This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
Erzgebirgisch (Standard German pronunciation: [ˈeːɐ̯tsɡəˌbɪʁɡɪʃ]; Erzgebirgisch: Arzgebirgsch[1]) is a (East) Central German dialect, spoken mainly in the central Ore Mountains in Saxony. It has received relatively little academic attention. Due to the high mobility of the population and the resulting contact with Upper Saxon, the high emigration rate and its low mutual intelligibility with other dialects, the number of speakers is decreasing.[not verified in body]
| Erzgebirgisch | |
|---|---|
| Arzgebirgsch | |
| Pronunciation | [ˈaːɰtsɡ̊əˌb̥ɛːɰjɡ̊ʃ] |
| Native to | Germany |
| Region | Saxony, Lower Saxony |
Early forms | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | – |
| Glottolog | oste1245 Osterzgebirgischwest2915 Westerzgebirgisch |
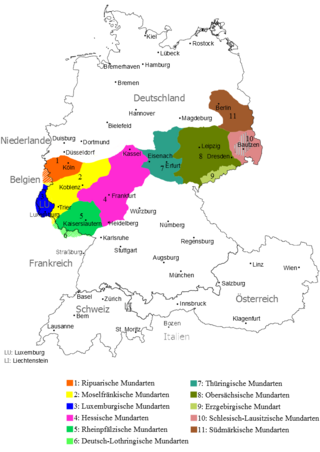 Central German dialects after 1945 and the expulsions of the Germans
Erzgebirgisch (9) | |
Language area and history
editAs the following sections will show, Erzgebirgisch is very close to Upper Saxon but also has commonalities with Upper German dialects.
As of today, the Erzgebirgisch area comprises roughly the districts of Mittweida (southern area), Stollberg, Central Ore Mountain District, Annaberg-Buchholz, Freiberg (South) and Aue-Schwarzenberg. Some more speakers live in the town of Lichtenstein, in the Chemnitzer Land district.
Another community live in the Upper Harz Mountains in the Clausthal-Zellerfeld region (Lower Saxony). Their ancestors were miners and emigrated in the 16th century. Here it is referred to as the Upper Harz dialect.
Up to 1929, Erzgebirgisch was also spoken in other parts of Mittweida and Freiberg, in Chemnitz, Zwickau and in the extreme West of the Weißeritzkreis, but these areas are now dominated by Thuringian–Upper Saxon dialects.
Until 1945, the bordering Sudetenland also harbored some Erzgebirgisch speakers, namely in the Kaaden-Duppau area, in whose dialect an anthology of words, proverbs and anecdotes was published (see references). After World War II these speakers had to leave Czechoslovakia and settled down all over the FRG and the GDR. This meant that dialect usage was reduced to the family homes, entailing a shift to the local varieties of their new home towns.
No official attempts to create an orthography have been made, nevertheless there are countless short stories, poems and songs written in Erzgebirgisch. The Sächsischer Heimatverein guidelines to writing in Erzgebirgisch were established in 1937, but are by and large not respected by the majority of authors. This means that linguistic analysis of this dialect has to be done in a field work setting with native speakers. An additional threat to Erzgebirgisch is the popular misconception that Erzgebirgisch was a hillbilly variety of Saxonian, which is an issue for conservation efforts.
Erzgebirgisch is classified as a Central German dialect in linguistics, but also includes Upper German features.
Linguistic features
editMany of these languages show a tendency to substitute the German verbal prefix er- by der- (Erzg. and Bair.) or ver- (Bair. and Swabian). (e.g. westerzgeb. derschloong [tɔɰˈʃloːŋ] German erschlagen 'to slaughter'; derzeeln [tɔɰˈtseːln] German erzählen 'to tell, to narrate').
Extended use of the particle fei is typical for Upper German and popular in Erzgebirgisch.
Furthermore, German [o/ɔ] corresponds to [u/ʊ] in the mentioned varieties (e.g. westerzgeb. huus [huːs] Hose), and German [a] corresponds to [A].[clarification needed]
An [n] in the coda, following a long vowel, is regularly deleted in Erzgebirgisch (e.g. Lichtenst. Huuschdee [huːʂʈeː] Hohenstein. Rarely, this is also found with monosyllabic words with a short vowel, which undergo compensatory vowel lengthening in the process (e.g. Lichtenst. màà [mʌː] Mann 'man').
Another typical feature of Upper German is the apocope of schwa and /ɪ/ (e.g. Lichtenst. Reedlz [ɣeːtˡl̩ts] Rödlitz)
The following table illustrates the similarities between Erzgebirgisch and Upper German dialects. Thuringian/Upper Saxon is listed as a control parameter. Areas marked with a tick means that the feature is present in most subdialects, whereas areas marked as 'partial' are only found in border areas.
| Feature | Erzgebirgisch | East Franconian | Bavarian-Austrian | Alemannic | Thuringian |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rendering of er- as der-/ver- | |||||
| Use of fei | |||||
| Pronunciation of [o/ɔ] as [u/ʊ] | Partial | ||||
| N-apocope | |||||
| Schwa-apocope | Partial | ||||
| Convergence of ch and sch | Partial |
Subdialects
editEastern Erzgebirgisch dialects indicate negation with ni(ch) [nɪ(ç)] whereas nèt [nɛt] is used in the West. However, this subdialectal boundary is not clearly demarcated. Thus, both forms are found in the town of Lichtenstein, which lies on the northwestern dialect boundary (although ni is perhaps more common).
