Declarations of war during World War II
This is a timeline of declarations of war during World War II.
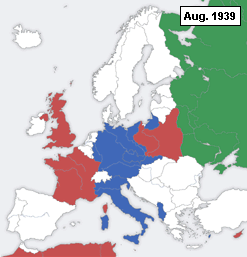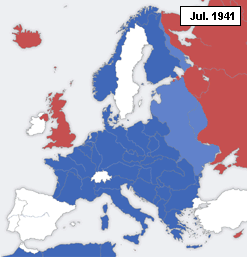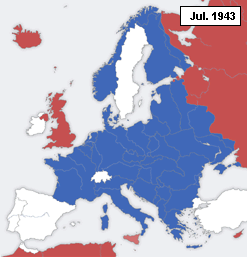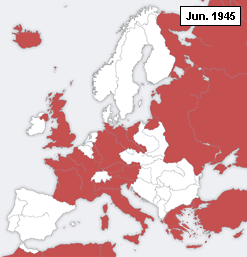
A declaration of war is a formal act by which one nation goes to war against another. The declaration is usually the act of delivering a performative speech or the presentation of a signed document by an authorized party of a national government in order to create a state of war between two or more sovereign states. The official international protocol for declaring war was defined in The Hague Peace Conference of 1907 (or Hague II).[1] For the diplomatic maneuvering behind these events, which led to hostilities between nations during World War II, see Diplomatic history of World War II.
List of war declarations
editBelow is a table showing the outbreak of wars between nations which occurred during World War II. Indicated are the dates (during the immediate build-up to, or during the course of, World War II), from which a de facto state of war existed between nations. The table shows both the "Initiator Nation(s)" and the nation at which the aggression was aimed, or "Targeted Nation(s)". Events listed include those in which there were simple diplomatic breaking of relations that did not involve any physical attack, as well as those involving overt declarations or acts of aggression. In rare cases, war between two nations occurred twice, with an intermittent period of peace. The list here does not include peace treaties or periods of any armistice.
| Key to type (fourth column): | |
| A | Attack without prior, formal declaration of war; |
| C | Declaration and/or attack without standard, formal procedure, sometimes preceded by a casus belli thus fait accompli; |
| U | State of war arrived at through use of ultimatum; |
| W | Formal declaration of war made. |
| Date | Initiator nation(s) | Targeted nation(s) | Type | Notes/comments | Document/event |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1939-09-01 | Germany | Poland | A | German attack began at 4:44 a.m., Berlin and Warsaw time.[2][better source needed][3][4] Germany claimed that the attack was defensive, citing the Gleiwitz incident, which was actually a false flag attack.[5] | Invasion |
| 1939-09-01 | Slovakia | Poland | A | Invasion | |
| 1939-09-03 | United Kingdom Australia New Zealand India Tonga Transjordan |
Germany | U[3][6] | At 11:15 a.m. London time,[7] British PM, Neville Chamberlain publicly delivered his Ultimatum Speech.[a][6][8] As the Statute of Westminster 1931 was not yet ratified by the parliaments of Australia and New Zealand, the British declaration of war on Germany also applied to those dominions. Tonga was not a British dominion, instead, as part of the British Commonwealth (a protected state of the UK and the British Empire) declared war separately, alongside Britain (since it administers their foreign affairs).[9] | United Kingdom declaration |
| 1939-09-03 | France | Germany | U | The French ultimatum to Germany expired a few hours after the British ultimatum, at 17:00. | French declaration |
| 1939-09-04 | Nepal | Germany | W | ||
| 1939-09-06 | South Africa | Germany | W[3][6] | Declaration | |
| 1939-09-10 | Bahrain Canada Oman |
Germany | W[3][6] | Canada's declaration several days after that of the United Kingdom is seen as a watershed moment in Canadian home rule and sovereignty.
