, but held de jure recognition abroad —Vytautas the Great by Sigismund, Holy Roman Emperor, and Mindaugas II by Pope Benedict XV.
Others were seen as kings of Lithuania even though they had only considered it and never took further action to claim the throne, as in the case of Gediminas who was recognised as king of Lithuania by Pope John XXII. The hereditary monarchy in Lithuania was first established in the 13th century during the reign of Mindaugas I and officially re-established as a constitutional monarchy on 11 July 1918, only to be abandoned soon afterwards on 2 November 1918. (Full article...) -
Image 8
The Act of the Re-Establishment of the State of Lithuania or Act of 11 March (Lithuanian: Aktas dėl Lietuvos nepriklausomos valstybės atstatymo) was an independence declaration by Lithuania adopted on 11 March 1990, signed by all members of the Supreme Council of the Republic of Lithuania led by Sąjūdis. The act emphasized restoration and legal continuity of the interwar-period Lithuania, which was occupied by the Soviet Union and annexed in June 1940. In March 1990, it was the first of the 15 Soviet republics to declare independence, with the rest following to continue for 21 months, concluding with Kazakhstan's independence in 1991. These events (part of the broader process dubbed the "parade of sovereignties") led to the dissolution of the Soviet Union in December 1991. (Full article...) -
Image 9The Kunda culture, which originated from the Swiderian culture, comprised Mesolithic hunter-gatherer communities of the Baltic forest zone extending eastwards through Latvia into northern Russia, dating to the period 8500–5000 BC according to calibrated radiocarbon dating. It is named after the Estonian town of Kunda, about 110 kilometres (70 mi) east of Tallinn along the Gulf of Finland, near where the first extensively studied settlement was discovered on Lammasmäe Hill and in the surrounding peat bog. The oldest known settlement of the Kunda culture in Estonia is Pulli. The Kunda culture was succeeded by the Narva culture, who used pottery and showed some traces of food production. (Full article...)
-
Image 10The history of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (1648–1764) covers a period in the history of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, from the time their joint state became the theater of wars and invasions fought on a great scale in the middle of the 17th century, to the time just before the election of Stanisław August Poniatowski, the last king of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth.
From the 17th century, the nobles' democracy, experienced devastating wars and fell into internal disorder and then anarchy, and as a result declined. The once powerful Commonwealth had become vulnerable to internal warfare and foreign intervention. In 1648 the Cossack Khmelnytsky Uprising engulfed the south and east of the vast Polish–Lithuanian state, and was soon followed by a Swedish invasion, which raged through core Polish lands. Warfare with the Cossacks and Russia left Ukraine divided; the eastern part, lost by the Commonwealth, became a dependency of the Tsardom of Russia. John III Sobieski, who fought protracted wars against the Ottoman Empire, revived the Commonwealth's military might once more. In one decisive engagement he helped in 1683 to deliver Vienna from a Turkish onslaught. (Full article...) -
Image 11

The Corded Ware culture comprises a broad archaeological horizon of Europe between c. 3000 BC – 2350 BC, thus from the late Neolithic, through the Copper Age, and ending in the early Bronze Age. Corded Ware culture encompassed a vast area, from the contact zone between the Yamnaya culture and the Corded Ware culture in south Central Europe, to the Rhine in the west and the Volga in the east, occupying parts of Northern Europe, Central Europe and Eastern Europe. Autosomal genetic studies suggest that the Corded Ware culture originated from the westward migration of Yamnaya-related people from the steppe-forest zone into the territory of late Neolithic European cultures, evolving in parallel with (although under significant influence from) the Yamnaya, with no evidence of direct male-line descent between them.
The Corded Ware culture is considered to be a likely vector for the spread of many of the Indo-European languages in Europe and Asia. (Full article...) -
Image 12