In both Eastern Erzgebirgisch and in the Lichtenstein dialect, word-initial clusters ⟨kl/gl⟩ and ⟨kn/gn⟩ in Standard German as realized as ⟨tl⟩ and ⟨tn⟩ respectively (e.g. dlee [tˡleː] klein 'small'; dnuchng [ˈtⁿnʊxŋ̍] Knochen 'bone').
It is not possible to include the Upper Harz varieties in either of these groups. Furthermore, there is a strong influence from the neighbouring non-Erzgebirgisch dialects in the region bordering Meißenisch, which makes subclassification cumbersome.
Through the summarizing of these findings, four dialects can be listed:
| Dialect | Present area | Historic area |
|---|---|---|
| Eastern Erzgebirgisch | Mittlerer Erzgebirgskreis, districts of Annaberg (northern half), Mittweida (south), Freiberg (south) | districts of Freiberg (northwest), Mittweida (west), Dippoldiswalde (western fringe), City of Chemnitz, Sudetenland (around Katharinaberg) |
| Western Erzgebirgisch | Districts of Aue-Schwarzenberg, Annaberg (southern half) | Sudetenland (triangle from Graslitz through Schlaggenwalde to Pressnitz) |
| Northern Erzgebirgisch | Rural districts of Chemnitzer Land (Region Lichtenstein), Stollberg | City and Rural District of Zwickau |
| Upper Harzisch | Clausthal-Zellerfeld Region and Sankt Andreasberg (Lower Saxony) |
Phonology
editAs mentioned above, there is no unified orthography. In order to render the language data close to their actual pronunciation, the following conventions have been established:
Consonants
editThe rendering of the consonants follows the notation commonly used for Bavarian. The following table lists the phonemes of the most important Erzgebirgisch dialects, with the IPA value and the corresponding character used in this article.
| Labial | Alveolar | Postalveolar/ Retroflex |
Palatal | Velar | Uvular | Glottal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stop | aspirated | kʰ ⟨k⟩ | ||||||
| unaspirated | p ⟨b⟩ | t ⟨d⟩ | k ⟨g⟩ | |||||
| Affricate | pf ⟨pf⟩ | ts ⟨z⟩ | tʃ / tʂ ⟨tsch⟩ | |||||
| Fricative | voiceless | f ⟨f⟩ | s ⟨s⟩ | ʃ/ʂ ⟨sch⟩ | ç ⟨ch⟩ | x ⟨ch⟩ | χ ⟨ch⟩ | h ⟨h⟩ |
| voiced | v ⟨w⟩ | ɣ ⟨r⟩ | ||||||
| Nasal | m ⟨m⟩ | n ⟨n⟩ | ŋ ⟨ng⟩ | |||||
| Lateral | l ⟨l⟩ | |||||||
| Approximant | j ⟨j⟩ | ɰ ⟨r⟩ | ||||||
- No subdialect shows phonemic contrast between postalveolar [tʃ, ʃ]) and retroflex [tʂ, ʂ]; they have one or the other.
- An important sound change in Erzgebirgisch is found with respect to /r/. When /r/ precedes a velar consonant, a [j] is inserted in between, as an example, Baarg (German Berg 'mountain') is pronounced [paːɰjk]. Since this phonological process is completely regular, it is not reflected in orthography.
- [ɰ] is normally realized as a velarization of the preceding vowel. However, for the sake of clarity, this article will use [ɰ] throughout.
Vowels
editThe writing of the vowels presented here follows in part the official Schwyzertütsch orthography. The orthographic representation of a vowel follows after the IPA characters, if different.
| Front | Central | Back | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| unrounded | rounded | |||
| Close | i ⟨i⟩ | u ⟨u⟩ | ||
| Near-close | ɪ ⟨i⟩ | ʊ ⟨u⟩ | ||
| (Close-)mid | e ⟨e⟩ | ə ⟨e⟩ | o ⟨o⟩ | |
| Open-mid | ɛ ⟨è⟩ | ʌ ⟨à⟩ | ɔ ⟨e/o⟩ | |
| (Near-)open | æ~a ⟨a⟩ | |||
- No subdialect has both [a] or [æ].
- /ə/ followed by ⟨r⟩ is pronounced as [ɔ], but still written as ⟨e⟩.
- The close back vowels [u, ʊ] are often rather unrounded.
- Vowel length is indicated by doubling the vowel sign in writing: ⟨aa⟩, ⟨àà⟩, ⟨ee⟩, ⟨èè⟩, ⟨ii⟩, ⟨oo⟩, ⟨uu⟩.
- All vowels (with the exception of ⟨a⟩ and /ə/) are angbr, i.e. that the back vowels ⟨à⟩, ⟨o⟩, ⟨u⟩ are more front, and the front vowels ⟨ee⟩, ⟨è⟩ und ⟨i⟩ more back than in Standard German.
- Short vowels preceding a stressed syllable are reduced to a schwa (e.g. gremàdig [kxəˈmʌtɪk] Grammatik 'grammar').
- A short vowel preceding a r is lengthened (e.g. Aarzgebèèrgsch).
- In dialects spoken at higher altitudes, ⟨àà⟩ is often realized like ⟨oo⟩.
- The pronunciation as ⟨àà⟩ is the default case for closed syllables. This might be due to overgeneralization of a pattern found in adjacent Saxonian dialects.