As for Bahrain, given its status as a protected state of the United Kingdom, it was technically at war as of Britain's declaration, this is an acknowledgement of the declaration of war by Britain (due to coercion by an advisor), Oman, under British influence, is coerced to participate in the war effort |
Declaration |
| 1939-09-17 | Soviet Union | Poland | A[3][6] | Invasion | |
| 1939-11-09 | Kuwait | Germany | W | Kuwaiti Declaration of War | |
| 1939-11-30 | Soviet Union | Finland | A[3][6] | Invasion | |
| 1940-04-09 | Germany | Denmark Norway |
A[3] | Invasion of Denmark Invasion of Norway | |
| 1940-04-12 | United Kingdom | Faroe Islands | A[6] | Invasion | |
| 1940-05-10 | Germany | Belgium Netherlands |
A/W[3][6] | Date of the German offensive in the West, W from Belgium and the Netherlands.[10] | |
| 1940-05-10 | Germany | Luxembourg | A[6] | Luxembourg | |
| 1940-05-10 | United Kingdom | Iceland | A | Invasion | |
| 1940-06-10 | Italy | France United Kingdom |
W[3][6] | France and the UK | |
| 1940-06-10 | Canada | Italy | W[3] | Declaration | |
| 1940-06-11 | South Africa Australia New Zealand France |
Italy | W[3] | ||
| 1940-07-03 | United Kingdom | Vichy France | A | Vichy France cuts off diplomatic relations with the United Kingdom on 8 July 1940. | Attack |
| 1940-09-09 | Italy | Egypt | A | Egypt never formally declared war on Italy. | Invasion |
| 1940-09-22 | Japan | Vichy France | A | Japanese troops occupy French Indochina | Invasion |
| 1940-09-23 | Free France United Kingdom Australia |
Vichy France | A | Invasion | |
| 1940-10-?? | Thailand | Vichy France | A | Franco-Thai War | |
| 1940-10-28 | Italy | Greece | U[6] | Italy invades Greece | Invasion |
| 1940-11-23 | Belgium (in-exile) | Italy | W[11] | Declaration | |
| 1941-02-05 | Free France | Italy | A | Invasion | |
| 1941-04-06 | Germany | Greece | W[3][6] | Invasion | |
| 1941-04-06 | Germany Italy |
Yugoslavia | A[3][6] | Invasion | |
| 1941-04-07 | Yugoslavia | Hungary | A[12] | After the German invasion, bombing of Hungarian locations | Invasion |
| 1941-04-14 | Germany | Egypt | A | Egypt did not formally declare war until 1945. | Invasion |
| 1941-05-02 | United Kingdom | Iraq | A | Invasion | |
| 1941-06-08 | Free France | Germany | A | [citation needed] | Invasion |
| 1941-06-22 | Germany Italy |
Soviet Union | W[6] | A timed declaration of war was given by Germany at the time of the attack[13] | Invasion |
| 1941-06-22/24 | Romania | Soviet Union | A | On June 22, Romanian leader Ion Antonescu declared a "holy war" to reclaim ancestral lands and against Bolshevism in an appeal to the nation.[14] The Romanian army began limited military operations. On June 24, Romania officially declared war on the Soviet Union.[14] | |
| 1941-06-22 | Tuva |
Germany | W | Tuva was a client state of the Soviet Union. Part of the USSR from 1944. | |
| 1941-06-24 | Bulgaria | Greece Yugoslavia |
A[6] | Bulgaria declares war on Greece and Yugoslavia. | |
| 1941-06-25 | Finland | Soviet Union | W | After the bombing of several Finnish locations, Finland recognized a state of war with the Soviet Union; third war between these nations. | Continuation War |
| 1941-06-27 | Hungary | Soviet Union | C[12] | After the bombing of several Hungarian locations, the Hungarian military concluded a Soviet attack, the Government had decided the two countries were already belligerent, without the consent of the Parliament, in absence of the Regent | Invasion |
| 1941-08-25 | Soviet Union United Kingdom Australia |
Iran | A | Invasion | |
| 1941-12-05 | United Kingdom India |
Finland Romania Hungary |
W[15] | Declaration | |
| 1941-12-06 | Finland Romania |
United Kingdom | W[6] | Declaration | |
| 1941-12-07 | United Kingdom | Hungary | W[16] | UK declaration of war from 1941-12-05 entered into force on 1941-12-07 1 minute after midnight | Declaration |
| 1941-12-07 | Japan | United States United Kingdom Thailand |
A | A formal message breaking off diplomatic talks was sent before but arrived after the attacks began, but this was not a declaration of war.[17] See Attack on Pearl Harbor § Japanese declaration of war |
