header
editThe flight and expulsion of Poles refers to forced migration of Poles from the former eastern territories of Poland towards the end and in the aftermath of World War II. More specifically it targeted over a million of inhabitants of the Polish areas annexed by the Soviet Union to the Ukrainian SSR, Belarusian SSR and Lithuanian SSR. The displacement of Polish nationals was agreed to by the allied leaders of the US, UK, and the USSR during the conferences at Tehran and Yalta. In effect, it became one of the largest of several post-war expulsions in Central and Eastern Europe which displaced a total of about twenty million people.[1] According to official data during the state-controlled expulsion between 1945 and 1946 roughly 1,167,000 Poles were allowed to leave the westernmost republics of the Soviet Union, less than 50% of those who registered for population transfer. [2]
The process is variously known as expulsion, deportation,[3][4] depatriation,[5][6][7] or repatriation[8] depending on the context. The latter term, while used officially in both communist-controlled Poland and the USSR, might be misleading, as in most cases the people to leave the area were leaving their homeland rather than return to it.[5] It is also sometimes referred to as the first repatriation, in contrast with the the second repatriation in the years 1955–1959. In a wider context, it is sometimes described as a culmination of a process of "de-Polonization" of the areas during and after the world war. [9] The process was planned and carried out by the communist regimes of the USSR and that of post-war Poland. Many of the repatriated Poles were settled in formerly German eastern provinces, after 1945, Recovered Territories of the People's Republic of Poland.
German
edit
As the Red Army advanced into German-settled areas in the last year of World War II, a considerable exodus of German refugees began from the areas near the front lines.[11] Many Germans fled spontaneously or under vague and haphazardly implemented evacuation orders of the German government in 1944 and in early 1945.[11] Most of those who remained in or returned to their homes were forced to leave by Communist local authorities between 1945 and 1950. Census figures in 1950 place the total number of ethnic Germans still living in Eastern Europe at approximately 2.6 million, about 12 percent of the pre-war total.[12]
Past research provided estimates ranging from 13.5 to 16.5 million people who fled or were evacuated, directly expelled, or died from all causes during the movements westward. Recent research places the number at more than 12 million, including all those who fled during or directly after the war to both the Western and Eastern zones of Germany and to Austria.[12] At least two million people perished during the evacuation and expulsion. Of these, 400,000 to 600,000 were killed either during military operations or murdered afterwards.[13]
Background
editThe history of Polish settlement in Ukraine dates back to 1030–31. Colonization of Ukraine by ethnic Poles intensified after the Union of Lublin in 1569 when most of Ukraine was incorporated into the Recz Pospolita. Escalation of conflict between the two ethnicities arose regarding the differences of religious practices between the Roman Catholic Poles and the Eastern Orthodox Ukrainians and the expansion of Roman catholicism in Ukraine. From 1657 to 1793 some 80 Roman Catholic Churches and monasteries were built in Volhynia alone. Pressure from the expansion of Catholicism in Lemkivshchyna, Chełm Land, Podlachia, Brześć land, Galicia, Volhynia and Right bank Ukraine was accompanied by the Polonization of some Ukrainians.
In 1914, there were 1,640,000 Poles in that region[14]. In 1917 the Polish population of Kiev was 42,800[15]. In July 1917, when relations between the Ukrainian People's Republic (UNR) and Russia became strained the Polish Democratic Council of Kiev supported the Ukrainian side in its conflict with Petrograd. During the period of the UNR a separate minister for Polish affairs was set up in November 1917 headed by M. Mickiewycz. During the period of the UNR 1,300 Polish schools functioned with 1,800 teachers and 84,000 students.
In the region of Podolia in 1917 there were 290 Polish schools. The Bolshevik actions of 1920 however encouraged the emigration of the Polish population to Poland. In 1922, 120,000 Poles were repatriated to Poland.
In the aftermath of the Polish-Soviet war, Ukraine failed to gain independence (despite the Polish-Ukrainian alliance) and in the Treaty of Riga in 1921 the disputed territories were split between the Second Polish Republic and the Ukrainian SSR (after 1923 a part of the Soviet Union). In Poland, a large number of Polish settlers moved to the Kresy (see osadnik). Tensions between the Ukrainian minority in Poland and Polish government escalated.
In the USSR, the Soviet government from the mid 1920s treated the Polish population (see Polish minority in USSR) as disloyal because of their close association with their Catholic faith and their deep anti-communist feelings. Inaccuracies appeared in the 1926 census where ethnic Poles were marked down as being of Russian or Ukrainian ethnicity[16].
Polish-Soviet relations soured after 1933 with the discovery of the existence of a secret Polish intelligence organization (see Prometheism). Those Poles found to have associations with this organization were arrested and shot.