Stress
editErzgebirgisch has lexical stress. There is a tendency to stress the first syllable even in French loanwords, where Standard German stresses the final syllable (e.g. biro [ˈpiːɣo] ⟨Büro⟩ 'office'), but loan words which follow the Standard German pattern are more numerous (e.g. dridewààr [txɪtəˈvʌːɰ] Gehsteig 'sidewalk' (from French trottoir)).
Morphology
editNominal morphology
editGender
editErzgebirgisch numbers three genders, masculine, feminine and neuter. Most Erzgebirgisch lexemes have the same gender as their Standard German equivalents.
| Gender | Erzgebirgisch | Standard German | Gloss (sg./pl.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| masculine | màà | Mann (m.) | man/men |
| gung | Junge (m.) | boy/boys | |
| baam | Baum (m.) | tree/trees | |
| feminine | fraa | Frau (f.) | woman/women |
| sub | Suppe (f.) | soup/soups | |
| dàsch | Tasche (f.) | bag/bags | |
| neuter | kind | Kind (n.) | child/children |
| dridewààr | Gehsteig (m.) | sidewalk | |
| dunl | Tunnel (m./n.) | tunnel |
Case
editIn distinction to Standard German, the Erzgebirgisch genitive is no longer productive. Other constructions have to be used to indicate possession. For animate possessors, a construction involving the possessor in the dative and an agreeing possessive pronoun is used (dem B sein A). For inanimate possessors, a construction involving f(u)n (German von) is used. A third possibility is compounding.
examples (North Western dialect):
| (1) | n'Hàns | seine | hitsch |
| de-m Hans | seine | Fuß-bank | |
| the-GEN. Hans | his | foot-bench | |
| "Hans's foot bench" | |||
| (2) | de | fansder | fun | den | haus | |
| the | windows | of | the | house | ||
| die | Fenster | des | Hauses | (Standard German - genitive) | ||
| "The windows of the house" | ||||||
The only case marking available for nouns is dative plural, which is marked by -n , but can often assimilate to other consonants. Nominative and accusative are not marked in the singular on nouns, but articles, adjectives and possessive pronouns help to disambiguate in these cases. Personal pronouns also have some special forms for nominative, accusative and dative.
The following table shows some Erzgebirgisch nominal declension paradigms.
| Case/Number | tree (m.) | bag (f.) | child (n.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nominative singular | der baam | de dàsch | s kind |
| Dative singular | n baam | der dàsch | n kind |
| Accusative singular | n baam | de dàsch | s kind |
| Nominative plural | de beeme | de dàschn | de kiner |
| Dative plural | n beemm | n dàschn | n kinern |
| Accusative plural | de beeme | de dàschn | de kiner |
For more information on articles, see below.
Number
editThere are different ways to form the plural in Erzgebirgisch, a feature shared with Standard German. Next to the suffixes -e, -er, -n and -s, ablaut can also be used. Some suffixes trigger umlaut.
There are some nouns which differ in their plural marking between Erzgebirgisch and Standard German. E.g. Erzgebirgisch has -n for nouns ending in -(e)l in the singular, where Standard German most often has umlaut.
Examples (North Western dialect):
| singular (Erzg.) | singular (Std.G.) | plural (Erzg.) | plural (Std.G.) | gloss |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| fuuchl | Vogel | fuuchl-n | Vögel | birds |
| nààchl | Nagel | nààchl-n | Nägel | nails |
| maadl | Mädchen | maadl-n | Mädchen | girls |
| màst | Mast | masd-e (along with mosd-n) | Masten | masts |
| kind | Kind | kin-er | Kinder | children |
| bàrg | Park | bààrg-s | Parks | parks |
| fuus | Fuß | fiis | Füße | feet |
| wààng | Wagen | weeng(-e) | Wagen | coaches |
Articles
editErzgebirgisch distinguishes three kinds of articles: emphatic definite article, atonal definite article, indefinite article. The emphatic definite articles are used where Standard German would use deictics like dieser and jener. The other two types closely resemble their Standard German counterparts.
All articles agree in gender, number and case with their head noun. The emphatic articles may also occur without a head noun and often replace the rarely used third person personal pronouns.
Erzgebirgisch has a negative indefinite article just like German, but the similarity to the positive indefinite article is less obvious.
The North-Western dialect has the following forms:
| Form | masculine | feminine | neuter |
|---|---|---|---|
| indefinite article | |||
| Nominative singular | e | ne | e |
| Dative singular | n | ner | n |
| Accusative singular | n | ne | e |
| non-stressed definite article | |||
| Nominative singular | der | de | s |
| Dative singular | (de)n | der | (de)n |
| Accusative singular | (de)n | de | s |
| Nominative plural | de | ||
| Dative plural | n | ||
| Accusative plural | de | ||
| stressed definite article | |||
| Nominative singular | daar | dii | dàs |
| Dative singular | daan/dèèn | daar | daan/dèèn |
| Accusative singular | daan/dèèn | dii | dàs |
| Nominative plural | dii | ||
| Dative plural | daann/dèènn | ||
| Accusative plural | dii | ||
| negative article | |||
| Nominative singular | kee | keene | kee |
| Dative singular | keen | keener | keen |
| Accusative singular | keen | keene | kee |
| Nominative plural | keene | ||
| Dative plural | keenn | ||
| Accusative plural | keene | ||
The article n assimilates in place of articulation to the preceding consonant. It is m before p, pf, f, w and m and ng before k, g, ch ([x] or [χ]) and ng.
