The thick-billed parrot (Rhynchopsitta pachyrhyncha) is a medium-sized parrot endemic to Mexico that formerly ranged into the southwestern United States. Its position in parrot phylogeny is the subject of ongoing discussion; it is sometimes referred to as thick-billed macaw or thick-billed conure. In Mexico, it is locally called guacamaya ("macaw") or cotorra serrana ("mountain parrot"). Classified internationally as Endangered through IUCN,[1] the thick-billed parrot's decline has been central to multiple controversies over wildlife management. In 2018, the estimated wild population in Mexico was 1,700.[1]
| Thick-billed parrot | |
|---|---|

| |
| Thick-billed parrots in a U.S. zoo | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Psittaciformes |
| Family: | Psittacidae |
| Genus: | Rhynchopsitta |
| Species: | R. pachyrhyncha
|
| Binomial name | |
| Rhynchopsitta pachyrhyncha (Swainson, 1827)
| |
| |
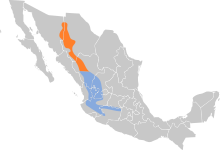
| Range map of thick-billed parrot orange:breeding, blue:non-breeding | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Macrocercus pachyrhynchus | |
Taxonomy
editPachyrhyncha is currently classified as a species of the genus Rhynchopsitta of macaw-like thick-billed parrots of which there are two extant species (the other being the maroon-fronted parrot), and one extinct species. However, recent molecular DNA studies indicate that pachyrhyncha and its sister species terrisi in genus Rhynchopsitta are conspecific subspecies.[3] Rhynchopsitta is one of numerous genera of New World long-tailed parrots in tribe Arini, which also includes the Central and South American macaws. Tribe Arini together with the amazonian parrots and a few miscellaneous genera make up subfamily Arinae of Neotropical parrots in the family Psittacidae of the true parrots.
The bird was first described by English naturalist and illustrator William John Swainson who designated it Macrocercus pachyrhynchus in Philosophical Magazine, new ser., 1, no. 6, p. 439 (1827). Swainson evidently thought that because of its size and heavy beak, that it was a macaw (at that time, any parrot of the genus Sittace, or Macrocercus). It was later placed in its own genus Rhynchopsitta by French naturalist Prince Charles Bonaparte in 1854. The name is derived from Ancient Greek rhynchos ("beak") and psittakos ("parrot") and pachy- ("thick") and rhynchos ("beak"), hence a "thick-beaked parrot".
Morphologically, Brazilian ornithologist Helmut Sick calls this bird "a highly modified macaw".[4] In a recent molecular study, genus Rhynchopsitta was placed in a large clade including all of tribe Arini and a few other genera; its closest relatives were similar in size to the parakeets in Enicognathus, Pyrrhura, Pionites, and Deroptyus genera of the clade. In a separate molecular analysis in the same study, Rhynchopsitta was placed in a clade in which it was sister to Pyrrhura but not other genera.[5]
"Thick-billed parrot" has been designated the official common name by the International Ornithologists' Union (IOC).[6]
Description
editThe thick-billed parrot is a medium-sized, bright green parrot with a large black bill and red forecrown, shoulder and thighs. Adult eyes are amber, while juveniles have brown eyes. The rest of the bird is bright green. Thick-billed parrots show red shoulders and leading edge on the underwing, followed by a blackish green stripe, then a yellow stripe, followed by the remaining underwing showing dark green. The tail is black.[7] It is 38 cm (15 in) long and weighs 315–370 g (11.1–13.1 oz). Thick-billed parrots have lived up to 33 years in captivity.[8] It is similar in appearance to the military macaw (Ara militaris), which is larger with a proportionally longer tail and blue flight feathers and rump, and the lilac-crowned amazon (Amazona finschi).[7] Note that these are not the phylogenetically closest relatives - see Taxonomy.
The voice of the thick-billed parrot resembles a high-pitched macaw and includes a variety of harsh, rolling calls described as similar to human laughter. Although readily becoming hand-tame, the species is nervous and difficult to breed in captivity, with very low reproduction rates. Captive birds are fair voice mimics and can learn a few phrases and words. However, their piercing calls and comparatively duller coloration has prevented them from becoming popular pet trade birds, and currently there is little demand for them as illegally wild-caught or captive bred birds.[9]
Like other parrots, they manipulate their food by holding it with one foot. Highly social, they may feed each other food stored in their crop (a pouch in the throat), and spend their free time preening each other. Groups of over 1,000 birds in one place are known from historical records.[citation needed]
Distribution and habitat
editThe thick-billed parrot lives in temperate conifer, pine, mature pine-oak and fir forests at elevation of 1200–3600 meters. It is largely restricted to the Sierra Madre Occidental in Chihuahua and Durango, Mexico.