The XII congress of the CPSU proposed the deportation of Poles in Ukraine to the Eastern regions of the USSR to add to the 58,000 Poles who were already living in Siberia. A list of 8,352 families marked for deportation was prepared.
Mass deportations started in the autumn of 1935 in order to remove Poles from the border regions and resettle these areas with ethnic Russians. In that year alone 1,500 families were deported from Ukraine. In 1936, a further 5,000 Polish families were deported to Kazakhstan. The deportations were accompanied by the gradual elimination of Polish cultural institutions. Polish language newspapers were closed as were Polish language courses in Pedagogical Institutes in Ukraine. By the 1937–8 census, the Polish population in Ukraine had officially fallen by 120,000.
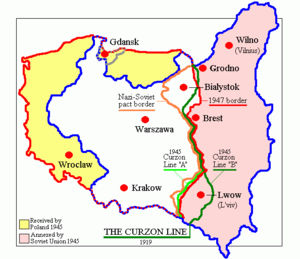
After the signing of the secret Molotov-Ribbentrop pact in 1939 between Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union, Germany invaded Western Poland. Two weeks later, the Soviet Union also invaded eastern Poland. As a result, Poland was divided between the Germans and the Soviets (see Polish areas annexed by the Soviet Union). With the annexation of the Kresy - Western Ukraine was annexed to Soviet Ukraine and Western Belarus to Soviet Belorussia - in 1939. The Polish population of the Kresy comprised up to 2,513.7 thousand.[citation needed].
During World War II, Polish settlements in Western Ukraine were used by the Soviets as bases for the support of Red Partisan movement (see also Soviet partisans). In the final period of World War II, these bases also actively fought against the Ukrainian nationalist insurgent groupings. This escalated the Ukrainian-Polish conflict, particularly in Volyn in 1943 resulting in ethnic cleansing operations where large numbers of Poles, including civilians were killed (see Massacres of Poles in Volhynia). By 1944, the population of ethnic Poles in Western Ukraine) was 1,182,100.
The Polish government in exile in London affirmed its position of retaining the 1939 borders. Nikita Krushchev, however, approached Stalin personally to keep the territories gained through the illegal and secret Molotov-Ribbentrop pact under continued Soviet occupation.
1944–1946
editThe document regarding the resettlement of Poles from Ukrainian and Belorussian SSR to Poland was signed 9 September 1944 in Lublin by Nikita Khrushchev and the head of the Polish Committee of National Liberation Edward Osóbka-Morawski (the corresponding document with Lithuanian SSR was signed on 22 September). The document further specified who was eligible for the resettlement, (it was primarily applicable to all Poles and Jews who were citizens of the Second Polish Republic before 17 September 1939 and their families) what property they could take with them and what aid they would receive from the corresponding governments. The resettlement was divided into two phases: first, the eligible citizens were registered as wishing to be resettled; second their request was to be reviewed and approved by the corresponding governments. About 750,000 Poles and Jews from the western regions of Ukraine were deported, as well as about 200,000 from western Belarus and from Lithuanian SSR each. The deportations continued until August 1 1946.
From Ukraine
editAfter World War II, tensions between Poles and Ukrainians were very high, escalated by the conflict between the nationalistic Ukrainian organizations such as OUN and UIA (see: Massacres of Poles in Volhynia) and the Polish AK. Although the Soviet government was actively trying to eradicate these organizations, it did little to support the Polish minority; and instead encouraged population transfer. The haste at which repatriation was done was such that the Polish leader Bolesław Bierut was forced to intercede and approach Stalin to retard this repatriation, as the post-war Polish government was overwhelmed by the sudden great number of refugees.
The Poles in southern Kresy (now Western Ukraine) were given the option of resettlement in Siberia or Poland and most chose Poland[17].
The Polish exile government in London sent out directives to their organizations (see Polish Secret State) in Lviv and other major centers in Western Ukraine to sit fast and not evacuate, promising that during peaceful discussions they would be able to keep Lviv within Poland. Khrushchev as a result of this directive introduced a different approach to dealing with this Polish problem. Until this time, Polish children could receive education in Polish according to the curriculum of pre-war Poland. Overnight this was discontinued and all Polish schools switched to the Soviet Ukrainian curriculum with classes only in Ukrainian and Russian. All males were also told to prepare for mobilization into labor brigades within the Red Army. These actions were introduced specifically to encourage Polish emigration to Poland.
The director of the Middle school in Rokotyniv, Stefania Kubrynowycz stated:
- "The Russians hate the Poles. (Soviet) Soldiers get changed in to the uniforms of bandits (Banderites) and wander into Polish villages where they suggest that they move to Poland. Those that do not want to move are threatened with death. If it were not England and America the Soviets would eat the Poles"[18].