Examples:
| (3) | S | kind | hàd | s | n | Hàns | gesààd |
| [skʰɪnt] | [hʌtsn̩] | [hʌns] | [kəsʌːt] | ||||
| Das | Kind | hat | es/dieses | einem | Hans | gesagt. | |
| The | child | has | it/that | to a | Hans | said. | |
| (4) | Der | Hàns | hàd | dàs | buuch | ng | màà | gaam |
| [tɔɰ] | [hʌns] | [hʌt] | [tʌs] | [puːxŋ̍] | [mʌː] | [kæːm] | ||
| Der | Hans | hat | dieses | Buch | einem | Mann | gegeben. | |
| The | Hans | has | this | book | to a | man | given. | |
| (5) | E | schiins | dleedl | hàd | dii | àà |
| [ə] | [ʂiːns] | [tˡleːtˡl̩] | [hʌt] | [tiː] | [ʌː] | |
| Ein | schönes | Kleidchen | hat | sie/diese | an. | |
| A | beautiful | dress.DIM | has | she/this one | on. |
| (6) | Ch | hàb | m | kinern | kee | gald | gaam |
| [ʂhʌpm̩] | [kʰɪnɔɰn] | [kʰeː] | [kælt] | [kæːm] | |||
| Ich | habe | den | Kindern | kein | Geld | gegeben. | |
| I | have | the | children | no | money | given. | |
Pronouns
editPersonal pronouns
editPersonal pronouns distinguish emphatic and atonal forms, just like articles. The emphatic forms are used to highlight a participant. They are free words, whereas the atonal forms are phonologically reduced clitics.
There is no emphatic form for third person personal pronouns. The emphatic forms of the definite article have to be used instead. To outsiders this may often come across as impolite.
Unlike nouns, personal pronouns distinguish both number and case.
| Person/Number/Gender | Nominative | Dative | Accusative |
|---|---|---|---|
| emphatic personal pronouns | |||
| 1. Person singular | iich | miir | miich |
| 2. Person singular | duu | diir | diich |
| 3. Person singular m. | daar | daan/dèèn | dann/dèèn |
| 3. Person singular f. | dii | daar | dii |
| 3. Person singular n. | dàs | daan/dèèn | dàs |
| 1. Person plural | miir | uns | uns |
| 2. Person plural | iir | eich | eich |
| 3. Person plural | dii | daann/dèènn | dii |
| Polite | sii | iinn | sii |
| atonal personal pronouns | |||
| 1. Person singular | (i)ch | mer | mich |
| 2. Person singular | de/du | der | dich/tsch |
| 3. Person singular m. | er | n | n |
| 3. Person singular f. | se | er | se |
| 3. Person singular n. | s | n | s |
| 1. Person plural | mer | uns | uns |
| 2. Person plural | er | eich | eich |
| 3. Person plural | se | n | se |
| Polite | se | iin(n) | se |
Pronouns with ch have sch in the Northwestern dialect. The atonal second person singular pronoun is de when it precedes a verb, and du when following. There are extra pronouns to express politeness, unlike German, which uses third person plural for this function.
Examples:
| (7) | Hàd | -er | -s | -n | schuu | gesààd |
| [hʌtɔɰsn̩] | [ʂuː] | [kəsʌːt] | ||||
| Hat | er | es | ihm | schon | gesagt? | |
| Has | he | it | to him | already | said? | |
| (8) | Ch | hàb | dèènn | nischd | gaam |
| [ʂhʌp] | [tɛːnn̩] | [nɪʂt] | [kæːm] | ||
| Ich | habe | denen/ihnen | nichts | gegeben. | |
| I | have | those ones/them | nothing | given. | |
Possessive pronouns
editPossessive pronouns agree in case, number and gender with their head noun.
| Person/Genus | singular | plural |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Person | mei(n)- | un(s)(e)r- |
| 2. Person | dei(n)- | ei(e)r- |
| 3. Person masc.. | sei(n)- | iir- |
| 3. Person fem. | iir- | iir- |
| 3. Person neut. | sei(n)- | iir- |
singular pronouns lose the n before another n or a -Ø-suffix.
First person plural loses the s everywhere but in the North Western dialect. First and second person plural lose the e before a suffix starting with a vowel.
| Form | masculine | feminine | neuter |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nominative singular | -Ø | -e | -Ø |
| Dative singular | -n | -er | -n |
| Accusative singular | -n | -e | -Ø |
| Nominative plural | -e | ||
| Dative plural | -n | ||
| Accusative plural | -e | ||
This paradigm makes use of only three letters e, n and r.
examples:
| (9) | mei | hund |
| [maɪ] | [hʊnt] | |
| mein | Hund | |
| my | dog |
| (10) | eirer | schwasder |
| [aɪɣɔɰ] | [ʂvastɔɰ] | |
| eurer | Schwester | |
| to y'all's | sister |
Third person pronouns make heavy use of the dative construction (see above), just like nouns.
