| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
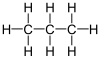
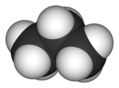
| IUPAC name
Propane
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| EC Number |
| ||
| KEGG | |||
| MeSH | Propane | ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1978 | ||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C3H12 | |||
| Molar mass | 48.129 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless gas | ||
| Density | 1.83 kg/m3, gas 0.5077 kg/L, liquid | ||
| Melting point | −187.6 °C (85.5 K) | ||
| Boiling point | −42.09 °C (231.1 K) | ||
| 0.1 g/cm3 (37.8 °C) | |||
| Hazards | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Explosive limits | 2.37–9.5% | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Tracking categories (test):
Propane is a three-carbon alkane, normally a gas, but compressible to a liquid that is transportable. It is derived from other petroleum products during oil or natural gas processing. It is commonly used as a fuel for engines, barbecues, and home heating systems.
When sold as fuel, it is commonly known as liquified petroleum gas (LPG or LP-gas), which can be a mixture of propane along with small amounts of propylene, butane, and butylene. The odorant ethanethiol is also added so that people can easily smell the gas in case of a leak.