In January 1945, the NKVD arrested 772 Poles in Lviv (where, according to Soviet sources, on October 1, 1944, Poles represented 66.7% of population), among them 14 professors, 6 doctors, 2 engineers, 3 artists, 5 Catholic priests. The reaction to these arrests in the Polish community was extremely negative. The Polish underground press in Lviv characterized these acts as attempts to hasten the deportation of Poles from their city. Those arrested were released after they signed papers agreeing to emigrate to Poland. It is difficult to establish the exact number of Poles expelled from Lviv, between 100,000 and 140,000.
From Belarus
editIn stark contrast to what took place in the Ukrainian SSR, the communist officials in the Belorussian SSR did not actively support deportation of Poles. Belorussian officials made it difficult for Polish activists to communicate with tuteishians - people who were undecided as to whether they considered themselves Polish or Belorussian.[19] Much of the rural population, which usually had no official documents of identity, were denied the right of repatriation on the basis that they did not have documents stating they were Polish citizens.[19] In what was described as the "fight for the people", Polish officials attempted to get as many people repatriated as possible, while the Belorussian officials tried to retain them, particularly the peasants, while deporting most of the Polish intelligentsia. It is estimated that about 150,000 to 250,000 people were deported from Belarus. Similar numbers were registered as Poles but forced by the Belorussian officials to remain. A similar number were denied registration as Poles in the Belorussian SSR.
From Lithuania
editThe Lithuanian repatriation suffered from numerous delays. Local Polish clergy was active agitating against leaving, and the underground press called those who had registered for repatriation traitors, hoping, that the post War Peace Conference would assign Vilnius region to Poland. After these hopes vanished, the number of people wanting to leave gradually increased.
Attitudes in the Lithuanian SSR were similar to those of the Belarusian officials. The Lithuanian communist party was dominated by a nationalist faction, which supported the removal of the Polish intelligentsia, particularly from the highly disputed Vilnius region.[20] The city of Vilnius (Polish - Wilno) itself is considered a historical capital of Lithuania, however in the early 20th century its population was around 60% Polish, 30% Jewish, with only about 2-3% self-declared Lithuanians. The rural Polish population was however seen as important for the economy, and an easy target for assimilation policies (Lithuanization).[19][20] The repatriation of Poles from Vilnius, on the other hand, was encouraged and facilitated; the result was a rapid depolonization and Lithuanization of the town.[20] Further, Lithuanian ideology declared that many of the individuals who declared themselves as Polish were in fact "polonized Lithuanians". Again, the rural population was denied the right to leave Lithuania due to their lack of official pre-war documentation of Polish citizenship.[19][20] Contrary to an agreement with Poland, many individuals were threatened with the repayment of debts or with arrests if they chose repatriation. Individuals connected to the Polish resistance (Armia Krajowa) and Polish Underground State) were persecuted by the Soviet occupier authorities. In the end, only about 50% of the registered 400,000 people were repatriated. Dovile Budryte estimates that about 150,000 people were repatriated.[21]
Lithuanian historians estimate, that about 10 percent of people who left for Poland were ethnic Lithuanians, looking for a way to escape the Soviet occupation and to flee to the West [citation needed].
Legality of the population transfers
editThe view of international law on population transfer underwent considerable evolution during the 20th century. Prior to World War II, a number of major population transfers were the result of bilateral treaties and had the support of international bodies such as the League of Nations.
The tide started to turn when the charter of the Nuremberg Trials of German Nazi leaders declared forced deportation of civilian populations during World War II to be both a war crime and a crime against humanity. This opinion was progressively adopted and refined through the remainder of the century. Underlying the change was the trend to also take into account the rights of the individual, thereby limiting the rights of nation-states to impose fiats which adversely affected them.
There is now little debate about the general legal status of involuntary population transfers:
- "Where population transfers used to be accepted as a means to settle ethnic conflict, today, forced population transfers are considered violations of international law." (Denver Journal of International Law and Policy, Spring 2001, p116).
No legal distinction is made between one-way and two-way transfers, since the rights of each individual are regarded as independent of the experience of others.
Thus, although the signatories to the Yalta and Potsdam Agreements and the expelling countries considered the expulsions to be legal under international law at the time, there are historians and scholars in international law and human rights who have revised their evaluation of the events and argue that the population transfer of Poles from Eastern Europe should be considered as episodes of ethnic cleansing, and thus a violation of human rights.
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ (in English) Jürgen Weber (2004). Germany, 1945-1990: A Parallel History. Budapest: Central European University Press. p. 2. ISBN 9639241709.