| (11) | daar | iire | dàsch |
| [taːɰ] | [iːɣə] | [tʌʂ] | |
| dieser/ihr | ihre | Tasche | |
| this one/her | her | bag | |
| "her bag" | |||
vgl.:
| (12) | daar | fraa | iire | dàsch |
| "die Tasche dieser Frau" | ||||
| "The woman's bag" | ||||
Prepositions
editThe following construction is found mainly in Western dialects, but also in Lichtenstein:
| (13) | nei | (n) | der | schdàd |
| hinein | in | der | Stadt | |
| inwards | in | the | town | |
| "in die Stadt (hinein)" | ||||
| "inwards in the town" | ||||
The canonic preposition n (in) is never deleted in Lichtenstein, but almost always in the western dialects due to the more widespread dropping of n. This leads to the impression that nei is the preposition. One should also notice that goal of motion is encoded by the dative, and not by the accusative as in Standard German. The motion component is expressed by nei. This construction is also found with many other prepositions: dràà der kèrch ("an der Kirche", "bei der Kirche" at the church).
Adjectives
editAgreement
editAdjectives agree with their head word in case, number, gender and definiteness. A difference to Standard German is the non-distinction of forms with indefinite article and forms without any article.
| Standard German | Erzgebirgisch | English |
|---|---|---|
| teur-em Schmuck | deier-n schmuk | for expensive jewels |
| einem teur-en Ring | n'deier-n ring | for an expensive ring |
The following table lists all agreement suffixes for adjectives:
| Form | masculine | feminine | neuter |
|---|---|---|---|
| without article/with indefinite article | |||
| Nominative singular | -er | -e | -(e)s |
| Dative singular | -n | -er | -n |
| Accusative singular | -n | -e | -(e)s |
| Nominative plural | -e | ||
| Dative plural | -n | ||
| Accusative plural | -e | ||
| with definite article | |||
| Nominative singular | -e | -e | -e |
| Dative singular | -n | -n | -n |
| Accusative singular | -n | -e | -e |
| Nominative plural | -n | ||
| Dative plural | -n | ||
| Accusative plural | -n | ||
More examples
| (14) | e | gruus-er | màà |
| [ə] | [kxuːsɔɰ] | [mʌː] | |
| ein | großer | Mann | |
| a | big | man |
| (15) | daar | schiin-n | fraa |
| [taːɰ] | [ʂiːnn̩] | [fxaː] | |
| dieser | schönen | Frau | |
| this | beautiful | woman | |
| to this beautiful woman | |||
Comparison
editThe comparative is formed with the suffix -er.
The standard of comparison is marked with the preposition wii (wie).
The superlative is obtained by adding -(e)sd. Agreement suffixes come after these suffixes.
examples:
| (16) | e | grès-(e)r-er | màà | wii | daar |
| [ə] | [kxɛsɔɣɔɰ] | [mʌː] | [viː] | [taːɰ] | |
| ein | größ-er-er | Mann | als | er/dieser | |
| a | bigger | man | than | he/this one |
| (17) | der | schèn-sd-n | fraa |
| [tɔɰ] | [ʂɛnstn̩] | [fxaː] | |
| der | schönsten | Frau | |
| to the | prettiest | woman |
Verbs
editThe verb agrees in person and number with the subject of the sentence. This is true of both full verbs and auxiliaries.
Two tense/aspects are morphologically distinguished, present tense and preterite. Use of the preterite is found almost exclusively with strong verbs, i.e. verbs involving ablaut.
The other tenses are formed with auxiliaries: Perfect, Pluperfect, Futur I and Futur II. Perfect and preterite are used interchangeably. Pluperfect expresses anteriority in the past. Futur II is mainly used for epistemic statements about past events (cf. German: Er wird wohl wieder nicht da gewesen sein. He has probably not attended again.)
Infinitive and participles
editThe infinitive and the present participle and the past participle are formed with the following affixes:
| Form | schbiil- | gii- | sei- | hàb- | wèèr- |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| class | weak | strong | irregular | irregular | irregular |
| Std.G. | spiel- | geh- | sei- | hab- | werd- |
| Engl. | play | go | be | have | become |
| Infinitive | schbiil-n | gii-n | sei(-n) | hà-m | wèèr-n |
| participle I | schbiil-end | gii-end | sei-end | hàà-md | wèèr-nd |
| participle II | ge-schbiil-d | (ge-)gàng-ng | ge-waas-n | ge-hà-d | ge-wur-n |
Present tense
editErzgebirgisch distinguishes strong verbs, involving ablaut, and weak verbs, without ablaut. Both classes take the same suffixes. The present tense can be used to refer to events in the present or future.
| Form | schbiil- | gii- | sei- | hàb- | wèèr- |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| class | weak | strong | irregular | irregular | irregular |
| Std.G. | spiel- | geh- | sei- | hab- | werd- |
| Engl. | play | go | be | have | become |
| 1. Person singular | schbiil-∅ | gii-∅ | bii-∅ | hàb-∅ | wèèr-∅ |
| 2. Person singular | schbiil-sd | gi(i)-sd | bi-sd | hà-sd | wèr-sd |
| 3. Person singular | schbiil-d | gi(i)-d | is | hà-d | wèr-d |
| 1. Person plural | schbiil-n | gii-n | sei-∅ | hà-m | wèèr-n |
| 2. Person plural | schbiil-d | gii-d | sei-d | hàb-d | wèèr-d |
| 3. Person plural | schbiil-n | gii-n | sei-∅ | hà-m | wèèr-n |
The suffixes are sometimes assimilated to the stem, as can be seen from hàm, `to have'.