Its former range included the United States including Arizona and New Mexico. Early accounts also place them in far west Texas (with famed ornithologist John James Audubon sighting them in El Paso in 1827), and possibly as far north as Utah. Accounts in both Arizona and New Mexico indicate birds visiting regularly, as well as over-wintering in Arizona.[10] However, these accounts co-occurred with heavy shooting, logging, and development that extirpated the thick-billed parrot from its US range.[11] The disruption of Native American ways of life greatly decreased the range of some bird species (like the boreal owl)[12] that utilized Native American irrigation and farm land, and it is possible that the thick-billed parrot also suffered from this effect of European colonization. Following the extinction of the Carolina parakeet (Conuropsis carolinensis) and the extirpation of this species, the green parakeet (Psittacara holochlorus) is currently the only extant native parrot species in the United States.
The last reliable reports of the birds in the southwestern United States were in 1935 and 1938 in the Chiricahua Mountains of Arizona.[13]
Behavior and diet
editThe thick-billed parrot, like most parrots, nests in tree cavities, especially old woodpecker holes. In the past it is believed to have relied extensively on abandoned nesting holes made by the now-probably-extinct imperial woodpecker (Campephilus imperialis), the world's largest woodpecker, also found in Mexico. Its decline and eventual extinction may have been a factor in the reduction of the parrot's range. In parts of its existing range, dead or living quaking aspens are the dominant tree selected for nesting.[14] It mainly feeds on seeds from various pine species. Mexican white pine appears to be a preferred species but the seeds of Douglas fir, Apache pine, Chihuahua pine, and yellow pine are also taken. The species is strongly dependent on the supply of conifer cones, breeding at the peak of pine seed production. The species is nomadic, following the variations of cone abundance. To a much lesser extent, they also feed upon acorns and pine buds.[11] They are adept fliers, and historical accounts describe the birds sleeping in one mountain range, and crossing vast distances to feed in another mountain range each day. They deal with deep snow by hanging upside-down and climbing on the bare underside of a snow-covered branch in order to access cones.[citation needed]
Conservation and threats
editPrincipal threats to the thick-billed parrot are illegal pet trade, habitat loss principally due to logging, climate change (hotter temperatures that raise the snow line and increasing fire threats), and predators especially hawks and owls. The species is listed as endangered on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species[1] and is on Appendix I of CITES meaning that commercial international trade is prohibited. It is also listed as endangered by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service.[11] NatureServe considers the species to be "Critically Imperiled".[15]
A 2004 BirdLife International survey suggested that there may be 2,000–2,800 mature individuals and only 100 active nests in the entire population, but notes that this may be an overestimate; the distribution of this species is only 600 square kilometres (230 sq mi). In June 2013, the population was estimated as 2,097 with the proviso that the number may be an underestimate. However, it is only somewhat established in captive breeding programs in zoos in the United States and Europe, so an ex situ captive conservation project is less feasible than in popularly bred parrots, such as the scarlet macaw.[7]
Arizona re-introduction
editBirds were reintroduced in Arizona in the 1980s, but this effort turned out to be unsuccessful. The re-introduction into the mountains of southeastern Arizona (the Madrean sky islands region) was dramatically affected by predation. Due to extensive human development, residency, agriculture, etc., high numbers of predator species exist, especially the American goshawk. The bird loss was especially high to these now well-emplaced predator species. The effort was abandoned in 1993, and the last of the introduced parrots was seen in 1995. The major components of the effort, such as keeping birds in a roughly 2-meter cube cage before release, and artificially implanting feathers onto birds who did not fly on their own, likely affected the bird's ability to survive. The AZA thick-billed parrot breeding studbook offers a critical review of the project's failures.[16] More modern approaches in captive release do not use adult animals that live in cages for long periods before release, as was the case in the 1980s re-introduction project.
In October 2020, it was announced that, working with Mexican officials, researchers in Arizona planned to reintroduce the thick-billed parrot to the state. A representative with the Arizona Game and Fish department stated that the birds' preferred habitat is "high elevation forests like the Chiricahuas."[17]
Relationship with Native Americans
editBones of thick-billed parrots used in religious burials, as well as painted sacred and decorative imagery, have been found in prehistoric Native American towns in the American Southwest. These sites are a large distance north of the current thick-billed parrot Mexican range. Sites include Wupatki Pueblo near Flagstaff, Arizona,[18] and Chaco Canyon in northwestern New Mexico.[19] A thick-billed parrot feather utilized in a medicine man fetish has been found in Colorado,[10] showing either trade in feathers or very northern excursions of this species. Considering there is no evidence of live trade of these birds, but ritual burials of parrots in the Southwest utilized live birds, the presence of thick-billed parrot burials at Chaco Canyon in northern New Mexico makes the possibility of northern populations or northern excursions by thick-billed parrots plausible.
