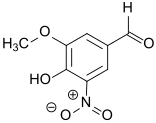
5-Nitrovanillin (4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-5-nitrobenzaldehyde) is a derivative of vanillin in which the hydrogen ortho- to the hydroxy group is substituted by a nitro group. Because it contains many reactive functional groups – in addition to the nitro group, a hydroxyl group, a methoxy group and an aldehyde group are present – 5-nitrovanillin is suitable as a starting material for the synthesis of phenethylamines, for coenzyme Q and for the inhibitors of catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT inhibitors) that are effective against Parkinson's disease.
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-5-nitrobenzaldehyde
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 1973746 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.026.940 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H7NO5 | |
| Molar mass | 197.14 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | yellow powder |
| Melting point | 172–175 °C (342–347 °F; 445–448 K) |
| Boiling point | 212.3 °C (414.1 °F; 485.4 K) |
| log P | 0.301 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Warning | |
| H315, H319 | |
| P264, P280, P302+P352, P305+P351+P338, P332+P313, P337+P313 | |
| Flash point | 97 °C (207 °F; 370 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Properties
edit5-Nitrovanillin is a yellow crystalline solid with a characteristic odor. It is sparingly soluble in water, readily soluble in alkali solutions on heating and in methanol. When recrystallized from acetic acid, the substance precipitates as pale yellow plate-like crystals, and from ethanol as needle-like crystals.[1]
Preparation
edit5-Nitrovanillin is obtained upon nitration of vanillin with concentrated nitric acid in glacial acetic acid with a 75% yield.[1]
With acetyl nitrate as the nitrating agent, yields of up to 88% are obtained in the presence of silica gel.[2]
Uses
edit5-Nitrovanillin was patented as a yellow hair dye in combination with other nitrobenzene dyes for consistent blonde to brown shades.[3]
Because of the low solubility of 5-nitrovanillin in water, the potassium salt, which is readily soluble in water, is used for methylation. It is reacted with dimethyl sulfate to form 3,4-dimethoxy-5-nitrobenzaldehyde (5-nitroveratraldehyde) in 91% yield.[1]
In early work on psychoactive phenethylamines,[1] 3,4-dimethoxy-5-nitrobenzaldehyde was condensed with nitromethane in a Knoevenagel reaction to give the corresponding nitrostyrene, which is reduced electrochemically to yield the corresponding β-phenylethylamine.
An important intermediate for the chemical synthesis of coenzyme Q is 2,3-dimethoxy-5-methyl-1,4-benzoquinone, which is accessible in a four-step synthesis from 5-nitrovanillin via 3,4-dimethoxy-5-nitrobenzaldehyde.[4] Demethylation of 5-nitrovanillin by ether cleavage using hydrobromic acid[5] or using lithium hydroxide and thiophenol in NMP[6] leads to 3,4-dihydroxy-5-nitrobenzaldehyde (DHNB), which is being discussed as an active ingredient for the treatment of hyperuricemia and gout.[7]
3,4-Dihydroxy-5-nitrobenzaldehyde (DHNB) has gained greater importance as a precursor for the synthesis of the COMT inhibitor entacapone for the treatment of Parkinson's disease.[8] A more recent patent application describes a synthetic route for the active ingredient opicapone, which has been approved in the EU since 2016, in which 5-nitrovanilline is initially reacted directly with hydroxylamine hydrochloride in DMSO to form the corresponding nitrile.[9]
The nitrile obtained reacts with a hydroxamic acid chloride to give a 3,5-disubstituted 1,2,4-oxadiazole as a further intermediate.
With hydrazides, the aldehyde 5-nitrovanillin forms hydrazones that can be cyclized with Chloramine-T to give substituted 1,3,4-oxadiazoles.[10]
References
edit- ^ a b c d Slotta KH, Szyszka G (1935-01-09). "Über β-Phenyl-äthylamine, IV. Mitteil.: Darstellung von β-[Amino-phenyl]-äthylaminen". Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft (A and B Series). 68 (1): 184–192. doi:10.1002/cber.19350680140. ISSN 0365-9488.
- ^ Rodrigues JA, de Oliveira Filho AP, Moran PJ, Custódio R (1999-05-28). "Regioselectivity of the nitration of phenol by acetyl nitrate adsorbed on silica gel". Tetrahedron. 55 (22): 6733–6738. doi:10.1016/S0040-4020(99)00320-8.
- ^ US patent 4668237, Grollier JF, Cotteret J, Rosenbaum G, "Dye composition containing 5-nitrovanillin and its use for dyeing keratinic fibres, and especially human hair", published 1987-05-26, assigned to L'Oreal SA
- ^ Sato K, Inoue S, Sato H (1972). "The Synthesis of 2,3-Dimethoxy-5-methyl- p -benzoquinone". Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan. 45 (11): 3455–3457. doi:10.1246/bcsj.45.3455. ISSN 0009-2673.
- ^ US Expired 4963590, Backstrom RJ, Heinola KE, Honkanen EJ, Kaakkola SK, Kairisalo PJ, Linden IB, Mannisto PT, Nissinen EA, Pohto P, Pippuri AK, Pystynen PJ, "Pharmacologically active compounds, methods for the preparation thereof and compositions containing the same", published 1990-10-16, assigned to Orion Oyj
- ^ EP Expired 0589948, Honkanen E, Lindholm S, "Method for the preparation of 3,4-dihydroxy-5-nitrobenzaldehyde", published 1994-04-06, assigned to Orion Oyj
- ^ Lü JM, Yao Q, Chen C (November 2013). "3,4-Dihydroxy-5-nitrobenzaldehyde (DHNB) is a potent inhibitor of xanthine oxidase: a potential therapeutic agent for treatment of hyperuricemia and gout". Biochemical Pharmacology. 86 (9): 1328–1337. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2013.08.011. PMC 3816736. PMID 23994369.
- ^ El-Shorbagi AN, Chaudhary S, Alshemali KA, Alabdulrazzaq RF, Alqahtani FY (2020-10-04). "A comprehensive review on management of Parkinson's disease, inclusive of drug discovery and pharmacological approaches". Journal of Applied Pharmaceutical Science. 10 (10): 130–150. doi:10.7324/JAPS.2020.1010015. S2CID 243243325.
- ^ EP Withdrawn 3421456, Nabold CF, Aebersold C, Grieco G, Aeschbacher RG, "New route of synthesis for Opicapone", published 2019-01-02, assigned to Azad Pharmaceutical Ingredients AG
- ^ Malghe YS, Thorat VV, Chowdhary AS, Bobade AS (2015). "Synthesis, characterization and biological activities of new bis-1,3,4-oxadiazoles". Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research. 7 (6): 392–398. ISSN 0975-7384.