Preterite
editAs mentioned above, the preterite form is only used with strong verbs. Weak verbs use the perfect instead. This is also gaining ground with strong verbs. Formation of the preterite does not always follow the same pattern as in Standard German e.g. schmecken `to taste' is a weak verb in Standard German (preterit schmeckte), but a strong verb is Erzgebirgisch (present tense: schmègng preterite: schmoog with ablaut. Another verb which is weak in Standard German but strong in Erzgebirgisch is frààn (Standard German fragen to ask), preterite fruuch (Standard German fragte, asked).
Agreement with the subject is indicated as follows:
| Form | gii- | sei- | hàb- | wèèr- |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| class | strong | irregular | irregular | irregular |
| Stg.G. | geh- | sei- | hab- | werd- |
| Engl. | go | be | have | become |
| 1. Person singular | ging-∅ | wààr-∅ | hàd-∅ | wurd-∅ |
| 2. Person singular | ging-sd | wààr-sd | hàd-sd | wurd-sd |
| 3. Person singular | ging-∅ | wààr-∅ | hàd-e | wurd-e |
| 1. Person plural | ging-ng | wààr-n | hàd-n | wurd-n |
| 2. Person plural | ging-d | wààr-d | hàd-ed | wurd-ed |
| 3. Person plural | ging-ng | wààr-n | hàd-n | wurd-n |
Perfect, pluperfect
editPerfect and pluperfect are construed with a finite form of the auxiliaries sei- and hàb- and the past participle of the full verb.
Examples:
| (18) | Miir | sei | gasdern | (a)f | der | kèèrms | gàngng |
| [miːɰ] | [saɪ] | [kæstɔɰn] | [(a/ə)f] | [tɔɰ] | [kʰɛːɰms] | [kʌŋŋ̍] | |
| Wir | sind | gestern | auf | der | Kirmes | gegangen. | |
| We | are | yesterday | on | the | funfair | gone. |
| (19) | Ch | hàd | -s | -n | ààwer | gesààd |
| [ʂhʌtsn̩] | [ʌːvɔɰ] | [kəsʌːt] | ||||
| Ich | hatte | es | ihm | aber | gesagt. | |
| I | had | it | him | nevertheless | said. | |
Future
editTwo future tenses are distinguished. Future I is used for any reference time in the future, Future II has the meaning of future anterior. Future is formed with the auxiliary wèèr- (Standard German werden). Future I adds the infinitive of the full verb, future II the auxiliary sei or hab in the infinitive and the past participle of the full verb.
Examples:
| (20) | Murng | wèrd | der | Hàns | nààch | Kams | fààrn |
| [moːɰjŋ] | [vɛɰt] | [tɔɰ] | [hʌns] | [nʌːχ] | [kʰæms] | [fʌːɰn] | |
| Morgen | wird | der | Hans | nach | Chemnitz | fahren. | |
| Tomorrow | will | the | Hans | to | Chemnitz | go. |
| (21) | Er | wèrd | wuu | wiider | nèd | doo | gewaasn | sei |
| [ɔɰ] | [vɛɰt] | [vuː] | [viːtɔɰ] | [nɛt] | [toː] | [kəvaːsn̩] | [saɪ] | |
| Er | wird | wohl | wieder | nicht | da | gewesen | sein. | |
| He | will | rather | again | not | there | been | be. |
Subjunctive
editErzgebirgisch has a productive subjunctive for most of the auxiliaries and some other frequently used verbs. The form is derived from the preterite by ablaut. Other verbs have to use duun support in order to appear in the subjunctive.
| Form | gii- | sei- | hàb- | wèèr- |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| class | strong | irregular | irregular | irregular |
| Std.G. | geh- | sei- | hab- | werd- |
| Engl. | go | be | have | become |
| 1. Person singular | gèng-∅ | waar-∅ | hèd-∅ | daad-∅ |
| 2. Person singular | gèng-sd | waar-sd | hèd-sd | daad-sd |
| 3. Person singular | gèng-∅ | waar-∅ | hèd-e | daad-∅ |
| 1. Person plural | gèng-ng | waar-n | hèd-n | daad-n |
| 2. Person plural | gèng-d | waar-d | hèd-ed | daad-ed |
| 3. Person plural | gèng-ng | waar-n | hèd-n | daad-n |
Imperative
editThe imperative is identical to first person present tense indicative. In order to obtain the plural imperative, -d is suffixed to the singular form.
example:
| (22) | Bii | nur | màà | ruich! |
| [piː] | [nəɰ] | [mʌː] | [ɣʊɪʂ] | |
| Sei | endlich | ruhig! | ||
| Be | finally | quiet! | ||
Passive
editThe passive is formed with the auxiliary wèèr- (German werden) and the past participle of the full verb.