The most well known of the thick-billed parrot images is from the Pottery Mound site in Southwestern New Mexico. This site has images of the three species most commonly found in religious use in the American Southwest, the scarlet macaw, military macaw, and thick-billed parrot.[10] The lack of a bare facial patch, as is seen in macaw images at the site, is widely considered diagnostic for the identity of the painted bird.[20]
In popular culture
editIn 2023 the thick-billed parrot was featured on a United States Postal Service Forever stamp as part of the Endangered Species set, based on a photograph from Joel Sartore's Photo Ark. The stamp was dedicated at a ceremony at the National Grasslands Visitor Center in Wall, South Dakota.[21]
References
edit- ^ a b c d BirdLife International (2017). "Rhynchopsitta pachyrhyncha". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2017: e.T22685766A110475642. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-1.RLTS.T22685766A110475642.en. Retrieved 13 November 2021.
- ^ "Appendices | CITES". cites.org. Retrieved 2022-01-14.
- ^ Urantowka, A.D.; Strzała, T.; Grabowski, K.A. (2014). "Complete mitochondrial genome of endangered Maroon-fronted Parrot (Rhynchopsitta terrisi) - conspecific relation of the species with Thick-billed Parrot (Rhynchopsitta pachyrhyncha)". Mitochondrial DNA. 25 (6): 424–426. doi:10.3109/19401736.2013.809440. PMID 23841618. S2CID 7865866.
- ^ Sick, Helmut (1990). "Notes on the Taxonomy of Brazilian Parrots". Ararajuba (1): 111–112.
- ^ Tavares, et.el., E. (June 2006). "Phylogenetic relationships and historical biogeography of neotropical parrots (Psittaciformes: Psittacidae: Arini) inferred from mitochondrial and nuclear DNA sequences". Systematic Biology. 55 (3): 454–70. doi:10.1080/10635150600697390. PMID 16861209.
- ^ Gill, Frank; Donsker, David, eds. (2021). "Parrots, cockatoos". World Bird List Version 11.2. International Ornithologists' Union. Retrieved 22 September 2021.
- ^ a b c "Birdlife International species factsheet". Birdlife International. Retrieved 9 Dec 2013.
- ^ Brouwer; et al. (2000). "Longevity records for Psittaciformes in captivity". International Zoo Yearbook. 37 (37): 299–316. doi:10.1111/j.1748-1090.2000.tb00735.x.
- ^ "The illegal parrot trade in Mexico" (PDF). Defenders of Wildlife.
- ^ a b c "Google map of locations related to thick billed parrots". Bird Recovery International.
- ^ a b c "Thick-Billed Parrot Draft Recovery Plan Addendum". US Fish and Wildlife Service.
- ^ Emslie, Steven D. (1981). "Birds and prehistoric agriculture: The New Mexican pueblos". Human Ecology. 9 (3): 305–329. doi:10.1007/bf00890740. S2CID 154860879.
- ^ Snyder, N. F.; Enkerlin-Hoeflich, E. C.; Cruz-Nieto, M. A. (2020). Poole, A. (ed.). "Thick-billed Parrot (Rhynchopsitta pachyrhyncha)". The Birds of North America Online. Ithaca, New York: Cornell Lab of Ornithology. doi:10.2173/bow.thbpar.01. S2CID 216343386. Retrieved 26 Jan 2017.
- ^ C. Tiberio; et al. (2006). "Gregarious nesting behaviour of thick-billed parrots (Rhynchopsitta pachyrhyncha) in aspen stands". The Wilson Journal of Ornithology. 118 (2): 237–243. doi:10.1676/05-039.1. S2CID 85693361.
- ^ "Rhynchopsitta pachyrhyncha". NatureServe Explorer An online encyclopedia of life. 7.1. NatureServe. Retrieved 31 March 2022.
- ^ Susan Y. Healy & Sacramento Zoo (2003). "Thick-billed parrot (Rynchopsitta pachyryncha): Studbook". San Diego Zoo Global Library.
- ^ Prange, Rick (Oct 12, 2020). "Game and Fish working to reintroduce parrots once native to Arizona". 12news.com. Retrieved 6 November 2020.
- ^ Hargrave, Lyndon L. (1939). "Bird bones from abandoned indian dwellings in Arizona and Utah" (PDF). The Condor. 41 (5): 206–210. doi:10.2307/1364349. JSTOR 1364349.
- ^ Rizo, Michael Joseph (1998). Scarlet Macaw productiona and trade at Paquime, Chihuahua (MS.c.). Arizona State University.
- ^ Wyckoff, Kristina Celeste (2009). Mimbres-Mesoamerican interaction: Macaws and parrots in the Mimbres Valley, southwestern New Mexico (PDF) (MS.c.). Oklahoma State University.
- ^ "Postal Service Spotlights Endangered Species". United States Postal Service. April 19, 2023. Retrieved May 11, 2023.
External links
edit- ITESM Site (in Spanish)
- Fact file - ARKive
- Stamps[usurped] for Mexico and the United States
- Videos, photos and sounds - Internet Bird Collection