Volunteers of the Lithuanian Army heading to the war in Vilkaviškis, 1919
The Lithuanian Wars of Independence, also known as the Freedom Struggles (Lithuanian: Laisvės kovos), refer to three wars Lithuania fought defending its independence at the end of World War I: with Bolshevik forces (December 1918 – August 1919), Bermontians (October 1919 – December 1919), and Poland (August 1920 – November 1920). The wars delayed international recognition of independent Lithuania and the formation of civil institutions. (Full article...) -
Image 13
The archaeological Neman culture (German: Memel-Kultur) existed from about 5100 to the 3rd millennium BC, starting in the Mesolithic and continued into the middle Neolithic. It was located in the upper basin of the Neman River (present-day northern Poland, southern Lithuania, western Belarus and Kaliningrad Oblast). In the north, the Neman culture bordered the Kunda culture during the Mesolithic and the Narva culture during the Neolithic. (Full article...) -
Image 14Early dukes of Lithuania (including Samogitia) reigned before Lithuanians were unified by Mindaugas into a state, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. While the Palemonids legend provides genealogy from the 10th century, only few dukes were mentioned by contemporary historical sources. All of them were mentioned in written sources the 13th century. Data about them is extremely scarce and is usually limited to few brief sentences. The primary sources are the Chronicle of Henry of Livonia and Hypatian Codex. (Full article...)
-
Image 15
The Lithuanian–Soviet War or Lithuanian–Bolshevik War (Lithuanian: karas su bolševikais) was fought between newly independent Lithuania and the Russian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic in the aftermath of World War I. It was part of the larger Soviet westward offensive of 1918–1919. The offensive followed the retreat of German troops and sought to establish Soviet republics in Ukraine, Belarus, Lithuania, Latvia, Estonia, Poland and link up with the German Revolution. By the end of December 1918 Soviet forces reached Lithuanian borders. Largely unopposed, they occupied one town after another and by the end of January 1919 controlled about two thirds of the Lithuanian territory. In February, the Soviet advance was stopped by Lithuanian and German volunteers, who prevented the Soviets from capturing Kaunas, the temporary capital of Lithuania. From April 1919, the Lithuanian war went parallel with the Polish–Soviet War. Poland had territorial claims over Lithuania, especially the Vilnius Region; these tensions spilt over into the Polish–Lithuanian War.
British-Polish historian Norman Davies summarized the situation: "the German army was supporting the Lithuanian nationalists, the Soviets were supporting the Lithuanian communists and the Polish Army was fighting them all." In mid-May, the Lithuanian army, now commanded by General Silvestras Žukauskas, began an offensive against the Soviets in Northeastern Lithuania. By mid-June, the Lithuanians reached the Latvian border and cornered the Soviets among lakes and hills near Zarasai, where the Soviets held out until the end of August 1919. The Soviets and Lithuanians, separated by the Daugava River, maintained their fronts until the Battle of Daugavpils in January 1920. As early as September 1919, the Soviets offered to negotiate a peace treaty, but talks began only in May 1920. The Soviet–Lithuanian Peace Treaty was signed on July 12, 1920. Soviet Russia fully recognized independent Lithuania. (Full article...)
Selected politics article
-
Image 1
The Speaker of the Seimas (Lithuanian: Seimo pirmininkas, literally translated as Chairman of the Seimas) is the presiding officer of the Seimas, the parliament of Lithuania. The speaker and deputy speakers are elected by the members of the Seimas during the session. (Full article...) -
Image 2
Parliamentary elections were held in Lithuania on 9 and 23 October 2016 to elect the 141 members of the Seimas. 71 were elected in single-member constituencies using the two-round system, and the remaining 70 in a single nationwide constituency using proportional representation. The first round was held on 9 October and the second round on 23 October. (Full article...) -
Image 3
The prime minister of Lithuania (Lithuanian: Lietuvos ministras pirmininkas) is the head of government of Lithuania. The prime minister is appointed by the president with the assent of the Lithuanian parliament, the Seimas. The modern office of prime minister was established in 1990, when Lithuania declared its independence, although the official title was "Chairperson of the Council of Ministers" until 25 November 1992. (Full article...) -
Image 4This article lists political parties in Lithuania.
Lithuania has a multi-party system with numerous political parties, in which no one party often has a chance of gaining power alone, and parties must work with each other to form coalition governments. As of October 2024[update], there are 22 active political parties, one party undergoing formal registration, one inactive political party, and four political parties that are in the process of disestablishment registered with the Ministry of Justice. (Full article...) -
Image 5
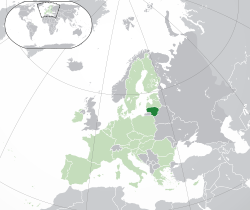
Location of Lithuania in the European Union
Lithuania is divided into three levels of administrative divisions. The first-level division consists of 10 counties (Lithuanian: singular – apskritis, plural – apskritys). These are sub-divided into 60 municipalities (Lithuanian: plural – savivaldybės, singular – savivaldybė), which in turn are further sub-divided into over 500 smaller groups, known as elderships (Lithuanian: plural – seniūnijos, singular – seniūnija). (Full article...) -
Image 6