Example:
| (23) | Wii | wèrd | dèè | dàs | gemàchd |
| [viː] | [vɛɰt] | [tɛː] | [tʌs] | [kəmʌχt] | |
| Wie | wird | denn | das | gemacht? | |
| How | is | now | this | made? |
A sample of Erzgebirgisch speech (Lichtenstein dialect)
edit| (24) | Wuu | kimsd | dee | duu | ize | haar? | |||
| [vuː] | [kʰɪmst] | [teː] | [tuː] | [ɪtsə] | [haːɰ] | ||||
| Where | comest | then | thou | now | from? | ||||
| Where | on | earth | are | you | coming | from | right | now? | |
| (25) | Dàs | kàà | (i)ch | der | fei | ni | sààn. | ||
| [tʌs] | [kʰʌː] | [(ɪ)ʂ] | [tɔɰ] | [faɪ] | [nɪ] | [sʌːn] | |||
| That | can | I | thee | at.all | not | say | |||
| I | cannot | tell | you | at | all. |
Sample text
editThe following snippet contains the introduction and the first stanza of a wedding poem from Clausthal (1759) and is written in the Oberharz dialect:[2]
Aſs t'r Niemeyer ſeine Schuſtern in de Kerch zur Trauer kefuͤhrt prengt aͤ Vugelſteller Vugel un hot Baͤden kratelirt iſs k'ſchaͤn d. 25. Oktober 1759. Clasthol kedruͤckt bey den Buchdrucker Wendeborn.
Klick auf mit enanner, ihr ſtatlig'n Harrn!
Do ſtellt ſich d'r Toffel ahch ein aus der Farrn,
Har hot ſich ju kraͤts ſchunt de Fraͤhaͤt kenumme,
Su iſs'r ahch diesmol mit reiner kekumme.
Se hahn ne ju ſuͤſt wos zu luͤſen[a] kekahn:
Ich hoh' ſchiene Vugel, wolln Sie ſe beſahn?
- Translation
When Niemeyer lead his bride to the church to marry her, a bird trapper brought birds and congratulated them; This happened on October 25 in 1759. Clausthal, printed at the Wendeborn Printing House.
Hello you all, you honorable men!
Here comes the lad from far away,
He has already taken the liberty,
So he came in this time again.
They have sometimes given him something to earn:
I have nice birds, do you want to have a look on them?
- ^ According to Borchers (1929), luͤſen 'to earn, get money' was pronounced [ˈliːsən] – Erzg. does not have the uͤ sound [y]. According to Radlof the standard German is lösen (which means remove, loosen, solve, buy in English depending on context). In Neues Vaterländisches Archiv it is spelled as lißen in the text, and as ließen – lösen. in the notes.
Lexicon
editLike all dialects, Erzgebirgisch has some words which are difficult to grasp for outsiders. These include contractions of long words, but also some words unknown to other dialects or even other subdialects of the same lineage.
Nouns
edit| Lexeme | pronunciation(NW dialect) | Standard German | English | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| aarb | werzg. [ˈaːɰp] | Arbeit | work | only in the western dialect |
| aardabl | [ˈaːɰtæpl̩] | Kartoffel | potato | literal: earth apple |
| ààziizeich | [ˈʌːˌtsiːtsaɪ̯ʂ] | Kleidung | clothing | literal: Anziehzeug |
| àbort | [ˈʌpɔɰt] | Toilette | loo (toilet) | |
| bèg | [ˈpɛk] | Bäcker | baker | |
| bèremèd | [ˌpɛɣəˈmɛt] | Weihnachtspyramide | Christmas pyramid | |
| bèrschd | [ˈpɛɰʂʈ] | Bürste | brush | |
| burschdwich | [ˈpʊɰʂʈvɪʂ] | Besen | broom | |
| dibl | [ˈtɪpl̩] | Tasse | cup | literal: Töpfchen |
| dridewààr | [ˌtxɪtəˈvʌːɰ] | Gehsteig | sidewalk | derived from French trottoir |
| fauns | [ˈfaʊ̯ns] | Ohrfeige | slap | |
| feier | [ˈfaɪ̯ɔ] | Feuer | fire | |
| fuuchlbaarbaam | [ˈfuːxl̩ˌpaːɰpaːm] | Eberesche | rowan | literal: bird berry tree (rowanberry tree) |
| gaacher | [ˈkæːχɔɰ] | Jäger | hunter | |
| gudsàger | [ˈkʊtsʌkɔɰ] | Friedhof | cemetery | literal: God's acre |
| hèm | [ˈhɛm] | Hemd | shirt | |
| hiidrààbradl | [ˈhiːˌtxʌːpxætl̩] | Serviertablett | tray | literal: little bring here tray |
| hitsch | [ˈhɪtʂ] | Fußbank | footbench | |
| huchtsch | [ˈhʊxtʂ] | Hochzeit | wedding | |
| lader | [ˈlætɔɰ] | Leiter | ladder | |
| nààmitsch | [ˈnʌːmɪtʂ] | Nachmittag | afternoon | |
| pfaar | [ˈpfaːɰ] | Pferd | horse | |
| reeng | [ˈɣeːŋ] | Regen | rain | |
| schdagng | [ˈʂʈækŋ̍] | Stecken, Stock | stick | |
| schduub | [ˈʂʈuːp] | Wohnzimmer, Stube | living room | |
| (scheier)hààder | [ˈʂaɪ̯ɔɰhʌːtɔɰ] | Wischtuch | cloth for wiping | |
| schmiich | [ˈʂmiːʂ] | Zollstock | yardstick | |
| zemitschasn | [tsəˈmɪtʂasn̩] | Mittagessen | lunch | literal: midday meal |
| zèrwànsd | [ˈtsɛɰvʌnst] | Akkordeon | accordion |
Verbs
editErzgebirgisch has many onomatopoetic verbs (see also I. Susanka). Due to the high precipitation in the Ore Mountains, many different verbs for different kinds of rain or drizzle exist.