Declaration published after: |
| 1941-12-07 | Canada Australia New Zealand |
Finland Romania Hungary |
W[6] | Declaration | |
| 1941-12-07 | Canada Panama Yugoslavia (in-exile) |
Japan | W[6] | Declaration | |
| 1941-12-08 | United Kingdom United States Canada Australia Costa Rica Dominican Republic El Salvador Free France Guatemala Greece (in-exile) |
Japan | W[6] | After the attack on Pearl Harbor, many countries declared a formal state of war on Japan |
British declaration
|
| 1941-12-08 | South Africa | Japan Finland Romania Hungary |
W[6] | South African declaration | |
| 1941-12-08 | Mongolia | Germany | W[citation needed] | ||
| 1941-12-08 | Manchukuo | United States | W[6] | ||
| 1941-12-08 | Japan | British Malaya | A | Invasion of Malaya | |
| 1941-12-09 | Cuba | Japan | W[6] | ||
| 1941-12-09 | China | Germany Italy Japan |
W[6] | China and Japan had been at undeclared war since 1937 | Second Sino-Japanese war |
| 1941-12-11 | Germany Italy |
United States | W[3][6] | ||
| 1941-12-11 | United States Cuba Costa Rica Dominican Republic Guatemala Nicaragua |
Germany Italy |
W[6] | Germany | |
| 1941-12-11 | Netherlands (in-exile) | Italy | W[6] | Declaration | |
| 1941-12-11 | Poland (in-exile) | Japan | W[3] | Japan rejected declaration of War. Prime Minister Hideki Tōjō's answer was: "We don't accept the Polish declaration of war. The Poles, fighting for their freedom, declared war under the British pressure"[citation needed]. | |
| 1941-12-12 | Romania Bulgaria Slovakia |
United States United Kingdom |
W[6] | ||
| 1941-12-12 | Haiti El Salvador Panama |
Germany Italy |
W[6] | Declaration | |
| 1941-12-12 | Australia Netherlands |
Portugal | A | Portugal maintained neutrality throughout World War II. | |
| 1941-12-13 | United Kingdom New Zealand South Africa |
Bulgaria | W[6] | ||
| 1941-12-13 | Honduras | Germany Italy |
W[6] | Declaration | |
| 1941-12-13 | Italy | Cuba Guatemala |
W[6] | Declaration | |
| 1941-12-14 | Independent State of Croatia | United States United Kingdom |
W[6] | Declaration | |
| 1941-12-15 | Hungary | United States | C[18] | The Prime Minister informed the U.S. ambassador without approval of the Parliament and the Regent, but initially denied it would mean "war" in fact, however two days later he declared it means the two countries became belligerent. As the ambassador refused to accept the verbal form of this act, the next day the Prime Minister in written reinforced it. | Declaration |
| 1941-12-16 | Czechoslovakia (in-exile) | Germany Italy Finland Romania Hungary Japan Bulgaria Independent State of Croatia Slovakia |
W[6] | Czechoslovakia declares war on all countries at war with the United States of America, Great Britain and the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. | Declaration |
| 1941-12-16 | Japan | Sarawak North Borneo Brunei |
A | Invasion | |
| 1941-12-17 | Albania | United States | W | Declaration | |
| 1941-12-19 | Nicaragua | Romania Hungary Bulgaria |
W[6] | Declaration | |
| 1941-12-19 | Romania | Nicaragua | W[19] | Out of the Axis countries only Romania reciprocated, declaring war on Nicaragua on the same day | Declaration |
| 1941-12-20 | Belgium (in-exile) | Japan | W | Declaration | |
| 1941-12-24 | Haiti | Romania Hungary Bulgaria |
W[6] | Declaration | |
| 1941-12-24 | Romania | Haiti | W[20] | Out of the Axis countries only Romania reciprocated, declaring war on Haiti on the same day | Declaration |
| 1941-12-25 | Greece (in-exile) | W | Declaration | ||
| 1942-01-01 | United Nations | Axis Powers | W | Declared during Arcadia Conference | Declaration |
| 1942-01-06 | Australia | Bulgaria | W | Declaration | |
| 1942-01-25 | Thailand | United Kingdom United States |
A | Declaration | |
| 1942-01-25 | United Kingdom New Zealand South Africa |
Thailand | W | ||
| 1942-02-19 | Japan | Portugal | A | Portugal maintained neutrality throughout World War II. | Invasion |
| 1942-03-02 | Australia | Thailand | W[6] | ||
| 1942-05-05 | South Africa Netherlands (in-exile) Poland |