Seniūnijos of Lithuania
A seniūnija (in English: eldership, elderate, ward, parish, or subdistrict) is the smallest administrative division of Lithuania. An eldership may comprise a very small region consisting of few villages, one single town, or a part of a big city. Elderships vary in size and population depending on their location and nature. A few elderships make up a municipality. Šilainiai, Dainava, Verkiai, Žirmūnai and Pašilaičiai are the most populous elderates, with population counts over 40,000, around twice the population of some entire municipalities. (Full article...) -
Image 7
The president of the Republic of Lithuania (Lithuanian: Lietuvos Respublikos Prezidentas) is the head of state of the Republic of Lithuania. The president directs and appoints the executive branch of the Government of Lithuania, represents the nation internationally and is the commander-in-chief of the Lithuanian Armed Forces. The president is directly elected by the citizens of Lithuania for a five-year term, with the office holder limited to serving two terms consecutively. The current president is Gitanas Nausėda who assumed office on July 12, 2019. (Full article...) -
Image 8

Gitanas Nausėda (Lithuanian: [ɡɪˈtɐ.nɐs nɐˈu.sʲeː.dɐ]; born 19 May 1964) is a Lithuanian politician, economist, and banker who is serving as the ninth and incumbent president of Lithuania since 2019. Born in Klaipėda, Nausėda graduated from Vilnius University with an economics degree in 1987. He was director of monetary policy at the Bank of Lithuania from 1996 to 2000 and chief economist to the chairman of SEB bankas from 2008 to 2018. (Full article...) -
Image 9
Ingrida Šimonytė (Lithuanian: [ɪŋʲɡʲrʲɪˈdˠɐ ʃʲɪmˠoːˈnʲîːtʲeː]; born 15 November 1974) is a Lithuanian politician, public servant and economist who served as the 17th prime minister of Lithuania since 2020. She has been a Member of the Seimas for the Antakalnis constituency since 2016 and was Minister of Finance in the second Kubilius cabinet from 2009 until 2012. Šimonytė was a candidate in the 2019 and 2024 presidential election, but lost in the second round runoff to Gitanas Nausėda both times. She has been a member of Homeland Union since 2022, having previously been an independent politician. (Full article...) -
Image 10

The Supreme Court of the Republic of Lithuania (Lithuanian: Lietuvos Respublikos Aukščiausiasis Teismas) is the only court of cassation in the Lithuania for reviewing effective judgements and rulings passed by the courts hearing criminal cases at the first and appeal instances as well as decisions and rulings in civil cases passed by the courts of appeals. It is the highest court of cassation, but it cannot interpret the constitution, since that is under the jurisdiction of the Constitutional Court of Lithuania. (Full article...) -
Image 11
Election campaign poster in Vilnius
The 2014 European Parliament election in Lithuania was an election of the delegation from Lithuania to the European Parliament in 2014. It was part of the wider 2014 European election. (Full article...) -
Image 12
Seimas Palace (Lithuanian: Seimo rūmai) is the seat of the Seimas, the Lithuanian parliament. It is located in Lithuania's capital Vilnius. (Full article...) -
Image 13

Constitutional Court of the Republic of Lithuania (in Lithuanian: Lietuvos Respublikos Konstitucinis Teismas) is the constitutional court of the Republic of Lithuania, established by the Constitution of the Republic of Lithuania of 1992. It began the activities after the adoption of the Law of Constitutional Court of the Republic of Lithuania on 3 February 1993. Since its inception, the court has been located in Vilnius. (Full article...) -
Image 14