- ^ (in Polish) various authors (1999). Stanisław Ciesielski (ed.). Przesiedlenie ludności polskiej z Kresów Wschodnich do Polski 1944-1947. Warsaw: Neriton. p. 468. ISBN 83-86842-56-3.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ (in English) Z. R. Rudzikas (2002). Antonino Zichichi, Richard C. Ragaini (ed.). "Democracy and Mathematics in Lithuania". International Seminar on Nuclear War and Planetary Emergencies, 34th Session. World Scientific: 190. ISBN 9780300106701. Retrieved 2009-07-10.
- ^ (in English) Timothy D. Snyder (January 2005). "The Local World War". Sketches from a Secret War: A Polish Artist's Mission to Liberate Soviet Ukraine. New Haven, Connecticut2007: Yale University Press. pp. 190–193. ISBN 0300125992.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - ^ a b (in Polish) Józef Poklewski (1994). Polskie życie artystyczne w międzywojennym Wilnie. Toruń: Toruń University Press. p. 321. ISBN 83-231-0542-1.
- ^ (in English) Krystyna Kersten (1991). The establishment of Communist rule in Poland, 1943-1948. Berkeley: University of California Press. p. 535. ISBN 0520062191.
- ^ (in Polish) Krystyna Kersten (1974). Repatriacja ludności polskiej po II wojnie światowej: studium historyczne. Wrocław: Polish Academy of Sciences, Ossolineum. p. 277.
- ^ (in English) Bogumiła Lisocka-Jaegermann (2006). "Post-War Migrations in Poland". In Mirosława Czerny (ed.). Poland in the geographical centre of Europe. Hauppauge, New York: Nova Science Publishers. pp. 71–87. ISBN 1-59454-603-7.
- ^ (in Polish) Jan Czerniakiewicz (1992). Stalinowska depolonizacja Kresów Wschodnich II Rzeczpospolitej (Stalinist de-Polonization of the Eastern Borderlands of the 2nd Republic). Warsaw: Centre for Eastern Studies, Warsaw University. p. 20.
- ^ Alfred de Zayas, A Terrible Revenge, Palgrave/Macmillan, 2006
- ^ a b Matthew J. Gibney, Randall Hansen, Immigration and Asylum: From 1900 to the Present, 2005, pp.197,198, ISBN 1576077969, 9781576077962
- ^ a b Richard Overy (1996). The Penguin Historical Atlas of the Third Reich (1st ed.). Penguin Books (Non-Classics). p. 144. ISBN 0140513302.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Germangovwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Entsyklopedia Ukrainoznavstva — Paris-NY, 1970. Vol 6 p. 2224
- ^ Entsyklopedia Ukrainoznavstva Vol. 6, P.2224
- ^ Serhiychuk p. 7
- ^ Serhiychuk, p. 24
- ^ Serhiychuk, p. 16
- ^ a b c d Philipp Ther, Ana Siljak, Redrawing nations: ethnic cleansing in East-Central Europe, 1944-1948, Rowman & Littlefield, 2001, ISBN 0742510948, Google Print, p.141
- ^ a b c d Timothy Snyder, The Reconstruction of Nations: Poland, Ukraine, Lithuania, Belarus, 1569-1999, Yale University Press, 2004, ISBN 030010586X, Google Print, p.91-93
- ^ Dovile Budryte, Taming nationalism?: political community building in the post-Soviet Baltic States, Ashgate Publishing, Ltd., 2005, ISBN 075464281X, Google Print, p.147
References
edit- (in Ukrainian) Volodymyr Serhijchuk, Deportatsiya Poliakiv z Ukrainy -Kyiv, 1999 ISBN 966-7060-15-2
Further reading
edit- (in Polish) Stanisław Ciesielski et al., "Przesiedlenie ludności polskiej z Kresów Wschodnich do Polski 1944–1947. Wybór dokumentów", Wybór, opracowanie i redakcja dokumentów. Introduction by Włodzimierz Borodziej, Stanisław Ciesielski, Jerzy Kochanowski. Docouments collected by Włodzimierz Borodziej, Ingo Eser, Stanisław Jankowiak, Jerzy Kochanowski, Claudia Kraft, Witold Stankowski, Katrin Steffen; Wydawnictwo NERITON, Warszawa 2000
- (in Polish) Grzegorz Hryciuk, Przemiany narodowościowe i ludnościowe w Galicji Wschodniej i na Wołyniu w latach 1931–1948
Category:Aftermath of World War II
Category:Ethnic groups in Ukraine
Category:Forced migration
Category:History of Poland (1939–1945)
Category:History of Poland (1945–1989)
Category:History of Ukraine
Category:History of the Soviet Union and Soviet Russia
Category:Poland–Ukraine relations
Category:Poland – Soviet Union relations