Vichy France | A | Invasion | |
| 1942-05-05 | United Kingdom Northern Rhodesia Southern Rhodesia South Africa Tanganyika Belgian Congo Poland (in-exile) |
Vichy France Japan |
A | Invasion | |
| 1942-05-22 | Mexico | Germany Italy Japan |
W[6] | Declaration | |
| 1942-06-05 | United States | Hungary Romania Bulgaria |
W[12] | United States Declaration of War upon Hungary United States Declaration of War upon Romania United States declaration of war upon Bulgaria | |
| 1942-06-13 | Iroquois Confederacy | Germany Italy Japan |
W | Having never made peace with Germany from the First World War, Haudenosaunee became the only Native American state to officially declare war on the Axis powers separately from the United States (other Native American nations issued declarations or declared war de facto alongside the United States as their tribal citizens enlisted in the Armed Forces[21]). | |
| 1942-08-22 | Brazil | Germany Italy |
W | Declaration | |
| 1942-11-08 | United States Canada |
Vichy France | A | Invasion | |
| 1942-11-10 | Germany Italy |
Vichy France | A | Invasion | |
| 1942-11-12 | Germany | Tunisia | A | German invasion via airlifting several divisions in reaction to Operation Torch, swiftly occupying Tunis and the eastern part of the country, and capturing the western portions after French Tunisian resistance before the allies reached the Tunisian border. In the resulting Tunisian campaign, the Allies finally defeated the Axis forces in Africa. | Invasion |
| 1942-12-14 | Ethiopia | Germany Italy Japan |
W | On 3 October 1935, Italy invaded Ethiopia without a formal declaration of war. In response to the Italian invasion, Ethiopia declared war on Italy. Most of Ethiopia was occupied by Italy in 1936, however parts of Ethiopia remained under the control of the Ethiopian Patriots Movement, which begun its guerrilla war against the occupying Italian forces the day Addis Ababa fell in May 1936. In May 1941, Addis Ababa was liberated by the Gideon Force, restoring sovereignty to Ethiopia. | Second Italo-Ethiopian War |
| 1943-01-09 | Reorganized National Government of China | United States United Kingdom |
W[6] | Declaration | |
| 1943-01-17 | Iraq | Germany Italy Japan |
W[6] | Declaration | |
| 1943-01-20 | Chile | Germany Italy |
W | Chile cuts off diplomatic relations with the German Reich and the Kingdom of Italy on 20 January 1943. | Declaration |
| 1943-04-07 | Bolivia | Germany Italy Japan Other axis nations |
W | Bolivia officially joined the Allies on 7 April 1943. Shortly after war was declared, the President, Enrique Peñaranda, was overthrown in a coup. Bolivian mines supplied needed tin to the Allies, but no troops or warplanes were sent overseas. Bolivians remained confident their geographic isolation would protect them from the war. | Declaration |
| 1943-08-01 | State of Burma | United States United Kingdom |
W[6] | Declaration | |
| 1943-09-08 | Germany | Italy Albania |
A | After Italy's capitulation to the Allied powers, Germany swiftly invaded both Italy and Italian-controlled territories (such as Albania, an Italian satellite state) to preempt a possible Allied intervention. | Operation Achse, German occupation of Albania |
| 1943-09-09 | Iran | Germany | W | Declaration | |
| 1943-10-13 | Italy | Germany | W[3] | Italy had changed sides after the fall of Mussolini. The Declaration of War was given by Pietro Badoglio to the German ambassador in Madrid.[3] | Declaration |
| 1943-11-26 | Colombia | Germany | W | See Colombia during World War II | Declaration |
| 1944-01-17 | Free France | Italian Social Republic | A | Invasion | |
| 1944-01-27 | Liberia | Germany Japan |
W | Declaration | |
| 1944-06-06 | France | Germany | A | Invasion | |
| 1944-07-25 | France | Japan | A | Invasion | |
| 1944-08-25 | Romania | Germany | W[6] | Romania switched sides | Declaration |
| 1944-09-05 | Soviet Union | Bulgaria | W | Declaration | |
| 1944-09-07 | Hungary | Romania | W[6] | Declaration | |
| 1944-09-07 | Romania | Hungary | W[6] | Declaration | |