The Seimas of the Republic of Lithuania (Lithuanian: Lietuvos Respublikos Seimas), or simply the Seimas (/ˈseɪməs/ SAY-məs; Lithuanian: [ˈsɛɪˑmɐs]), is the unicameral legislative body of the Republic of Lithuania. The Seimas constitutes the legislative branch of government in Lithuania, enacting laws and amendments to the Constitution, passing the budget, confirming the Prime Minister and the Government and controlling their activities. (Full article...) -
Image 15There have been fifteen referendums in Lithuania since it declared independence from the Soviet Union on 11 March 1990. Because of strict requirements, only four referendums have been successful. Older Lithuanian laws required that more than half of all registered voters (not half of voters who participate) would vote in support of a proposal for it to become a binding obligation to the government. In 2002, this requirement was lowered to one third of all registered voters. (Full article...)
Selected biography
-
Image 1Žilvinas Tratas, also known as James Tratas (born 10 December 1988) is a Lithuanian actor, screenwriter and TV personality. (Full article...)
-
Image 2

Vagnorius in 1996
Gediminas Vagnorius (born 10 June 1957) is a Lithuanian politician and signatory of the Act of the Re-Establishment of the State of Lithuania. He served as the Prime Minister of Lithuania, heading the government between 1991 and 1992, and again from 1996 until 1999.
After Lithuania regained its independence in 1990, its temporary currency, the Lithuanian talonas, was popularly known as vagnorkė or vagnorėlis after Vagnorius' name. (Full article...) -
Image 3
Jonas Valančiūnas (/ˈjoʊnəs/ /ˌvælənˈtʃunəs/ YOH-nəss VAL-ən-CHOO-nəs; Lithuanian pronunciation: [ˈjoːnɐs vɐɫɐnʲˈtɕûːnɐs]; born 6 May 1992) is a Lithuanian professional basketball player for the Washington Wizards of the National Basketball Association (NBA). He was selected by the Toronto Raptors with the fifth overall pick in the 2011 NBA draft. At the 2019 trade deadline, he was traded to the Memphis Grizzlies. In the 2021 offseason he was traded to the New Orleans Pelicans.
Valančiūnas has been a member of the Lithuania men's national basketball team since age 19. He won two EuroBasket silver medals in EuroBasket 2013 and EuroBasket 2015, earning All-Tournament honours in the latter. Valančiūnas also appeared in the documentary The Other Dream Team. (Full article...) -
Image 4Motiejūnas with Lithuania men's national basketball team in 2023
Donatas Motiejūnas (Lithuanian pronunciation: [dɔˈnaːtɐs moːtʲiəˈjûːnɐs]; born September 20, 1990) is a Lithuanian professional basketball player for AS Monaco Basket of the French LNB Pro A and the EuroLeague. He was drafted 20th overall in the 2011 NBA draft by the Minnesota Timberwolves before going on to win the 2012 Polish Basketball League championship with Asseco Prokom Gdynia. After spending four seasons with the Houston Rockets from 2012 to 2016, Motiejūnas joined the New Orleans Pelicans in January 2017. (Full article...) -
Image 5

Eliyahu Eliezer Dessler (1892 – 31 December 1953) was an Orthodox rabbi, Talmudic scholar, and Jewish philosopher of the 20th century. He is best known for being the mashgiach ruchani ("spiritual counselor") of the Ponevezh yeshiva in Israel and through collections of his writings published posthumously by his pupils. (Full article...) -
Image 6
Robert Lee Zemeckis (born May 14, 1952) is an American filmmaker known for directing and producing a range of successful and influential movies, often blending cutting-edge visual effects with storytelling. He has received several accolades including an Academy Award and a Golden Globe Award as well as nominations for five British Academy Film Awards and a Daytime Emmy Award.
Zemeckis started his career directing the comedy films I Wanna Hold Your Hand (1978), Used Cars (1980), and Romancing the Stone (1984). He gained prominence directing the science-fiction comedy Back to the Future trilogy (1985–1990), the fantasy comedy Who Framed Roger Rabbit (1988), and the comedy-drama Forrest Gump (1994), the latter of which won Academy Awards for Best Picture and Best Director. (Full article...) -
Image 7Bieksa with the Vancouver Canucks in March 2012
Kevin Francesco Bieksa (born June 16, 1981) is a Canadian former professional ice hockey defenceman. Bieksa started and played most of his career with the Vancouver Canucks and later played for the Anaheim Ducks. After a three-year career in the Ontario Junior Hockey League (OJHL) with the Burlington Cougars, Bieksa was awarded a scholarship to Bowling Green State University. He was a one-time All-CCHA honourable mention during his four-year tenure with the Falcons of the Central Collegiate Hockey Association (CCHA). He graduated from the university with a bachelor's degree (B.A.) in finance, and was a two-time CCHA All-Academic honourable mention in 2003 and 2004. Bieksa now co-hosts Hockey Night in Canada.
Bieksa represented his country in the 2014 IIHF World Championship in Minsk, Belarus. He was selected as team captain and named 1 of 3 top players for Canada in the tournament. Bieksa represented Canada for the second time in his career at the 2018 Spengler Cup. (Full article...) -
Image 8