| Word | Pronunciation(Northwest dialect) | Standard German | English | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| besuudln | [pəˈsuːtl̩n] | beschmutzen | (get) dirty | |
| blààtschn | [ˈplʌːtʂn̩] | stark regnen (Platzregen) | heavy shower | |
| blèègng | [ˈplɛːkŋ̍] | laut schreien | scream | |
| deebern | [ˈteːpɔɰn] | toben, schimpfen | be angry | |
| derlaam | werzg. [tɔɰˈlaːm] | erleben | experience | not in northwest dialect |
| drààschn | [ˈtxʌːʂn̩] | stark regnen (Dauerregen) | continuous heavy rain | |
| eisàgng | [ˈaɪ̯sʌkŋ̍] | einfüllen, einpacken | take, put in | Literal: einsacken |
| gwèstern | [ˈkvɛstɔɰn] | immer wieder rein und raus gehen | repeatedly getting in and out | |
| kambln | [ˈkʰæmpl̩n] | sich prügeln | beat each other | |
| siifern | [ˈsiːfɔɰn] | leicht nieseln | light drizzle |
Other words
editLike many other German dialects, Erzgebirgisch is rich in adverbs, like the notorious fei, whose use is extremely complex and needs further research. It appears in commands (Gii fei wag!, Go away!), but also in affirmations (S´reengd fei, It's raining, by the way.).
| Lexeme | Pronunciation(Nordwestdial.) | Standard German | English | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| dingenauf | [ˌtɪŋəˈnaʊ̯f] | bergauf, nach oben | uphill, upward | |
| emènde | [əˈmɛndə] | möglicherweise | possibly | literal: at the end |
| feeder | [ˈfeːtɔɰ] | vorwärts, weiter | further | from English |
| fei | [ˈfaɪ̯] | aber, nämlich, endlich, ziemlich | but, indeed, finally, quite | |
| fiir | [ˈfiːɰ] | vor | for | also in expressions |
| gaaling | [ˈɡæːlɪŋ] | heftig | vehement | |
| heier | [ˈhaɪ̯ɔɰ] | dieses Jahr | this year | |
| hèm | [ˈhɛm] | nach Hause | at home | literal: home |
| hiimundriim | [ˌhiːmʊnˈtxiːm] | auf beiden Seiten | on both sides | literal: hüben und drüben |
| hinewiider | [ˌhɪnəˈviːtɔɰ] | hin und her | here and there | |
| ize | [ˈɪtsə] | jetzt | now | |
| nààchert | [ˈnʌːxɔɰt] | nachher | to here | |
| zàm | [ˈtsʌm] | zusammen | together |
Interjections
editThe interjections used in Erzgebirgisch differ considerably from the Standard German ones. The language area being dominated by mining, some linguistic patterns peculiar to this business have attained general usage, like the salute Glig auf! (dt. "Glück auf").
English does not have a specialized form to affirm negative questions, unlike French (si), Dutch (jawel) or German (doch). Erzgebirgisch uses Ujuu! [ˈʊjuː], or sometimes Ajuu! [ˈajuː], (dt. "Doch!") in these contexts. For the negation of a question expecting a positive answer È(schà)! [ˈɛ(ʂʌ)] (dt. "Nein!") is used. This interjection is also used to express surprise, albeit with a different intonation.
References
edit- ^ Hendrik Heidler's 400 Seiten Echtes Erzgebirgisch: Wuu de Hasen Hoosn haaßn un de Hosen Huusn do sei mir drhamm. Das Original Wörterbuch. 5th ed., BoD [Books on Demand], Norderstedt 2020, p. 28f. ISBN 978-3-7347-6356-4
- ^ Mustersaal aller teutschen Mund-arten, enthaltend Gedichte, prosaische Aufsätze und kleine Lustspiele in den verschiedenen Mund-arten aufgesetzt; und mit kurzen Erläuterungen versehen von Dr. Joh. Gottl. Radlof. Erster Band, Bonn, 1821, pp. 275ff. (google):
Differently in Neues Vaterländisches Archiv oder Beiträge zur allseitigen Kenntniß des Königreichs Hannover und des Herzogthums Braunschweig. Begründet von G. H. G. Spiel. Fortgesetzt von Ernst Spangenberg. Jahrgang 1831. Erster Band, Lüneburg, 1831, pp. 279ff. (google);
Differently cited in Erich Borchers: Sprach- und Gründungsgeschichte der erzgebirgischen Kolonie im Oberharz. Marburg, 1929. pp. 135–136.
Literature
editGrammars and other linguistic publications
edit- Oswin Böttger: Der Satzbau der erzgebirgischen Mundart. Leipzig 1904. – An analysis of the syntax.
- Erich Borchers: Sprach- und Gründungsgeschichte der erzgebirgischen Kolonie im Oberharz. Marburg 1929. – Grammar of the Upper Harz variety.
Other literature
edit- Irmtraud Susanka: Wie mir drham geredt homm. Unsere Mundart im Bezirke Kaaden-Duppau. Verlag des Kaadener Heimatbriefs, Bayreuth (no year, no ISBN). – Collection of words, phrases, poems and short stories of the southern variety formerly spoken in the Sudetenland.
External links
edit- A western Erzg. wordlist and some further literature
- A wordlist of the variety in Thalheim
- Some poems in Erzg.
- Some short stories in Erzg.