| 1944-09-08 | Bulgaria | Germany | W [citation needed] | Bulgaria switched sides | Declaration |
| 1944-09-15 | Germany | Finland | A | Lapland War | |
| 1944-09-21 | San Marino | Germany Italian Social Republic |
W[22] | Battle of San Marino | |
| 1944-09-23 | Second Philippine Republic | United States United Kingdom |
W[23] | Philippine declaration | |
| 1944-12-28 | Hungary | Germany | W[24] | The Provisional National Government, which had been established under Soviet protection in the city of Debrecen, declared war on Germany. The German-backed Arrow Cross regime was still at war with the Soviet Union and its troops were still in action. As it had not switched sides of its own accord, Hungary was never recognized as having defected to the Allies. | Hungarian declaration |
| 1945-02-02 | Ecuador | Germany Japan |
W | Ecuadorian declaration | |
| 1945-02-07 | Paraguay | Germany Japan |
W | Paraguayan declaration | |
| 1945-02-12 | Peru | Germany Japan |
W[6] | Declaration | |
| 1945-02-15 | Venezuela Uruguay |
Germany Japan |
W | ||
| 1945-02-23 | Turkey | Germany Japan |
W | Declaration | |
| 1945-02-24 | Egypt | Germany Japan |
W | Declaration | |
| 1945-02-26 | Syria Lebanon |
Germany Japan |
W | Declaration | |
| 1945-02-28 | Saudi Arabia | Germany | W | Declaration | |
| 1945-03-01 | Saudi Arabia | Japan | W[6] | Declaration | |
| 1945-03-01 | Iran | Japan | W[6] | Iran declares war on Japan retroactive to the previous day (Feb. 28, 1945) | Declaration |
| 1945-03-03 | Finland | Germany | W | Finland declares war on Germany retroactive to Sept. 15, 1944 following terms of 1944 Moscow Armistice | Lapland War |
| 1945-03-07 | Romania | Japan | W[6] | Declaration | |
| 1945-03-27 | Argentina | Germany Japan |
W | ||
| 1945-04-11 | Chile | Japan | W | Declaration | |
| 1945-06-07 | Brazil | Japan | W[6] | Declaration | |
| 1945-07-09 | Norway (in-exile) | Japan | W | Norwegian government-in-exile announces that it had declared war on Japan on December 7, 1941 | Declaration[25] |
| 1945-07-14 | Italy | Japan | W | Declaration | |
| 1945-08-08 | Soviet Union | Japan | W[3] | Last outbreak of war during the entire Second World War. | Soviet–Japanese War |
| 1945-08-10 | Mongolia | Japan | W[26] | W (de jure) A (de facto 1945-08-09) War declared 24 hours after crossing the border with Soviet troops |
Gallery
edit-
German ambassador, Hans-Adolf von Moltke, Polish leader Józef Piłsudski, German propaganda minister Joseph Goebbels and Józef Beck, Polish Foreign minister meeting in Warsaw on June 15, 1934, five months after signing the Polish-German Non-Aggression Pact.
-
British Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain, landing at Heston aerodrome on 30 September 1938 after his meeting with Hitler at Munich. In his hand he holds the peace agreement between Britain and Germany.
-
Common parade of German Wehrmacht and Soviet Red Army on September 23, 1939 in Brest, Eastern Poland at the end of the Poland Campaign. In the center is Major General Heinz Guderian; and on the right is Brigadier General Semyon Krivoshein.
-
Counsellor of state J.K. Paasikivi and his team arriving from Moscow for the first round of negotiations on 16 October 1939. From left, minister Aarno Yrjö-Koskinen, J.K. Paasikivi, chief of staff Johan Nykopp and colonel Aladár Paasonen.
-
German paratroopers taking the Greek island of Crete, May 1941.
-
Photograph from a Japanese plane of Battleship Row at the beginning of the surprise Attack on Pearl Harbor. The explosion in the center is a torpedo strike on the USS Oklahoma. Two attacking Japanese planes can be seen: one over the USS Neosho and one over the Naval Yard.
See also
editNotes
edit- ^ Included in the speech: "...This morning, the British Ambassador in Berlin handed the German Government a final note, stating that unless we heard from them by 11 O'clock that they were prepared at once to withdraw their troops from Poland a state of war would exist between us. I have to tell you now that no such undertaking has been received and that consequently this country is at war with Germany..."