Jurgita Štreimikytė (born 14 May 1972 in Alytus, Lithuania) is a Lithuanian former basketball forward who played the WNBA for Indiana Fever and the Euroleague Women with Kaunas, Valenciennes Olympic and SG Comense among others. She was a member of the Lithuanian national team, winning the 1997 Eurobasket. She retired from international basketball following the 2006 World Championship.
After retiring in 2010, she currently serves as Kaunas' second coach. (Full article...) -
Image 9
Juras Požela (12 April 1982 – 16 October 2016) was a Lithuanian politician who served as the Minister of Health of Lithuania from March 2016 until his death on 16 October 2016 from pancreatitis. He was also a Seimas member, Youth and Sports Affairs Committee Chairman and a presidium member of the Social Democratic Party of Lithuania. (Full article...) -
Image 10Mindaugas Kalonas (born 28 February 1984) is a Lithuanian former professional footballer who played as a midfielder. (Full article...)
-
Image 11Arlauskis with Watford in 2015
Giedrius Arlauskis (born 1 December 1987) is a Lithuanian former professional footballer who plays as a goalkeeper.
Arlauskis started out as a senior at FK Šiauliai, before moving to Romanian side Unirea Urziceni in 2008. He is one of the most decorated players of the Liga I, having won seven Romanian league titles with Urziceni, Steaua București and CFR Cluj combined. Apart from his native Lithuania and the latter country, Arlauskis represented teams in Russia, England, Spain and Saudi Arabia, respectively. (Full article...) -
Image 12

John Mondy Shimkus (/ˈʃɪmkəs/, born February 21, 1958) is an American politician who served as a U.S. representative from 1997 to 2021, representing the 20th, 19th and 15th congressional districts of Illinois.
Shimkus is a member of the Republican Party. On August 30, 2019, he announced that he would not seek re-election for his seat in 2020 and was succeeded by fellow Republican Mary Miller. (Full article...) -
Image 13Rasa Polikevičiūtė during the introductions prior to one of the stages of the 2002 Women's Challenge stage race. She is wearing the Rainbow Jersey which signifies that she was the (then) current World Road Race Champion.
Rasa Polikevičiūtė (born September 25, 1970 in Panevėžys) is a Lithuanian cycle racer. One of her Lithuanian cycling contemporaries is her identical twin, Jolanta Polikevičiūtė.
She began cycling at age 13 under the influence of her childhood athletic coach and made her professional debut in 1990. In 1997, she won the Women's Challenge bicycle race and later went on to win the 2001 World Road Race Championships. (Full article...)
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus

































































![Image 68The earliest known Lithuanian glosses (between 1520 and 1530) written in the margins of Johann Herolt book Liber Discipuli de eruditione Christifidelium. Words: teprÿdav[ſ]ʒÿ (let it strike), vbagÿſte (indigence). (from Lithuania)](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/f/f6/The_earliest_known_Lithuanian_glosses_%28~1520%E2%80%931530%29%2C_words_%28tepridau%C5%BEia%2C_ubagyst%C4%97%29.jpg/120px-The_earliest_known_Lithuanian_glosses_%28~1520%E2%80%931530%29%2C_words_%28tepridau%C5%BEia%2C_ubagyst%C4%97%29.jpg)




















































































