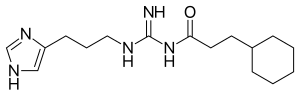
UR-AK49 is a drug used in scientific research which acts as a potent antagonist for the Neuropeptide Y / Pancreatic polypeptide receptor Y4, and also as a partial agonist at the histamine receptors H1 and H2.[1] UR-AK49 is a pure antagonist at Y4 with no partial agonist effects, and although it is only slightly selective for Y4 over the related Y1 and Y5 receptors, as the first non-peptide Y4 antagonist developed UR-AK49 is expected to be useful in the study of this receptor and its role in the body.[2]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | UR-AK49 |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C16H27N5O |
| Molar mass | 305.426 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
References
edit- ^ Xie SX, Kraus A, Ghorai P, Ye QZ, Elz S, Buschauer A, Seifert R (June 2006). "N1-(3-cyclohexylbutanoyl)-N2-[3-(1H-imidazol-4-yl)propyl]guanidine (UR-AK57), a potent partial agonist for the human histamine H1- and H2-receptors" (PDF). The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 317 (3): 1262–1268. doi:10.1124/jpet.106.102897. PMID 16554355. S2CID 26028129.
- ^ Ziemek R, Schneider E, Kraus A, Cabrele C, Beck-Sickinger AG, Bernhardt G, Buschauer A (2007). "Determination of affinity and activity of ligands at the human neuropeptide Y Y4 receptor by flow cytometry and aequorin luminescence". Journal of Receptor and Signal Transduction Research. 27 (4): 217–233. doi:10.1080/10799890701505206. PMID 17885919. S2CID 26579625.