References
edit- ^ On the Opening of Hostilities; 1907; Yale Law School Library; retrieved March 2014.
- ^ "Germans invade Poland". History.com. Retrieved 1 December 2019.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r "2194 Days of War"; (1977); Salmaggi, C. & Pallasvini, A.; ISBN 91-582-0426-1; per tables included. [Italian; American]
- ^ "BBC ON THIS DAY | 1". news.bbc.co.uk.
- ^ Polak-Springer, Peter (2015). Recovered Territory: A German-Polish Conflict over Land and Culture, 1919-1989. Berghahn Books. p. 1. ISBN 978-1-78238-888-3.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq ar as at au av Doody, Richard, "Chronology of World War II Diplomacy 1939 - 1945", World at War, archived from the original on May 5, 2016
- ^ Mann, Andrea. "September 3, 1939: Britain declares war on Germany after Hitler's troops invade Poland". BT.com. Retrieved 1 December 2019.
- ^ 1939: Britain and France declare war on Germany, BBC
- ^ a b "The United States Invasion of Tonga In 1942". Archived from the original on 25 February 2005. Retrieved 23 July 2021.
- ^ Swedish Encyklopedia; "Bonniers Lexikon" (Vol. 1); (c.1960s); table in article by Andra Världskriget: The Second World War; Pp. 461-462.
- ^ Veranneman, Jean-Michel (30 September 2014). Belgium in WWII. Pen and Sword. ISBN 9781783376070.
- ^ a b c "Táblázat az egyes államok hadiállapotba kerüléséről". arcanum.hu. Arcanum Adatbázis Kft.
- ^ "The Rise and Fall of the Third Reich"; Shirer, William L
- ^ a b Boog et al. 1998, p. 408.
- ^ "BBC - WW2 People's War - Timeline". www.bbc.co.uk.
- ^ "Hadiállapot Magyarország és Nagy-Britannia között". arcanum.hu. Arcanum Adatbázis Kft.
- ^ Prange, Goldstein & Dillon 1981, p. 485. "[The] fourteenth part was not a formal declaration of war. It did not even rupture diplomatic relations. It merely broke off the discussions."
- ^ Draveczki-Ury, Ádám (11 December 2011). "Hetven éve történt: hadüzenet az Egyesült Államoknak". honvedelem.hu. Honvédelmi Minisztérium. Archived from the original on 29 September 2019. Retrieved 23 April 2020.
- ^ Dr Erik Goldstein, Routledge, 2005, Wars and Peace Treaties: 1816 to 1991, p. 218
- ^ Dr Erik Goldstein, Routledge, 2005, Wars and Peace Treaties: 1816 to 1991, p. 217
- ^ Morgan, Thomas D. (Fall 1995). "Native Americans in World War II". Army History: The Professional Bulletin of Army History (35): 22–27. Archived from the original on 2017-03-27. Retrieved 2013-04-17 – via www.shsu.edu.
- ^ "A Timeline of Diplomatic Ruptures, Unannounced Invasions, Declarations of War, Armistices and Surrenders". WorldAtWar. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
- ^ "1. United States/Philippines (1898-1946)".
- ^ "Az új államiság kiépítése Magyarországon | Magyarok a II. világháborúban | Kézikönyvtár". www.arcanum.hu. Retrieved 2021-04-01.
- ^ "Norway Declares War on Japan". Canberra Times (Act : 1926 - 1995). 9 July 1945. p. 1.
- ^ Christopher P. Atwood (1999), "Sino-Soviet Diplomacy and the Second Partition of Mongolia, 1945–1946", Mongolia in the Twentieth Century: Landlocked Cosmopolitan, Bruce A. Elleman and Stephen Kotkin, eds. (Armonk, NY: M. E. Sharpe), 147.
Bibliography
edit- Boog, Horst; Förster, Jürgen; Hoffmann, Joachim; Klink, Ernst; Müller, Rolf-Dieter; Ueberschär, Gerd R. (1998). Germany and the Second World War. Vol. 4. Oxford: Clarendon Press.
- Prange, Gordon William; Goldstein, Donald M.; Dillon, Katherine V. (1981). At Dawn We Slept: The Untold Story of Pearl Harbor. McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0-07-050669-8.